Now I have stacked all three modules to start python programming:
(1) Motor (N20 x 2),
(2) Motor Driver (TB66112FNG x 1)
(3) MCU (Pico x 1)
/ to continue, …

Now I have stacked all three modules to start python programming:
(1) Motor (N20 x 2),
(2) Motor Driver (TB66112FNG x 1)
(3) MCU (Pico x 1)
/ to continue, …
I am reading my old post to refresh memory on how to drive a DC motor. Last time I followed Tom’s Hardware tutorial to use Pico and MX1508 motor driver to drive only one motor TT130. Everything goes well.
This time I am modifying Tom’s Hardware’s python program to control my 2WD’s two N20 motors. I am also using the TB6612FNG motor controller. As I understand, for my simple applications, any common driver (L298N, DRV8833), and common motors TT130, N20) can be used.
Now I am testing moving only one N20 motor, and using Pico to control only IN1, IN2. The Standby and PWM signals are manually hardwired.
And the full program listing.
# Program Name
# move_dc_motor_v02.py - tlfong01 2021jul10hkt1132
# Reference
# Pi-Top Forum - making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
# https://forum.pi-top.com/t/making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
# Configuration
# Thonny 3.3.3, Windows 10 (64-bit), Python 3.7.9 (32-bit), Tk 8.6.9, USB COM Port #4
# Intepreter
# Micropython (Rapsberry Pi Pico)
# DC Motor
# (a) TT130 DC3~6V DC Gear Motor - AliEXpress US$1
# https://www.aliexpress.com/item/32855311589.html
# (b) N20 Gear Motor
#
# DC Motor Driver
# (a) MX1508 2~10V, 1.5A, Dual H-Bridge DC Motor Driver - AliExpress US$1
# https://www.aliexpress.com/item/32688083107.html
# (b) TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver
# Program Function
# Move DC motor forward, backward, and stop
# User Guide
# (a) Connect PWMA to High (Vcc)
# (b) Connect Standby to High
# (c) Run code to move motor forward, backward, and stop
import utime
from machine import Pin
motor1a = Pin(10, Pin.OUT)
motor1b = Pin(11, Pin.OUT)
def moveMotorForward():
motor1a.low()
motor1b.high()
def moveMotorBackward():
motor1a.high()
motor1b.low()
def stopMotor():
motor1a.low()
motor1b.low()
def test():
print(' Begin move motor test()')
moveMotorForward()
utime.sleep(1)
moveMotorBackward()
utime.sleep(1)
stopMotor()
print(' End test()')
for i in range(2):
print('Test ', i)
test()
# *** End of program ***
# *** Sample Output - tlfong01 2021jul01hkt1707
'''
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Test 0
Begin move motor test()
End test()
Test 1
Begin move motor test()
End test()
>>>
'''
Now I have written motor driver dictionaries and tested them OK, to make it easy to scale up 1WD to 2WD for two motors, and later 4WD for four motors. The program is fully listed below:
$ Program Name
$ move_dc_motor_v04.py - tlfong01 2021jul10hkt1558
$ Reference
$ Pi-Top Forum - making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
$ Making a Rpi Pico Based Smart Vehicle
$ Configuration
$ Thonny 3.3.3, Windows 10 (64-bit), Python 3.7.9 (32-bit), Tk 8.6.9, USB COM Port #4
$ Intepreter
$ Micropython (Rapsberry Pi Pico)
$ DC Motor
$ (a) TT130 DC3~6V DC Gear Motor - AliEXpress US$1
$ https://www.aliexpress.com/item/32855311589.html
$ (b) N20 Gear Motor x 2
$
$ DC Motor Driver
$ (a) MX1508 2~10V, 1.5A, Dual H-Bridge DC Motor Driver - AliExpress US$1
$ https://www.aliexpress.com/item/32688083107.html
$ (b) TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver
$ Program Function
$ Move two N20 DC motors forward, backward, and stop
$ User Guide
$ (a) Configuration
$ GP10 - Motor1 IN1
$ GP11 - Motor1 IN2
$ GP12 - Motor1 PWMA
$ GP13 - Motor2 IN1
$ GP14 - Motor2 IN2
$ GP15 - Motor2 PWMB
$ GP9 - Motor1, 2, Standby
$ (b) Run program to move in sequence, two motors forward, backward, and stop
import utime
from machine import Pin
$ Configuration
multiMotorDriverDict01 = {
‘Title’ : ‘Motor Driver Dict For 4WD’,
‘STBY’ : 9,
‘1’ : {‘IN1’ : 10,
‘IN2’ : 11,
‘PWM’ : 12,
},
‘2’ : {‘IN1’ : 13,
‘IN2’ : 14,
‘PWM’ : 15,
},
‘3’ : {‘IN1’ : 0,
‘IN2’ : 0,
‘PWM’ : 0,
},
‘4’ : {‘IN1’ : 0,
‘IN2’ : 0,
‘PWM’ : 0,
},
}
multiMotorDriverDictDict = {
‘1’: multiMotorDriverDict01,
‘1’: multiMotorDriverDict01,
}
def setupMotor(multiMotorDriverDictDictNum, motorDriverNum):
motorDriverDict = multiMotorDriverDictDict[str(multiMotorDriverDictDictNum)]
in1PinNum = motorDriverDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['IN1']
in2PinNum = motorDriverDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['IN2']
pwmPinNum = motorDriverDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['PWM']
print('In1PinNum =', in1PinNum)
print('In2PinNum =', in2PinNum)
print('pwmPinNum =', pwmPinNum)
in1Pin = Pin(in1PinNum, Pin.OUT)
in2Pin = Pin(in2PinNum, Pin.OUT)
pwmPin = Pin(pwmPinNum, Pin.OUT)
picoMotorDriverControlPinDict = {'IN1': in1Pin, 'IN2': in2Pin, 'PWM': pwmPin}
return picoMotorDriverControlPinDict
def moveMotorForward(motorDriverDict):
in1Pin = motorDriverDict[‘IN1’]
in2Pin = motorDriverDict[‘IN2’]
pwmPin = motorDriverDict[‘PWM’]
in1Pin.low()
in2Pin.high()
pwmPin.high()
return
def moveMotorBackward(motorDriverDict):
in1Pin = motorDriverDict[‘IN1’]
in2Pin = motorDriverDict[‘IN2’]
pwmPin = motorDriverDict[‘PWM’]
in1Pin.high()
in2Pin.low()
pwmPin.high()
return
def stopMotor(motorDriverDict):
in1Pin = motorDriverDict[‘IN1’]
in2Pin = motorDriverDict[‘IN2’]
pwmPin = motorDriverDict[‘PWM’]
in1Pin.low()
in2Pin.low()
pwmPin.high()
return
$ Main $
$ Test Motors #1, #2
motorDictDictNum = 1
motorNumList = [1, 2]
for motorNum in motorNumList:
motorDriverDict = setupMotor(motorDictDictNum, motorNum)
moveMotorForward(motorDriverDict)
utime.sleep(1)
moveMotorBackward(motorDriverDict)
utime.sleep(1)
stopMotor(motorDriverDict)
$ End of program
Next step is writing functions to turn vehicle right and left.
/ to continue, …
The turn right/left functions are easy to write and test. The ‘#’ symbol crashes with the forum editor. So I replaced the symbol to ‘$’
$ Program Name
$ move_dc_motor_v08.py - tlfong01 2021jul10hkt1625
$ Reference
$ Pi-Top Forum - making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
$ https://forum.pi-top.com/t/making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
$ Configuration
$ Thonny 3.3.3, Windows 10 (64-bit), Python 3.7.9 (32-bit), Tk 8.6.9, USB COM Port $4
$ Intepreter
$ Micropython (Rapsberry Pi Pico)
$ DC Motor
$ (a) TT130 DC3~6V DC Gear Motor - AliEXpress US$1$
$ (b) N20 Gear Motor x 2
$
$ DC Motor Driver
$ (a) MX1508 2~10V, 1.5A, Dual H-Bridge DC Motor Driver - AliExpress US$1
$ https://www.aliexpress.com/item/32688083107.html
$ (b) TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver
$ Program Functions
$ (a) Move two N20 DC motors forward, backward, and stop.
$ (b) Move left motor forward, right motor backward, so to turn vehicle right.
$ (c) Similarly, left motor backward, right motor forward, so to turn vehicle left
$ User Guide
$ (a) Configuration
$ GP10 - Motor1 IN1
$ GP11 - Motor1 IN2
$ GP12 - Motor1 PWMA
$ GP13 - Motor2 IN1
$ GP14 - Motor2 IN2
$ GP15 - Motor2 PWMB
$ GP9 - Motor1, 2, Standby
$ (b) Run program to move in sequence, two motors forward, backward, and stop
import utime
from machine import Pin
$ Configuration
multiMotorDriverDict01 = {
'Title' : 'Motor Driver Dict For 4WD',
'STBY' : 9,
'1' : {'IN1' : 10,
'IN2' : 11,
'PWM' : 12,
},
'2' : {'IN1' : 13,
'IN2' : 14,
'PWM' : 15,
},
'3' : {'IN1' : 0,
'IN2' : 0,
'PWM' : 0,
},
'4' : {'IN1' : 0,
'IN2' : 0,
'PWM' : 0,
},
}
multiMotorDriverDictDict = {
'1': multiMotorDriverDict01,
'1': multiMotorDriverDict01,
}
$ ***
def setupMotor(multiMotorDriverDictDictNum, motorDriverNum):
motorDriverDict = multiMotorDriverDictDict[str(multiMotorDriverDictDictNum)]
in1PinNum = motorDriverDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['IN1']
in2PinNum = motorDriverDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['IN2']
pwmPinNum = motorDriverDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['PWM']
print('In1PinNum =', in1PinNum)
print('In2PinNum =', in2PinNum)
print('pwmPinNum =', pwmPinNum)
in1Pin = Pin(in1PinNum, Pin.OUT)
in2Pin = Pin(in2PinNum, Pin.OUT)
pwmPin = Pin(pwmPinNum, Pin.OUT)
picoMotorDriverControlPinDict = {'IN1': in1Pin, 'IN2': in2Pin, 'PWM': pwmPin}
return picoMotorDriverControlPinDict
def moveMotorForward(motorDriverDict):
in1Pin = motorDriverDict['IN1']
in2Pin = motorDriverDict['IN2']
pwmPin = motorDriverDict['PWM']
in1Pin.low()
in2Pin.high()
pwmPin.high()
return
def moveMotorBackward(motorDriverDict):
in1Pin = motorDriverDict['IN1']
in2Pin = motorDriverDict['IN2']
pwmPin = motorDriverDict['PWM']
in1Pin.high()
in2Pin.low()
pwmPin.high()
return
def stopMotor(motorDriverDict):
in1Pin = motorDriverDict['IN1']
in2Pin = motorDriverDict['IN2']
pwmPin = motorDriverDict['PWM']
in1Pin.low()
in2Pin.low()
pwmPin.high()
return
def turnVehicleRight(motorDriverDictLeft, motorDriverDictRight):
moveMotorForward(motorDriverDictLeft)
moveMotorBackward(motorDriverDictRight)
return
def turnVehicleLeft(motorDriverDictLeft, motorDriverDictRight):
moveMotorForward(motorDriverDictRight)
moveMotorBackward(motorDriverDictLeft)
return
$ Main test functions
def testSequentiallyMoveTwoMotorsForwardBackwardAndStop():
motorDictDictNum = 1
motorNumList = [1, 2]
for motorNum in motorNumList:
motorDriverDict = setupMotor(motorDictDictNum, motorNum)
moveMotorForward(motorDriverDict)
utime.sleep(1)
moveMotorBackward(motorDriverDict)
utime.sleep(1)
stopMotor(motorDriverDict)
return
def testTurnVehicleRightOneSecondThenLeftOneSecond():
motorDictDictNum = 1
leftMotorDriverDict = setupMotor(motorDictDictNum, 1)
rightMotorDriverDict = setupMotor(motorDictDictNum, 2)
turnVehicleRight(leftMotorDriverDict, rightMotorDriverDict)
utime.sleep(2)
turnVehicleLeft(leftMotorDriverDict, rightMotorDriverDict)
utime.sleep(2)
stopMotor(leftMotorDriverDict)
stopMotor(rightMotorDriverDict)
$ Main $
$ testSequentiallyMoveTwoMotorsForwardBackwardAndStop()
testTurnVehicleRightOneSecondThenLeftOneSecond()
$ End of program
Now that I have completed the point to point wiring of Pico GB6~9 pins to the two N20 encoder outputs. Next step is to write a Pico microPython to do all motor control in software.
I forgot I need first to do some calibration of the N20 motor encoder signal vs speed (rpm) off line (ie no Pico software). So I disconnect the Pico GP signal and use manual jumper wires to give the control signals, and use my 50MHz scope to check the motor speed. as shown below.
Now I am analysing the N20 Motor 1 Encoder signal Output 1, and see if we can calculate the motor speed from this signal. Avery rough formula is 600uS ~= 30 rpm. Next step is is see how to do the time stamping use micro python.
MicroPython utime – time related functions
https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/library/utime.html
Description - The utime module provides functions for getting the current time and date, measuring time intervals, and for delays.
I read the docs for utime and found it similar to Thonny python, except a little bet smaller. I found user friendly examples on how to use the utime (now I know the “u” of utime means “micro”!  ). One good such example has limit of time calculation less than 500us, but N20 motor’s timing is of the order of 600uS, in other words, just NOT make. I am too lazy to modify my demo programs to it my N20 applications. So lazy me go to Tom’s Hardware for help. I remember Tom;s Hardware has developed a big number of tutorials for newbies, as listed below.
). One good such example has limit of time calculation less than 500us, but N20 motor’s timing is of the order of 600uS, in other words, just NOT make. I am too lazy to modify my demo programs to it my N20 applications. So lazy me go to Tom’s Hardware for help. I remember Tom;s Hardware has developed a big number of tutorials for newbies, as listed below.
Tom’s Hardware Tutorials on Rpi Pico
In the relatively short time that the Pico has been on the market, the Raspberry Pi community has already developed a ton of resources. At Tom’s Hardware, we’ve been publishing our fair share of Pico how-tos, which you can find below.
Tutorial #7 on DC motors is useful for my N20 motor 2WD project here. There is also a useful demo program on the use of buttons. The critical statements are highlighted in pink.
Resuming Long Stalled SPV (Smart Pico Vehicle) Project
Part 1
This project has be stalled for over a month, and I have forgotten what I did last time. So I need now to refresh my memory. The first thing is to make sure the basic Pico hardware still running OK. My first test procedure is to run the “toggle system led program”. Luckily all looks well. Below is the updated toggle led program, with sample output.
# Program Name
# toggle_pico_system_led_v04.py - tlfong01 2021aug16hkt1606
# Configuration
# Thonny 3.3.3, Acer Intel CORE i5 Chinese Windows 10 (64-bit), Python 3.7.9 (32-bit), Tk 8.6.9, USB COM Port #4
# Intepreter
# Micropython (Rapsberry Pi Pico)
# Program Function
# Toggle Pico system LED at GPIO pin 15 (run program to switch on LED, run again to switch off)
# User Guide
# Run code to toggle LED from On to Off or Off to On
from machine import Pin
systemLed = Pin(25, Pin.OUT)
print('Testing Toggling Pcio System LED, v0.4 tlfong01 2021aug16hkt1613')
systemLed.toggle()
# END
# Sample Output - tlfong01 2021aug16hkt1614
'''
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Testing Toggling Pcio System LED, v0.4 tlfong01 2021aug16hkt1613
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Testing Toggling Pcio System LED, v0.4 tlfong01 2021aug16hkt1613
>>>
'''
Part 2 - Checking the 2WD Wiring
I vaguely remember that I first tested one TT130 toy motor with the very simple MX1508 driver, as described by the Tom’s Hardware tutorial. Then I moved on to used TB6616 motr driver, with two N20 motors with speed encoders. I vaguely remember that I used Pico GPIO to read the one of the two encoder output signals, and got a rough idea of the motor speed vs encoder signal periods. So I need to resume from this point. But before that, I need to make sure the motor driver and motor can still move. First step is check out the hardware setup and wiring, and run the basic test program.
Actually I forgot the details of the hardware. So I read my old post to refresh my memory: Making a Rpi Pico Based Smart Vehicle.
The following image is a good memory refresher:
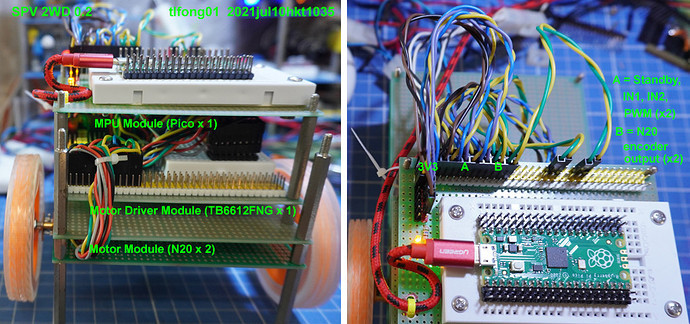
Part 3 - Manual Jumper Wire Motor Moving Testing
Now I am using the following cheat sheet to refresh my memory on how to use jumper wires to off line testing moving motors
To move Motor 1 CW, Motor 2 CCW, I am using the following conifg/wiring
IN1, IN2 (Yellow, Blue) to Low High or High Low
PWM (Purple) = High
StdBy (Brown) = High
Part 4 - Using MicroPython to test moving motors
Now I am using the following Pico MicroPython program is move one motor forward, backward, and stop, and found everything OK.
# Program Name
# move_one_motor_v01.py - tlfong01 2021aug16hkt2218
# Reference
# Pi-Top Forum - making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
# https://forum.pi-top.com/t/making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
# Configuration
# Thonny 3.3.3, Windows 10 (64-bit), Python 3.7.9 (32-bit), Tk 8.6.9, USB COM Port #4
# Intepreter
# Micropython (Rapsberry Pi Pico)
# DC Motor
# (a) TT130 DC3~6V DC Gear Motor - AliEXpress US$1
# https://www.aliexpress.com/item/32855311589.html
# (b) N20 Gear Motor
#
# DC Motor Driver
# (a) MX1508 2~10V, 1.5A, Dual H-Bridge DC Motor Driver - AliExpress US$1
# https://www.aliexpress.com/item/32688083107.html
# (b) TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver
# Program Function
# Move DC motor forward, backward, and stop
# User Guide
# (a) Connect PWMA (purple), PWMB (purple) to High (Vcc)
# (b) Connect Standby (brown) to High
# (c) Run program to move motor forward, backward, and stop
import utime
from machine import Pin
motor1a = Pin(10, Pin.OUT)
motor1b = Pin(11, Pin.OUT)
def moveMotorForward():
motor1a.low()
motor1b.high()
def moveMotorBackward():
motor1a.high()
motor1b.low()
def stopMotor():
motor1a.low()
motor1b.low()
def test():
print(' Begin move motor test()')
moveMotorForward()
utime.sleep(1)
moveMotorBackward()
utime.sleep(1)
stopMotor()
print(' End test()')
for i in range(2):
print('Test ', i)
test()
# *** End of program ***
# *** Sample Output - tlfong01 2021jul01hkt1707
'''
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Test 0
Begin move motor test()
End test()
Test 1
Begin move motor test()
End test()
>>>
'''
Part 5 - Moving two motors
Now that my little demo microPython program moving one N20 motor goes well, I am now upgrading it to move two motors. Now I have a problem of mixing up the getting complicated jumper wires, and therefore find it difficult to do troubleshooting. So I need to do some proper documentation, starting with the photo below.
Now the time has come to use Pico MicroPython to move two motors. The following program is tested OK.
# Program Name
# move_two_motors_v05.py - tlfong01 2021aug17hkt1607
# Reference
# Pi-Top Forum - making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
# https://forum.pi-top.com/t/making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
#
# Configuration
# Acer Intel COIRE i5 PC Chinese Windows 10 (64-bit), Thonny 3.3.3, Python 3.7.9 (32-bit), Tk 8.6.9, USB COM Port #4
#
# Thonny MicroPython Intepreter
# Micropython (Rapsberry Pi Pico)
# DC Motor
# N20 1:48 6V DC Gear Motor with quadrature encoder signals A, B
#
# DC Motor Driver
# TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver
# Program Function
# Move Two DC motors forward, backward, and stop
# User Guide
# (a) Connect PWMA (purple), PWMB (purple) to High (Vcc)
# (b) Connect Standby (brown) to High (Vcc)
# (c) Pico GP 10, 11 (Blk, Bwn) to Motor Driver AIN1, AIN2 (Yel, Blu)
# (d) Pico GP 12, 13 (Red, Orn) to Motor Driver BIN1, BIN2 (Yel, Blu)
# (c) Run program to move motor forward, backward, and stop
import utime
from machine import Pin
motorDict01 = {
'1': {'IN1': 10, 'IN2': 11},
'2': {'IN1': 12, 'IN2': 13},
'3': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0},
'4': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0},
}
motorDictDict = {
'1': motorDict01,
'2': motorDict01,
}
def setupMotor(motorDictNum, motorNum):
motorDict = motorDictDict[str(motorDictNum)]
motorIn1 = Pin(motorDict[str(motorNum)]['IN1'], Pin.OUT)
motorIn2 = Pin(motorDict[str(motorNum)]['IN2'], Pin.OUT)
motorInList = [motorIn1, motorIn2]
return motorInList
def moveMotorForward(motorDictNum, motorNum):
motorInList = setupMotor(motorDictNum, motorNum)
motorInList[0].high()
motorInList[1].low()
return motorInList
def moveMotorBackward(motorDictNum, motorNum):
motorInList = setupMotor(motorDictNum, motorNum)
motorInList[0].low()
motorInList[1].high()
return motorInList
def moveMotorStop(motorDictNum, motorNum):
motorInList = setupMotor(motorDictNum, motorNum)
motorInList[0].low()
motorInList[1].low()
return motorInList
# *** Tests ***
moveMotorForward(motorDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1)
utime.sleep(1)
moveMotorBackward(motorDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1)
utime.sleep(1)
moveMotorStop(motorDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1)
moveMotorForward(motorDictNum = 1, motorNum = 2)
utime.sleep(2)
moveMotorBackward(motorDictNum = 1, motorNum = 2)
utime.sleep(2)
moveMotorStop(motorDictNum = 1, motorNum = 2)
# *** End of program ***
# *** Sample Output - tlfong01 2021jul01hkt1707
'''
'''
Part 6 - Moving two motors with program controlling StandBy and PWM
The following program moving two motor and program control StandBy and PWM is tested OK.
# Program Name
# move_two_motors_v09.py - tlfong01 2021aug17hkt2014
# Reference
# Pi-Top Forum - making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
# https://forum.pi-top.com/t/making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
#
# Configuration
# Acer Intel COIRE i5 PC Chinese Windows 10 (64-bit), Thonny 3.3.3, Python 3.7.9 (32-bit), Tk 8.6.9, USB COM Port #4
#
# Thonny MicroPython Intepreter
# Micropython (Rapsberry Pi Pico)
# DC Motor
# N20 1:48 6V DC Gear Motor with quadrature encoder signals A, B
#
# DC Motor Driver
# TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver
# Program Function
# Move Two DC motors forward, backward, and stop
# User Guide
# (a) Connect PWMA (purple), PWMB (purple) to High (Vcc)
# (b) Connect Standby (brown) to High (Vcc)
# (c) Pico GP 10, 11 (Blk, Bwn) to Motor Driver AIN1, AIN2 (Yel, Blu)
# (d) Pico GP 12, 13 (Red, Orn) to Motor Driver BIN1, BIN2 (Yel, Blu)
# (c) Run program to move motor forward, backward, and stop
import utime
from machine import Pin
driverDict01 = {
'Title' : 'TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver',
'STANDBY' : 5,
'1': {'IN1': 10, 'IN2': 11, 'PWM' : 3, 'ENCODE': 14},
'2': {'IN1': 12, 'IN2': 13, 'PWM' : 4, 'ENCODE': 15},
'3': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0},
'4': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0},
}
driverDictDict = {
'1': driverDict01,
'2': driverDict01,
}
def setupDriver(driverDictNum):
driverDict = driverDictDict[str(driverDictNum)]
standBy = Pin(driverDict['STANDBY'], Pin.OUT)
standBy.high()
return
def setupMotor(driverDictNum, motorNum):
driverDict = driverDictDict[str(driverDictNum)]
motorIn1 = Pin(driverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN1'], Pin.OUT)
motorIn2 = Pin(driverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN2'], Pin.OUT)
motorPwm = Pin(driverDict[str(motorNum)]['PWM'], Pin.OUT)
motorControlPinList = [motorIn1, motorIn2, motorPwm]
return motorControlPinList
def moveMotorForward(driverDictNum, motorNum):
motorControlPinList = setupMotor(driverDictNum, motorNum)
motorControlPinList[0].low()
motorControlPinList[1].high()
motorControlPinList[2].high()
return
def moveMotorBackward(driverDictNum, motorNum):
motorControlPinList = setupMotor(driverDictNum, motorNum)
motorControlPinList[0].high()
motorControlPinList[1].low()
motorControlPinList[2].high()
return
def moveMotorStop(driverDictNum, motorNum):
motorControlPinList = setupMotor(driverDictNum, motorNum)
motorControlPinList[0].low()
motorControlPinList[1].low()
motorControlPinList[2].high()
return
# *** Motor Test Functions ***
def motorTest01(driverDictNum, motorNum):
# *** Setup Driver ***
setupDriver(driverDictNum)
# *** Move motor forward ***
moveMotorForward(driverDictNum, motorNum)
utime.sleep(1)
# *** Move motor backward ***
moveMotorBackward(driverDictNum, motorNum)
utime.sleep(1)
# *** Move motor stop ***
moveMotorStop(driverDictNum, motorNum)
return
# *** Main Tests ***
# Setup motor driver, Move Motor 1 forward, backward, stop
motorTest01(driverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1)
# Setup motor driver, Move Motor 2 forward, backward, stop
motorTest01(driverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 2)
# *** End of program ***
# *** Sample Output - tlfong01 2021jul01hkt1707
'''
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
'''
Part 6 - Reading Encoder Signals
The following program give N20 1:100 gear speed of around 400rpm
# Program Name
# measure_motor_speed_v09.py - tlfong01 2021aug18hkt1120
# Reference
# Pi-Top Forum - making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
# https://forum.pi-top.com/t/making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
#
# Configuration
# Acer Intel COIRE i5 PC Chinese Windows 10 (64-bit), Thonny 3.3.3, Python 3.7.9 (32-bit), Tk 8.6.9, USB COM Port #4
#
# Thonny MicroPython Intepreter
# Micropython (Rapsberry Pi Pico)
#
# DC Motor
# N20 1:100 6V DC Gear Motor with quadrature encoder signals A, B
# N20 Gear Motor Spec (6V gear 1:100 no load speed = 300 rpm (https://www.pololu.com/search/compare/173)
#
# DC Motor Driver
# TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver
# Program Function
# Measure speed of DC motor N20 with quadrature encoder
import utime
from machine import Pin
driverDict01 = {
'Title' : 'TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver',
'STANDBY' : 5,
'1': {'IN1': 10, 'IN2': 11, 'PWM' : 3, 'ENCODE': 14},
'2': {'IN1': 12, 'IN2': 13, 'PWM' : 4, 'ENCODE': 15},
'3': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0},
'4': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0},
}
driverDictDict = {
'1': driverDict01,
'2': driverDict01,
}
def setupDriver(driverDictNum):
driverDict = driverDictDict[str(driverDictNum)]
standBy = Pin(driverDict['STANDBY'], Pin.OUT)
standBy.high()
return
def setupMotor(driverDictNum, motorNum):
driverDict = driverDictDict[str(driverDictNum)]
motorIn1 = Pin(driverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN1'], Pin.OUT)
motorIn2 = Pin(driverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN2'], Pin.OUT)
motorPwm = Pin(driverDict[str(motorNum)]['PWM'], Pin.OUT)
motorEncode = Pin(driverDict[str(motorNum)]['ENCODE'], Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
motorControlPinList = [motorIn1, motorIn2, motorPwm, motorEncode]
return motorControlPinList
def moveMotorForward(driverDictNum, motorNum):
motorControlPinList = setupMotor(driverDictNum, motorNum)
motorControlPinList[0].low()
motorControlPinList[1].high()
motorControlPinList[2].high()
return
def moveMotorBackward(driverDictNum, motorNum):
motorControlPinList = setupMotor(driverDictNum, motorNum)
motorControlPinList[0].high()
motorControlPinList[1].low()
motorControlPinList[2].high()
return
def moveMotorStop(driverDictNum, motorNum):
motorControlPinList = setupMotor(driverDictNum, motorNum)
motorControlPinList[0].low()
motorControlPinList[1].low()
motorControlPinList[2].high()
return
def readMotorEncodeValue(driverDictNum, motorNum):
motorControlPinList = setupMotor(driverDictNum, motorNum)
encodeValue = motorControlPinList[3].value()
return encodeValue
# *** Motor Test Functions ***
def testMoveMotor01(driverDictNum, motorNum):
# *** Setup Driver ***
setupDriver(driverDictNum)
# *** Move motor forward ***
moveMotorForward(driverDictNum, motorNum)
utime.sleep(1)
# *** Move motor backward ***
moveMotorBackward(driverDictNum, motorNum)
utime.sleep(1)
# *** Move motor stop ***
moveMotorStop(driverDictNum, motorNum)
return
def testReadMotorEncodeValue01(driverDictNum, motorNum):
# *** Setup Driver ***
setupDriver(driverDictNum)
# *** Read motor encode value ***
print('Move motor by hand and read encode value every second, ...')
for secondCount in range(100):
encodeValue = readMotorEncodeValue(driverDictNum, motorNum)
print(' motor encode value =', encodeValue)
utime.sleep(1)
return
def testReadMotorEncodeValue02(driverDictNum, motorNum):
# *** Setup Driver ***
setupDriver(driverDictNum)
# *** Move motor forward ***
moveMotorForward(driverDictNum, motorNum)
# *** Read motor encode value ***
print('Move motor by hand and read encode value every second, ...')
for secondCount in range(100):
encodeValue = readMotorEncodeValue(driverDictNum, motorNum)
print(' motor encode value =', encodeValue)
utime.sleep(1)
return
def testMeasureMotorSpeed01(driverDictNum, motorNum):
# *** Setup Driver ***
setupDriver(driverDictNum)
# *** Move motor forward ***
moveMotorForward(driverDictNum, motorNum)
# *** Measure Motor Speed ***
# *** Start counting 10 revolutions ***
usTicks1 = utime.ticks_us()
# *** Find lapse time of 100 revolutions ***
revCount = 0
while revCount < 10:
if readMotorEncodeValue(driverDictNum, motorNum) == 0:
revCount = revCount + 1
utime.sleep(0.000001)
usTicks2 = utime.ticks_us()
rev10Us = utime.ticks_diff(usTicks2, usTicks1)
revUs = int(rev10Us / 10)
rps = int(1000000 / revUs)
rpmRaw = int(rps * 60)
rpmGear100 = int(rpmRaw / 100)
print('revUs =', revUs)
print('rps =', rps)
print('rpm raw =', rpmRaw)
print('rpm 100 =', rpmGear100)
moveMotorStop(driverDictNum, motorNum)
return
# *** Main Tests ***
# *** Test move motor forward, backward, stop ***
# testMoveMotor01(driverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1)
# testMoveMotor01(driverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 2)
# *** Test measure motor speed ***
testMeasureMotorSpeed01(driverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1)
# ***
#moveMotorStop(driverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1)
# *** End of program ***
# *** Sample Output - tlfong01 2021aug18hkt1120
'''
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
revUs = 1250
rps = 800
rpm raw = 48000
rpm 100 = 480
>>>
'''
Part 7 - Using PWM to control speed of N20 Motor
Now I have written the following program to test basic PWM functions. I need to use my scope to display the 1kHz, 50% duty cycle waveform, before trying to use this PWM signal to control the speed of the N20 motor.
# *** PWM Functions ***
def setupPwm(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
motorDriverDict = motorDriverDictDict[str(motorDriverDictNum)]
pwmPinNum = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['PWM']
motorPwm = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum))
motorPwm.freq(pwmFreq)
motorPwm.duty_u16(int(65536 / 100) * dutyCycle)
print('PWM freq (Hz) =', motorPwm.freq())
print('PWM duty (%) =', int((motorPwm.duty_u16() / 65536) * 100))
print('PWM width (ns) =', motorPwm.duty_ns())
return
# *** Motor Test Functions ***
def testMoveMotor01(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum):
# *** Setup Driver ***
setupMotorDriver(motorDriverDictNum)
# *** Move motor forward ***
moveMotorForward(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
utime.sleep(1)
# *** Move motor backward ***
moveMotorBackward(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
utime.sleep(1)
# *** Move motor stop ***
moveMotorStop(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
return
def testMeasureMotorSpeed01(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum):
measureMotorSpeed(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
return
def testSetupMotorPwm01(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
setupPwm(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
return
# *** Main Tests ***
# *** Test move motor forward, backward, stop ***
# print('Test Motor #1 Move Forward, Backward, Stop')
# testMoveMotor01(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1)
# print('Test Motor #2 Move Forward, Backward, Stop')
# testMoveMotor01(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 2)
# *** Test measure motor speed ***
# print('\nTest Measure Motor #1 Speed')
#testMeasureMotorSpeed01(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1)
# *** Test PWM Funcions ***
print('\nTest PWM Funcions')
testSetupMotorPwm01(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum =1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 50)
# *** End of program ***
# *** Sample Output - tlfong01 2021aug18hkt1120
'''
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
revUs = 1250
rps = 800
rpm raw = 48000
rpm 100 = 480
>>>
'''
'''
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Test PWM Funcions
PWM freq (Hz) = 1000
PWM duty (%) = 49
PWM width (ns) = 499728
>>>
'''
I have modified my old program to use PWM pin to control the speed of the motor (earlier I only used PWM pin as high/low logical signal to turn motor fully on or off. Now I am using PWM 1kHz and duty cycle 0~100% to control speed of motor. I found, as expected, motor moves slowly with duty cycle small and quickly with high duty cycle. However, I found the speed measurement function not reliable, mainly because I use counting 100 logical low level signals/revolutions from encoder, and I did not set the between low levels appropriately. Now I am thinking of using interrupt to detect number of high to low falling edges in a specified time period to calculate the motor speed. This way the measurement of speed should be more accurate.
Anyway, I am listing my old speed measurement program to do interrupt driven method to compare and contrast.
Note - I found that this long post exceeds the forum’s 32k words limit. So I am deleting some functions to fit the bill.
# Program Name
# measure_motor_speed_v16.py - tlfong01 2021aug19hkt1132
# docs and functions deleted
import utime
from machine import Pin, PWM
# *** Configuration ***
motorDriverDict01 = {
'TITLE' : 'TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver Dictionary',
'STANDBY' : 5,
'1': {'IN1': 10, 'IN2': 11, 'PWM' : 3, 'ENCODE': 14},
'2': {'IN1': 12, 'IN2': 13, 'PWM' : 4, 'ENCODE': 15},
'3': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0, 'ENCODE': 0},
'4': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0, 'ENCODE': 0},
}
motorDriverDictDict = {
'1': motorDriverDict01,
'2': motorDriverDict01,
}
# *** Read Motor Encoder, Measure Motor Speed ***
def readMotorEncodeValue(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum):
motorControlPinList = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
encodeValue = motorControlPinList[3].value()
return encodeValue
def measureMotorSpeed(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum):
# *** Setup Motor Driver ***
setupMotorDriver(motorDriverDictNum)
# *** Move motor forward ***
moveMotorForward(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
# *** Measure Motor Speed ***
# *** Start counting 10 revolutions ***
usTicks1 = utime.ticks_us()
# *** Find lapse time of 100 revolutions ***
revCount = 0
while revCount < 10:
if readMotorEncodeValue(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum) == 0:
revCount = revCount + 1
utime.sleep(0.000001)
usTicks2 = utime.ticks_us()
rev10Us = utime.ticks_diff(usTicks2, usTicks1)
revUs = int(rev10Us / 10)
rps = int(1000000 / revUs)
rpmRaw = int(rps * 60)
rpmGear100 = int(rpmRaw / 100)
print(' uS per revolution =', revUs)
print(' rps raw =', rps)
print(' rpm raw =', rpmRaw)
print(' rpm gear 1:100 =', rpmGear100)
return rpmGear100
# *** PWM Functions ***
def setupMotorDriverPwm(motorDriverDictNum):
motorDriverDict = motorDriverDictDict[str(motorDriverDictNum)]
# print(' motDriverDictNum =', motorDriverDictNum)
standBy = Pin(motorDriverDict['STANDBY'], Pin.OUT)
standBy.high()
return
def setupMotorPwm(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
motorDriverDict = motorDriverDictDict[str(motorDriverDictNum)]
motorIn1Pin = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN1']
motorIn2Pin = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN2']
motorPwmPin = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['PWM']
# print(' IN1 pinNum =', motorIn1Pin)
# print(' IN2 pinNum =', motorIn2Pin)
# print(' PWM pinNum =', motorPwmPin)
motorIn1 = Pin(motorIn1Pin, Pin.OUT)
motorIn2 = Pin(motorIn2Pin, Pin.OUT)
motorPwm = PWM(Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['PWM']))
motorPwm.freq(pwmFreq)
motorPwm.duty_u16(int(65536 / 100) * dutyCycle)
pwmPinNum = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['PWM']
# print(' Setup PWM')
# print(' PWM freq (Hz) =', motorPwm.freq())
# print(' PWM duty (%) =', int((motorPwm.duty_u16() / 65536) * 100))
# print(' PWM width (ns) =', motorPwm.duty_ns())
motorEncode = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['ENCODE'], Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
motorControlPinList = [motorIn1, motorIn2, motorPwm, motorEncode]
return motorControlPinList
def moveMotorForwardPwm(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
motorControlPinList = setupMotorPwm(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
motorControlPinList[0].low()
motorControlPinList[1].high()
motorControlPinList[2].freq(pwmFreq)
motorControlPinList[2].duty_u16(int(65536 / 100) * dutyCycle)
return
def measureMotorSpeedPwm(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum):
# *** Setup Motor Driver ***
# setupMotorDriver(motorDriverDictNum)
# *** Move motor forward ***
# moveMotorForwardPwm(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
# *** Measure Motor Speed ***
# *** Start counting 10 revolutions ***
usTicks1 = utime.ticks_us()
# *** Find lapse time of 100 revolutions ***
revCount = 0
while revCount < 10:
if readMotorEncodeValue(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum) == 0:
revCount = revCount + 1
utime.sleep(0.0001) # <<<<<<<<<<<<
usTicks2 = utime.ticks_us()
rev10Us = utime.ticks_diff(usTicks2, usTicks1)
revUs = int(rev10Us / 10)
rps = int(1000000 / revUs)
rpmRaw = int(rps * 60)
rpmGear100 = int(rpmRaw / 100)
# print(' uS per revolution =', revUs)
# print(' rps raw =', rps)
# print(' rpm raw =', rpmRaw)
# print(' rpm gear 1:100 =', rpmGear100)
return rpmGear100
# *** Motor Test Functions ***
def testMoveMotor01(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum):
# *** Setup Driver ***
setupMotorDriver(motorDriverDictNum)
# *** Move motor forward ***
moveMotorForward(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
utime.sleep(1)
# *** Move motor backward ***
moveMotorBackward(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
utime.sleep(1)
# *** Move motor stop ***
moveMotorStop(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
return
def testMeasureMotorSpeed01(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum):
measureMotorSpeed(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
return
#def testSetupMotorPwm01(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
# setupPwm(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
# return
def testMoveMotorForwardPwm01(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
setupMotorDriverPwm(motorDriverDictNum)
moveMotorForwardPwm(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(4)
moveMotorStop(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
return
def testMeasureMotorSpeedPwm01(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
setupMotorDriverPwm(motorDriverDictNum)
moveMotorForwardPwm(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(2)
speedRpmGear = measureMotorSpeedPwm(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
print('dutyCycle =', dutyCycle)
print('speed (rpmGear) =', speedRpmGear)
# moveMotorStop(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
return
# *** Main Tests ***
# *** Test move motor forward, backward, stop ***
# print('Test Motor #1 Move Forward, Backward, Stop')
# testMoveMotor01(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1)
# print('\nTest Motor #2 Move Forward, Backward, Stop')
# testMoveMotor01(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 2)
# *** Test measure motor speed ***
# print('\nTest Measure Motor #1 Speed')
# testMeasureMotorSpeed01(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1)
# *** Test Move Motor / Measure Speed PWM Funcions ***
print('Test Move Motor Forward')
# testMoveMotorForwardPwm01(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 100)
# testMoveMotorForwardPwm01(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 50)
# testMoveMotorForwardPwm01(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 10)
print('Test Measure Motor Speed')
testMeasureMotorSpeedPwm01(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 80)
print('Test Measure Motor Speed')
testMeasureMotorSpeedPwm01(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 50)
print('Test Measure Motor Speed')
testMeasureMotorSpeedPwm01(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 40)
print('Stop Motor')
moveMotorStop(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1)
# *** End of program ***
# *** Sample Output - tlfong01 2021aug18hkt1120
'''
MicroPython v1.16 on 2021-06-18; Raspberry Pi Pico with RP2040
Type "help()" for more information.
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Test Move Motor Forward
Test Measure Motor Speed
dutyCycle = 80
speed (rpmGear) = 479
Test Measure Motor Speed
dutyCycle = 50
speed (rpmGear) = 479
Test Measure Motor Speed
dutyCycle = 40
speed (rpmGear) = 524
Stop Motor
>>>
'''
'''
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Test PWM Funcions
PWM freq (Hz) = 1000
PWM duty (%) = 49
PWM width (ns) = 499728
>>>
'''
Note - This reply post is getting too long, exceeding the forum’s 32k word limit. So I am breaking up to another reply.
/ to continue, …
This reply follows from the early long reply. I am starting to study how to use microPython interrupt, to write a new function to measure the speed of the N20 geared motor with encoders.
Interrupt Learning Notes
I know interrupt handlers (Interrupt Service Routines, ISR’s) are very difficult to debug. So my goal is try to write an interrupt handler as simple as possible, but not simpler.
Below are the tutorials I will start reading, before writing the very simple interrupt handler for measuring the speed of the N20 motor.
(1) Raspberry Pi GPIO Interrupts Tutorial
(2) MicroPython Writing interrupt handlers
(3) Dual Cores & Interrupts on Pi Pico (Using Thonny) - By tonygo2
MicroPython Writing interrupt handlers - Reading Notes
Tips and recommended practices
…
Where an ISR returns multiple bytes use a pre-allocated bytearray. If multiple integers are to be shared between an ISR and the main program consider an array (array.array).
Where data is shared between the main program and an ISR, consider disabling interrupts prior to accessing the data in the main program and re-enabling them immediately afterwards (see Critical Sections).
Simplicity
For a variety of reasons it is important to keep ISR code as short and simple as possible. It should do only what has to be done immediately after the event which caused it: operations which can be deferred should be delegated to the main program loop. Typically an ISR will deal with the hardware device which caused the interrupt, making it ready for the next interrupt to occur. It will communicate with the main loop by updating shared data to indicate that the interrupt has occurred, and it will return. An ISR should return control to the main loop as quickly as possible.
Communication between an ISR and the main program
Normally an ISR needs to communicate with the main program. The simplest means of doing this is via one or more shared data objects, either declared as global or shared via a class (see below). There are various restrictions and hazards around doing this, which are covered in more detail below. Integers, bytes and bytearray objects are commonly used for this purpose along with arrays (from the array module) which can store various data types.
Creation of Python objects
One way to avoid this issue is for the ISR to use pre-allocated buffers. For example a class constructor creates a bytearray instance and a boolean flag. The ISR method assigns data to locations in the buffer and sets the flag. The memory allocation occurs in the main program code when the object is instantiated rather than in the ISR.
N20 Motor Speed Measurement Function Using 2 Core Pico and Interrupts - Part 1
I skimmed all three tutorials above and found Ref 1 good as a general introduction to interrupts. But it is based on Rpi4, not on Pico, so not too useful else. Ref 2 is base on MicroPython, but a bit too advanced for newbies. Ref 3 by TonyGo2 is very good, very newbie friend and can be used as a template to adapt to my motor speed measurement function. It uses 2 core Pico and also Thonny MicroPython. So I am thinking a learning 2 core programming using this example.
Last reply exceeded the forum’s 32k words limit. So this time I am using the Penzu stuff to make this reply’s program listing shorter, as show below.
Motor Speed Measure v0.1 Program Listing
I found the TonyGo2 tutorial on interrupt handler good, but not easy to adapt to my simple applications. So I searched for more newbie friendly tutorials and found the first two of the following three tutorials good.
(2) How to use the two Cores of the Pi Pico? And how fast are Interrupts? - Andreas Spiess, 71,479 views, 2021feb21 (Two thread/core at 5:03, Interrupt at 8:04, frequency ounter at 8:54, PIO fast counter at 11:04)
(3) Rpi Pico hardware_irq Hardware APIs - SDK Documentation
The first tutorial from RoboCraze is simple, so I will be using it to adapt to my N20 motor speed measurement. Andreas Spiess’s tutorial is very comprehensive. So I might use it to improve my first trial of speed measurement.
Now I am looking closely at RoboCraze’s interrupt program example, which I think is excellent for newbies, because it is what I used to say “Make it as simple as possible, but not simpler” or often called the Ockham’s Razor. RoboCraze’s example is good in that it does not even use any global variable/flag/counter. The main part is shown below:
Now I have debugged a preliminary version of the N20 speed measurement function spv30310.py.
This version does the following:
1. Setup and move motor forward
2. Setup and move motor backward
3. Setup and measure motor speed
# Program Name
# spv31313_2021aug2101.py - tlfong01 2021aug21hkt2058
# Reference
# Pi-Top Forum - making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
# https://forum.pi-top.com/t/making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
#
# Configuration
# Acer Aspire Intel COIRE i5 PC Chinese Windows 10 (64-bit), Thonny 3.3.3, Python 3.7.9 (32-bit), Tk 8.6.9, USB COM Port #4
#
# Thonny MicroPython Intepreter
# Micropython (Rapsberry Pi Pico)
#
# DC Motor
# N20 1:100 6V DC Gear Motor with quadrature encoder signals A, B
# N20 Gear Motor Spec (6V gear 1:100 no load speed = 300 rpm (https://www.pololu.com/search/compare/173)
#
# DC Motor Driver
# TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver
# Brief Description of Program Function
# 1. Move DC motor N20 forward, backware, stop.
# 2. Use PWM to control motor speed
# 3. Use N20 motor encoder to measure speed
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
import utime
from machine import Pin, PWM
# *** Configuration ***
motorDriverDict01 = {
'TITLE' : 'TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver Dictionary v0.1 tlfong01 2021aug21hkt0949',
'STANDBY' : 5,
'1': {'IN1': 10, 'IN2': 11, 'PWM' : 3, 'ENCODE': 14},
'2': {'IN1': 12, 'IN2': 13, 'PWM' : 4, 'ENCODE': 15},
'3': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0, 'ENCODE': 0},
'4': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0, 'ENCODE': 0},
}
motorDriverDictDict = {
'1': motorDriverDict01,
'2': motorDriverDict01,
}
# *** Motor Functions ***
def setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
motorDriverDict = motorDriverDictDict[str(motorDriverDictNum)] # Get driver dict
driverStandBy = Pin(motorDriverDict['STANDBY'], Pin.OUT) # create driverStandBy pin object
motorIn1 = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN1'], Pin.OUT) # Create Motor # motorNum In1 pin object
motorIn2 = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN2'], Pin.OUT) # Create Motor # motorNum In2 pin object
motorPwm = PWM(Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['PWM'])) # Create Motor # motorNum Pwm pin object
motorEncode = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['ENCODE'], Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN) # Create Motor # motorNum Encode pin object
motorConfigDict = {'StdBy': driverStandBy, 'In1': motorIn1, 'In2': motorIn2, 'Pwm': motorPwm, 'Encode': motorEncode, \
'PwmFreq': pwmFreq, 'DutyCycle': dutyCycle}
motorConfigDict['StdBy'].high() # enable motor driver normal operation, (low = disable)
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].freq(pwmFreq) # setup frequency
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].duty_u16(int(65536 / 100) * dutyCycle) # and duty cycle
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return motorConfigDict
def moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict):
motorConfigDict['In1'].low() # move motor
motorConfigDict['In2'].high() # backward
return
def stopMotor(motorConfigDict):
motorConfigDict['In1'].low()
motorConfigDict['In2'].low()
return
def moveMotorForward(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds):
motorConfigDict['In1'].low()
motorConfigDict['In2'].high()
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def moveMotorBackward(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds):
motorConfigDict['In1'].high()
motorConfigDict['In2'].low()
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
# *** Test Functions ***
def testMoveMotorForward(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle, moveSeconds):
print('\ntestMoveMotorForward()')
motorConfigDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
moveMotorForward(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def testMoveMotorBackward(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle, moveSeconds):
print('\ntestMoveMotorBackward()')
motorConfigDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
moveMotorBackward(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def testMeasureMotorSpeed(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
print('\ntestMeasureMotorSpeed(), ...')
# *** Setup motor and move motor forward ***
motorConfigDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
# *** Define callback funtion ***
def encodeIntCallBack(pin):
global encodeIntEventCount
encodeIntEventCount = encodeIntEventCount + 1
return
# *** Setup callback function ***
motorConfigDict['Encode'].irq(encodeIntCallBack, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
# *** Count Encode Interrupt Events Every Second ***
global encodeIntEventCount
encodeIntEventCount = 0
totalSecondCount = 4
#print('totalSecondCount =', totalSecondCount)
for secondCount in range(totalSecondCount):
#print('TotalEncodeIntEventCount =', encodeIntEventCount)
utime.sleep(1)
avgEncodeIntEventCount = int(encodeIntEventCount / totalSecondCount)
#print('pwmFreq =', motorConfigDict['PwmFreq'])
print('dutyCycle =', motorConfigDict['DutyCycle'])
#print('average encodeIntEventCount Per Second =', avgEncodeIntEventCount)
print('N20 rpm =', int((avgEncodeIntEventCount * 60)/100))
return
# *** Main ***
testMoveMotorForward(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 90, moveSeconds = 1)
testMoveMotorBackward(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 90, moveSeconds = 1)
testMeasureMotorSpeed(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 100)
testMeasureMotorSpeed(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 50)
testMeasureMotorSpeed(motorDriverDictNum = 1, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 10)
# End
'''
Sample output - tlfong01 2021aug21
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
testMoveMotorForward()
testMoveMotorBackward()
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), ...
dutyCycle = 100
N20 rpm = 960
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), ...
dutyCycle = 50
N20 rpm = 454
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), ...
dutyCycle = 10
N20 rpm = 52
>>>
'''
Now I am plotting N20 motor rpm speed vs dutyCycle using the following speed measurement results
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), …
dutyCycle = 100
N20 rpm = 964
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), …
dutyCycle = 955
N20 rpm = 67
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), …
dutyCycle = 90
N20 rpm = 868
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), …
dutyCycle = 80
N20 rpm = 769
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), …
dutyCycle = 70
N20 rpm = 661
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), …
dutyCycle = 60
N20 rpm = 553
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), …
dutyCycle = 50
N20 rpm = 448
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), …
dutyCycle = 40
N20 rpm = 351
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), …
dutyCycle = 30
N20 rpm = 247
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), …
dutyCycle = 20
N20 rpm = 150
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), …
dutyCycle = 10
N20 rpm = 50
testMeasureMotorSpeed(), …
dutyCycle = 5
N20 rpm = 0
I am glad to see that the N20 motor rpm speed vs pwm duty cycle is very linear.
Motor to motor speed difference
I tested two motors and found the following difference.
motorNum = 1 dutyCycle = 50 N20 rpm = 445
motorNum = 2 dutyCycle = 50 N20 rpm = 473
The speed difference is about 473 / 445 ~=6%
This means that if both motors are moved with duty cycle 50%, the wheel speed is about 6%, or in other words the vehicle will not move in a straight line.
So if I want the vehicle move in a straight line, I need to adjust the duty cycle of each motor.
Distance traveled vs motor moving time
Now I am modifying the program to find the distance of a 6.3cm diameter wheel traveled in 4 seconds.
Sample Output (my dodgy calculation not verified! :))
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
motorNum = 1 dutyCycle = 50 seconds moved = 4
revolution made = 2883
1/100 geared wheel revolutions made = 28
distance traveled (cm) = 570
>>>
Errata - I forgot that the quadrature encoder might have 6, 12 or more pulses/counts per revolution. So the actual distance traveled in the above calculation should be 570 / 12 ~= 50cm.
Note - But I am not too sure. I am using only the falling edge of only Signal A of the quadrature encoder. Some specs says Count Per Revolution (CPR) is 4 times of Pulses Per Revolution (PPR), because CPR takes care of both Signals A, and B, and both falling and rising edges.
How to move a specified distance
So I moved on to write a function to move to a specified distance, say 1 metre. I timed the time required to move one revolution and calculate the specified distance by the distance of one revolution, and get the number of revolution required distance. However, I found this trick does not work, because the time for the first or second revolution is longer that the later revolutions (because it take time to start moving motor and more time to settle down to a steady speed). So I think a better way is to calculate the number of encode interrupts for one revolution, instead of the time required for one revolution. This distance vs encode interrupt counts is also good, because it is independent of speed, PWM frequency, and duty cycle magnitude.
Anyway, the program for using the wrong trick is listed below.
Bad program for moving to a specified distance
Number of Encode Interrupt Counts Per Revolution
I found that for pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 50, time required to move motor for one revolution is about 1.38 seconds, and
the more precise number of interrupt counts for one revolution is 983, which is a very important number for my later programs.
Refactoring
spv31325.py can now move a number of encode interrupts/revolutions/distance
Considering trying two core interrupts
Now that my motor moving program using interrupts is working properly, I am thinking of try out two core interrupt as described in the TonyGo2 tutorial. I found the trick is simple, but makes the processing more complicated. So I am not try it for now. Anyway, I summarized TonyGo2’s programming below, for later reference.
TonyGo2' Tutorial (https://www.instructables.com/Dual-Cores-Interrupts-on-Pi-Pico/)
1. Break down into 3 parts.
a. Setting up and activating the cores
b. Shutting down the cores in sequence
c. Using interrupts
2. Two Core/Process/Thread operation
a. Core 0 process/thread counts (button pushing) interrupts and does something when counts up (to 30)
b. Core 1 process/thread blinks LEDs
3. Programming
a. Imports _thread module
b. Imports gc (garbage module)
c. Two Core 0 process/tasks
Two interrupt pins associated with two interrupt events (and Interrupt Service Routines (IsRS):
(i) "LedDirectionTask(pin)" triggered by "Led direction pin signal rising edge"
(ii) "HaltTask(pin), triggered by "Halt pin signal rising edge"
d. One Core 1 process/task
(i) main process running LEDs, thread exits if not "running".
(ii) garbage collect if interrupt counts to 100
Testing two motors
How to drive the 2WD (1) in a straight line, (b) in a circle, © in a square
Now that I know how to count Encoder signals in a time period, it is time to do more fancy things, like driving the 2WD in a straight line. Before that, I need to ‘sync’ the two motor’s encoder interrupt count, distance traveled etc. A sample output of the calibration is shown below:
'''
Sample output - tlfong01 2021aug25hkt1145
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 1 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 100 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 1563
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 2 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 100 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 1941
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 1 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 50 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 1077
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 2 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 50 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 830
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 1 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 10 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 193
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 2 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 10 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 88
>>>
'''
And the program listed below:
Realtime Sync Design Notes
I found the sync by interrupt count not very reliable on order of seconds, as summarized below.
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 1 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 55 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 809
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 2 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 48 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 808
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 1 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 55 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 810
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 2 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 48 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 824
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 1 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 55 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 808
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 2 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 48 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 814
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 1 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 55 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 809
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 2 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 48 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 820
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 1 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 55 MoveSeconds =, 10 encodeIntCount = 8390
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 2 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 48 MoveSeconds =, 10 encodeIntCount = 7388
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 1 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 55 MoveSeconds =, 100 encodeIntCount = 84405
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 2 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 48 MoveSeconds =, 100 encodeIntCount = 72700
>>>
The root problem is that the differential speed error accumulates, with the result that it is not practical to use this trick the drive the vehicle move in a straight line, not to mention in a circle or a square. So I now need to do realtime sync, not in seconds resolution, but in milliseconds. The idea is to watch speed/distance millisecond by millisecond and adjust one or both duty cycles to minimize the difference.
This reply is getting too long and confusing. So I am making a new reply with a selfie walk through of what I have bee doing, and finally reached this point as a milestone. The following version of program is working version of all the testing functions at the motor level. Next reply will move up to the 2WD vehicle’s wheel level. In Object Oriented Programming sense, the new classes at wheel level is higher than the motor level. In Functional Programming sense, the MicroPython dictionaries at moving from motor to wheels/vehicle level.
SPV v4.0 Program
/ to continue, …
SPV(Smart Pico Vehicle)v4.0 - Introduction
This is reply to the last 13 or so replies of this smart vehicle project. I know that using the term “reply” is a bit confusing. Actually I am, in effect, writing a “blog” of the project. I think the term “blog” better reflects the situation, that it is like a diary, with dates of my project progress, especially the mistakes I have been making, which is revealed when doing the tests to verify my project design and direction is more or less OK. I need to remind myself that I am doing TDD (Test Driven Development), or PBL (Problem Based Learning), or Agile/Prototyping, or a mix of all the three approaches. The other thing I need to remind myself is that I am doing sort of structured programming, distributed processing, multiprocessing/multithreading, functional programming (but not object oriented programming).
Now I will do a brief selfie walk through, or an intermittent progress report, in the form of casual, random notes.
I started with Rpi Pico MCU, and N20 geared motor with quadrature encoder, because I read other users proposed these two things.
I got my Pico’s some months ago, but have been a bit lazy to try it out. I did read about Tom’s Hardware tutorials, and other interesting YouTube videos (especially those by the funny Swiss guy) which I think is good for newbies to start off.
I have been using popular DC motor drivers such as L298N to drive two motor vehicles, but only at the start off stage, controlling by PWM by Rpi3/4. I remember one motor driver tutorial challenged to do more advanced things such as moving the two wheeled car/robot in a square. I noticed that no newbies reported that they did it. So I think there is a steep learning curve on how to teach the 2WD to do smart things, like move in a straight line, in a circle, in a square etc.
It was only when I tried out different things, like motor encoder signal interrupts, especially with 2 core Pico, that the stuff is very tricky, especially for newbies. That is why that I need to look back the over ambitious goals I hope to reach, and mistakes I made, before I move on my smart vehicle project.
Now let me report what I am getting stuck at this point. I found moving the N20 motor with a simple spec or requirement such as (1) number of revolutions, (2) number of motor encoder signals/pulses, (3) distance, eg, 1 or 2 meters, is difficult, if precision is needed (eg 5% accuracy/resolution), not to mention synchronizing two or four motors.
So now I am going back a bit and redo some of the tests and calibrations, as a preparation of doing this seemingly easy thing:
Moving a 2WD in a straight line
First thing I need to do is to calibrate the N20 motor encoder interrupt signal timing. I am using the following scope to display the waveforms.
Digital Oscilloscope ATTEN ADS1102CAL+
ATTEN ADS100 User Manual
Now I am using my 100MHz DSO to display the N20 motor encoders pulse signal waveform. I found that for PWM frequency 1kHz, Duty cycle 50%, both motor’s encoders give about 700 pulses per second. I will be using this number 770Hz as calibration/bench mark for my future tests.
And the time has come to try to move my 2WD in a straight line, before trying out the more advanced tricks of Pi Top [4] DIY 2WD, such as autonomous driving in a straight line.
Discrepancy between python program measurement and scope display
I lookded back what I measured earlier using python program, with the following results:
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 1 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 50 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 1077
MotorDriverDictNum = 2 MotorNum = 2 PWM Freq = 1000 DutyCycle = 50 MoveSeconds =, 1 encodeIntCount = 830
It is weird that software results 1077 and 830 interrupt counts per second, but scope measure around 760~770 interrupt counts per second. I need to find out why software counts more interrupts hardware scope. If software results are not reliable or inaccurate, then it would be difficult o sync two motors/wheels to move vehicle in a straight. Perhaps I need to use more motor samples to find out the cause of discrepancy.
PiTop [4] and PiPico Gesture Control
I remember PiTop [4] is using MPU6050 to do smart things like gesture control. So I am hoping to use the same or similar gyro and accelero for fun. This morning I read a newbie friendly tutorial on using MPU6050. So I will try it later.
Using Gyroscope and accelerometer with MPU6050, Rpi Pico and MicroPython - Peppr80, 2021aug85
Pi-Top Encoder Motor API
Now I am read the Pi-Top Encoder API, to see what classes, functions, and parameters are used in their library. There are parameters I understand, such as wheel diameter and circumference. But are some I don’t understand exactly what they are, for example, two types of stopping the motor.
Pi-Top Encoder Motor API - Pi-Top
6. API - pi-top Maker Architecture (PMA) Components
6.3. Encoder Motor
Note
This is a Motor Component which connects to a MotorEncoder Port [M0-M3].
from pitop import (
EncoderMotor,
ForwardDirection,
BrakingType
)
from time import sleep
# Setup the motor
motor = EncoderMotor("M0", ForwardDirection.COUNTER_CLOCKWISE)
motor.braking_type = BrakingType.COAST
# Move in both directions
rpm_speed = 100
for _ in range(4):
motor.set_target_rpm(rpm_speed)
sleep(2)
motor.set_target_rpm(-rpm_speed)
sleep(2)
motor.stop()
classpitop.pma.EncoderMotor(port_name, forward_direction, braking_type=<BrakingType.COAST: 0>, wheel_diameter=0.075, name=None)[source]
Represents a pi-top motor encoder component.
Note that pi-top motor encoders use a built-in closed-loop control system, that feeds the readings from an encoder sensor to an PID controller. This controller will actively modify the motor’s current to move at the desired speed or position, even if a load is applied to the shaft.
This internal controller is used when moving the motor through set_target_rpm or set_target_speed methods, while using the set_power method will make the motor work in open-loop, not using the controller.
Note
Note that some methods allow to use distance and speed settings in meters and meters per second. These will only make sense when using a wheel attached to the shaft of the motor.
The conversions between angle, rotations and RPM used by the motor to meters and meters/second are performed considering the wheel_diameter parameter. This parameter defaults to the diameter of the wheel included with MMK. If a wheel of different dimmensions is attached to the motor, you’ll need to measure it’s diameter, in order for these methods to work properly.
Parameters:
port_name (str) – The ID for the port to which this component is connected.
forward_direction (ForwardDirection) – The type of rotation of the motor shaft that corresponds to forward motion.
braking_type (BrakingType) – The braking type of the motor. Defaults to coast.
wheel_diameter (int or float) – The diameter of the wheel attached to the motor.
backward(target_speed, distance=0.0)[source]
Run the wheel backwards at the desired speed in meters per second.
This method is a simple interface to move the wheel that wraps a call to set_target_speed, specifying the back direction.
If desired, a distance to travel can also be specified in meters, after which the motor will stop. Setting distance to 0 will set the motor to run indefinitely until stopped.
Note
Note that for this method to move the wheel the expected distance, the correct wheel_circumference value needs to be used.
Parameters:
target_speed (int or float) – Desired speed in m/s
distance (int or float) – Total distance to travel in m. Set to 0 to run indefinitely.
braking_type
Returns the type of braking used by the motor when it’s stopping after a movement.
Setting this property will change the way the motor stops a movement:
BrakingType.COAST will make the motor coast to a halt when stopped.
BrakingType.BRAKE will cause the motor to actively brake when stopped.
Parameters: braking_type (BrakingType) – The braking type of the motor.
current_rpm
Returns the actual RPM currently being achieved at the output shaft, measured by the encoder sensor.
This value might differ from the target RPM set through set_target_rpm.
current_speed
Returns the speed currently being achieved by the motor in meters per second.
This value may differ from the target speed set through set_target_speed.
distance
Returns the distance the wheel has travelled in meters.
This value depends on the correct wheel_circumference value being set.
forward(target_speed, distance=0.0)[source]
Run the wheel forward at the desired speed in meters per second.
This method is a simple interface to move the motor that wraps a call to set_target_speed, specifying the forward direction.
If desired, a distance to travel can also be specified in meters, after which the motor will stop. Setting distance to 0 will set the motor to run indefinitely until stopped.
Note
Note that for this method to move the wheel the expected distance, the correct wheel_circumference value needs to be used.
Parameters:
target_speed (int or float) – Desired speed in m/s
distance (int or float) – Total distance to travel in m. Set to 0 to run indefinitely.
forward_direction
Represents the forward direction setting used by the motor.
Setting this property will determine on which direction the motor will turn whenever a movement in a particular direction is requested.
Parameters: forward_direction (ForwardDirection) – The direction that corresponds to forward motion.
max_rpm
Returns the approximate maximum RPM capable given the motor and gear ratio.
max_speed
The approximate maximum speed possible for the wheel attached to the motor shaft, given the motor specs, gear ratio and wheel circumference.
This value depends on the correct wheel_circumference value being set.
own_state
Representation of an object state that will be used to determine the current state of an object.
power()[source]
Get the current power of the motor.
Returns a value from -1.0 to +1.0, assuming the user is controlling the motor using the set_power method (motor is in control mode 0). If this is not the case, returns None.
rotation_counter
Returns the total or partial number of rotations performed by the motor shaft.
Rotations will increment when moving forward, and decrement when moving backward. This value is a float with many decimal points of accuracy, so can be used to monitor even very small turns of the output shaft.
set_power(power, direction=<Direction.FORWARD: 1>)[source]
Turn the motor on at the power level provided, in the range -1.0 to +1.0, where:
1.0: motor will turn with full power in the direction provided as argument.
0.0: motor will not move.
-1.0: motor will turn with full power in the direction contrary to direction.
Warning
Setting a power value out of range will cause the method to raise an exception.
Parameters:
power (int or float) – Motor power, in the range -1.0 to +1.0
direction (Direction) – Direction to rotate the motor
set_target_rpm(target_rpm, direction=<Direction.FORWARD: 1>, total_rotations=0.0)[source]
Run the motor at the specified target_rpm RPM.
If desired, a number of full or partial rotations can also be set through the total_rotations parameter. Once reached, the motor will stop. Setting total_rotations to 0 will set the motor to run indefinitely until stopped.
If the desired RPM setting cannot be achieved, torque_limited will be set to True and the motor will run at the maximum possible RPM it is capable of for the instantaneous torque. This means that if the torque lowers, then the RPM will continue to rise until it meets the desired level.
Care needs to be taken here if you want to drive a vehicle forward in a straight line, as the motors are not guaranteed to spin at the same rate if they are torque-limited.
Warning
Setting a target_rpm higher than the maximum allowed will cause the method to throw an exception. To determine what the maximum possible target RPM for the motor is, use the max_rpm method.
Parameters:
target_rpm (int or float) – Desired RPM of output shaft
direction (Direction) – Direction to rotate the motor. Defaults to forward.
total_rotations (int or float) – Total number of rotations to be execute. Set to 0 to run indefinitely.
set_target_speed(target_speed, direction=<Direction.FORWARD: 1>, distance=0.0)[source]
Run the wheel at the specified target speed in meters per second.
If desired, a distance to travel can also be specified in meters, after which the motor will stop. Setting distance to 0 will set the motor to run indefinitely until stopped.
Warning
Setting a target_speed higher than the maximum allowed will cause the method to throw an exception. To determine what the maximum possible target speed for the motor is, use the max_speed method.
Note
Note that for this method to move the wheel the expected distance, the correct wheel_diameter value needs to be used.
Parameters:
target_speed (int or float) – Desired speed in m/s
direction (Direction) – Direction to rotate the motor. Defaults to forward.
distance (int or float) – Total distance to travel in m. Set to 0 to run indefinitely.
stop()[source]
Stop the motor in all circumstances.
target_rpm()[source]
Get the desired RPM of the motor output shaft, assuming the user is controlling the motor using set_target_rpm (motor is in control mode 1).
If this is not the case, returns None.
torque_limited
Check if the actual motor speed or RPM does not match the target speed or RPM.
Returns a boolean value, True if the motor is torque- limited and False if it is not.
wheel_circumference
wheel_diameter
Represents the diameter of the wheel attached to the motor in meters.
This parameter is important if using library functions to measure speed or distance, as these rely on knowing the diameter of the wheel in order to function correctly. Use one of the predefined pi-top wheel and tyre types, or define your own wheel size.
Note
Note the following diameters:
pi-top MMK Standard Wheel: 0.060.0m
pi-top MMK Standard Wheel with Rubber Tyre: 0.065m
pi-top MMK Standard Wheel with tank track: 0.070m
Parameters: wheel_diameter (int or float) – Wheel diameter in meters.
6.3.1. Parameters
classpitop.pma.parameters.BrakingType[source]
Braking types.
BRAKE= 1
COAST= 0
classpitop.pma.parameters.ForwardDirection[source]
Forward directions.
CLOCKWISE= 1
COUNTER_CLOCKWISE= -1
classpitop.pma.parameters.Direction[source]
Directions.
BACK= -1
FORWARD= 1
.END
Using I2C and SPI for LCD Display, MPU6050 etc
I found MagPi 109 has 20 interesting Pico projects, some of which is useful for my projects here. So I am summarizing here. PiTop 4’s Line Follower is based ofn Rpi4B. I need to modify it for Pico, and the first project listed here is very useful for my reference.
Line Follower Robot using Pico - Raspberry Pi Pico Projects
Raspberry Pi Pico Line Follower Robot | Raspberry Pi Pico Projects 1,572 views Apr 14, 2021
Raspberry Pi Pico: digital communication protocols I2C and SPI to control LCD Display - Page 54 MagPi 109
MagPi109 on Pico Controlled Automated Model Railroad
MagPi Issue 109 (2021sept) also has an interesting project on Raspberry Pi Pico Controlled Simple Model Railway
Raspberry Pi Pico Controlled Simple Automated Model Railroad | Model Railroad Automation - By KushagraK7 2,62316Featured
Raspberry Pi Pico Controlled Simple Model Railway | Model Railroad Automation
TB6612FNG H-Bridge Motor Controller - Better than L298N? - 81,466 views 2019dec16
Note - This tutorial explains why I am using TB6612FNG and not the very popular L298N.
Note - There is one other exclusive feature of TB6612 which make it to do 2WD or 4WD superior than L298N, …
Pi-Top Encoder Motor vs TT130 Motor
Pi-Top Servo Motor is sort of a black box. So I am checking out MiaowLab’s TT encode motor to compare and contrast.
PiTop [4] DIY with Rpi4B / To consider later, …
Installing the Raspberry Pi 4 into your pi-top [4] DIY Edition 8,310 viewsSep 23, 2020
Swapping N20 encoder motor with TT130 encoder motor
Now I have swapped N20 motor with TT130 motor
TT130 Motor TB6612FNG Driver Test 2021aug2901
Pico GPIO Libraries
This couple of weeks I have been mainly using Tom’s Hardware tutorials as a newbie’s guide on how to write python app code. So far so good, except that when I hope to dig deeper to expand my code, eg. from one motor to two motors or 4 motors, I need to write my own code. I tried to good pico GPIO libraries without luck. I only found Rpi3/4, but no Pico ones, as described below.
GPIO Programming on the Raspberry Pi: Python Libraries - Sebastian 2021apr30
TT130 Motors replacing N20 motors
One reason that I am trying TT130 motor is that its stall torques is stronger, 2.5kg-cm, compared with N20’s 0.4kg-cm.
The test program
# Program Name
# spv4002_2021aug2801.py - tlfong01 2021aug28hkt2114
# Reference
# Pi-Top Forum - making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
# https://forum.pi-top.com/t/making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
#
# Configuration
# Acer Aspire Intel COIRE i5 PC Chinese Windows 10 (64-bit), Thonny 3.3.3, Python 3.7.9 (32-bit), Tk 8.6.9, USB COM Port #4
#
# Thonny MicroPython Intepreter
# Micropython (Rapsberry Pi Pico)
#
# DC Motor
# N20 1:100 6V DC Gear Motor with quadrature encoder signals A, B
# N20 Gear Motor Spec (6V gear 1:100 no load speed = 300 rpm (https://www.pololu.com/search/compare/173)
#
# DC Motor Driver
# TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver
# Brief Description of Program Function
# 1. Move DC motor N20 forward, backware, stop.
# 2. Use PWM to control motor speed
# 3. Use N20 motor encoder to measure speed
# 4. Use encoder signals to help driving a 2WD to move in a straight line
# Digital Oscilloscope ATTEN ADS1102CAL+
# https://toolboom.com/en/digital-oscilloscope-atten-ads1102calplus/
# ATTEN ADS100 User Manual
# https://micromir.ucoz.ru/Oscil/Atten/ADS1000_User_Manual.pdf
import utime
from machine import Pin, PWM
# *** Configuration ***
# *** Vehicle/Wheel Config ***
wheelDict01 = {
'FRONT_LEFT' : {'MOTOR_DRIVER_DICT_NUM': 2, 'MOTOR_NUM': 1},
'FRONT_RIGHT': {'MOTOR_DRIVER_DICT_NUM': 2, 'MOTOR_NUM': 2},
'BACK_LEFT' : {'MOTOR_DRIVER_DICT_NUM': 2, 'MOTOR_NUM': 3},
'BACK_RIGHT' : {'MOTOR_DRIVER_DICT_NUM': 2, 'MOTOR_NUM': 4},
}
wheelDictDict = {
'1': wheelDict01,
'2': wheelDict01,
}
FrontLeftWheel = {'WheelDictNum': 1,
'DefaultPulsesPerSecond': 980,
'DefaultPwmFreqDutycycle': {'Freq': 1000, 'DutyCycle': 80},
'TestSeconds': 1,
}
# *** Motor Dicts ***
motorDriverDict02 = {
'TITLE' : 'TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver Dictionary v0.2 tlfong01 2021aug23hkt1009',
'STANDBY' : 5,
'1': {'IN1': 10, 'IN2': 11, 'PWM' : 3, 'ENCODE': 14, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
'2': {'IN1': 12, 'IN2': 13, 'PWM' : 4, 'ENCODE': 15, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
'3': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0, 'ENCODE': 0, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
'4': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0, 'ENCODE': 0, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
}
motorDriverDictDict = {
'1': motorDriverDict02,
'2': motorDriverDict02,
}
# *** Motor Functions ***
def setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum):
motorDriverDict = motorDriverDictDict[str(motorDriverDictNum)] # Get driver dict
driverStandBy = Pin(motorDriverDict['STANDBY'], Pin.OUT) # create driverStandBy pin object
motorIn1 = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN1'], Pin.OUT) # Create Motor # motorNum In1 pin object
motorIn2 = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN2'], Pin.OUT) # Create Motor # motorNum In2 pin object
motorPwm = PWM(Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['PWM'])) # Create Motor # motorNum Pwm pin object
motorEncode = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['ENCODE'], Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN) # Create Motor # motorNum Encode pin object
motorPwmFreq = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ']
motorDutyCycle = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE']
motorEncIntCntRev = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION']
motorConfigDict = {'StdBy': driverStandBy, 'In1': motorIn1, 'In2': motorIn2, 'Pwm': motorPwm, 'Encode': motorEncode}
motorStateDict = {'PwmFreq': motorPwmFreq, 'DutyCycle': motorDutyCycle, 'EncodeIntCntRev': motorEncIntCntRev}
motorDict = {'MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT': motorConfigDict, 'MOTOR_STATE_DICT': motorStateDict}
motorConfigDict['StdBy'].high() # enable motor driver normal operation, (low = disable)
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].freq(motorStateDict['PwmFreq']) # setup frequency
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].duty_u16(int(65536 / 100) * motorStateDict['DutyCycle']) # and duty cycle
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return motorDict
def changeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycle(motorDict, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
motorStateDict = motorDict['MOTOR_STATE_DICT']
motorStateDict['PwmFreq'] = pwmFreq
motorStateDict['DutyCycle'] = dutyCycle
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].freq(motorStateDict['PwmFreq'])
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].duty_u16(int(65536 / 100) * motorStateDict['DutyCycle'])
return
def stopMotor(motorConfigDict):
motorConfigDict['In1'].low()
motorConfigDict['In2'].low()
return
def moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict):
motorConfigDict['In1'].low() # move motor
motorConfigDict['In2'].high() # backward
return
def moveMotorForwardSeconds(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds):
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def moveMotorBackwardNonStop(motorConfigDict):
motorConfigDict['In1'].low() # move motor
motorConfigDict['In2'].high() # backward
return
def moveMotorBackwardSeconds(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds):
moveMotorBackwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
# *** Interrupt funtion ***
def encodeIntCallBack(pin):
global encodeIntCount
encodeIntCount = encodeIntCount + 1
return
def readEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle, moveSeconds):
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorStateDict = motorDict['MOTOR_STATE_DICT']
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
changeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycle(motorDict, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
motorConfigDict['Encode'].irq(encodeIntCallBack, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
global encodeIntCount
encodeIntCount = 0
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
totalEncodeIntCount = encodeIntCount
return totalEncodeIntCount
# *** Move revoloutions and distance ***
def moveMotorEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, encodeIntCount):
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
#intCountPerSecond = 983
intCountPerSecond = 750
print(' encodeIntCount =', encodeIntCount)
print(' intCountPerSecond =', intCountPerSecond)
moveSeconds = encodeIntCount / intCountPerSecond
print(' moveSeconds =', moveSeconds)
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def moveMotorRevolutions(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, revolutions):
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
intCountPerRevolution = 983
intCountPerSecond = 750
moveSeconds = (revolutions * intCountPerRevolution) / intCountPerSecond
print(' intCountPerRevolution =', intCountPerRevolution)
print(' intCountPerSecond =', intCountPerSecond)
print(' moveSeconds =', moveSeconds)
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
# *** Test Functions ***
snipped, because 32k words limit reached
# *** Main ***
#testMoveMotorEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, encodeIntCount = 70000)
#testMeasureEncodeIntCountMoveSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 50, moveSeconds = 60)
#testStopMotor(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1)
#testMeasureEncodeIntCountMoveSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 2, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 50, moveSeconds = 60)
testStopMotor(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 2)
# End
/ to continue, …
SPV v50.01 Development Notes
Last reply was hitting this forum’s 30k words limit. So I am making this new reply. Let me make a briefly progress report.
(1) Progress so far
I started with a copy cat of Tom’sHardware tutorial of using a motor driver to drive a single motor (MX1508 driving TT130). Everything went OK.
I then used the TB6612FNG motor driver to drive two N20 motor. Everything also went well.
I then used the TB6612FNG motor driver to drive two TT130 motors, and I had a big problem of intermittent failures when trying to sequentially test one motor and then the other, and found that one or other motor could not start, or only could start if I used my hand to help start moving. One starts moving, the motor can move happily. It took me some 4 or 5 hours to conclude that the non start problem might be a software problem, and a software reset might solve the problem. Anyway, I tidied up the program, version 50.01 which can almost always start one motor then another motor, and the other way round. I am saving this almost very good program for later reference.
(2) Troubleshooting by swapping
I have been using the swapping/pairing trick which I found very effective to locate the trouble making place. Very briefly, I test two motors, with two sets of hardware and wiring. So I can swap motor, connector, wring in seconds, as show in the photo below. Actually I have 4 or 5 identical sets of motors and duPont connectors for fast swapping.
Rpi Pico TB6612FNG TT130 Motor Schematic V5.0
Sticky Motor 2 Cannot Always Self Start Problem
I use the following test to sequentially run Motor 1 and Motor 2 four times.
for count in range(4):
testMeasureEncodeIntCountMoveSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 100, moveSeconds = 2)
testStopMotor(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1)
utime.sleep(1)
testMeasureEncodeIntCountMoveSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 2, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 100, moveSeconds = 2)
testStopMotor(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 2)
utime.sleep(1)
I still find Motor has a problem to start, and I need to push it a little bit to help it to start. I am not sure if it is the motor’s stick gear box problem, or the motor driver’s second channel sticky problem. I need to do some swapping troubleshooting tomorrow.
TT130 Encoder Motor Calibration Notes
I am going to measure the speeds of a range of motor power, 9V, 7.2V, 6V, 4.5V, and 3V. The picture below shows 9V motor power gives 70rpm.
Now below is the complete list of Vm (V motor) vs speed (rpm)
9.0V = 350mA = 240uS = 70rpm
7.2V = 270mA = 300us = 55rpm
6.0V = 250mA = 340us = 49rpm
4.5V = 200mA = 400us = 42rpm
3.0V = 150mA = 660us = 25rpm
Now what I am curious to know or to calibrate is if I use Vm motor power = 9V, what is the corresponding (PWM freq = 1000Hz) Duty Cycle of 7.2V/55rpm, 6.0V 49rpm 4.5V/42rpm, 3.0V/25rpm?
TT130 Motor Vm vs speed (rpm)
I found speed vs Vm (yellow line) is rather linear. I also need to plot speed vs duty cycle, as I did for N20 motor earlier. So far so good. So I will take a longer break this time.
Vehicle Dictionary Config
So far we have been assigning each of the two motors by two numbers: motorDictNum, motorNum. So far so good. We have tested OK all the motor dependant functions by two numbers motorDictNum, motorNum
Now we are going the motor dictionary one level up, to vehicle dictionary vechicleDict. Each vehicleDict configs on vehicle which has two motors.
Earlier to setup two motors, we need to set two motors one by one. Now we can set up the two motors of one vehicle in one go, by just saying setup vehicle,
All the low functions stays the same, it is only the higher vehicle dictionaries and functions are new. In other words if the vehicle dicts and function are working, all the lower calling functions should work without any problem (this is the beauty of “Functional Programming”.
The new vehicle dictionaries and functions are listed below:
# *** Vehicle Config ***
vehicleDict01 = {
'MOTOR_DRIVER_DICT_NUM': 2,
}
vehicleDictDict = {
'1': vehicleDict01,
'2': vehicleDict01,
}
# *** Vehicle Functions ***
def setupVehicle(vehicleNum):
motorDriverDictNum = vehicleDictDict[str(vehicleNum)]['MOTOR_DRIVER_DICT_NUM']
setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, 1)
setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, 2)
return
Vehicle Abstract Level Functions
Now I am starting off to write the first coouple of vehicle level functions. Below is an example.
# *** Old Motor Abstract Level Function ***
# Motor Level ADT (Abstract Data Type) on moving motor forward
def testMoveMotorForwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, moveSeconds):
print('\ntestmoveMotorForwardSeconds()')
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
moveMotorForwardSeconds(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
# Example call
testMoveMotorForwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, moveSeconds = 2)
# *** Proposed New Vehicle Abstract Level Functions ***
def testVehicleMoveOneMotor(vehicleNum, wheelNum, actionNum, speedNum, moveSeconds):
...
return
Progress report of writing vehicle level functions
Writing the vehicle functions has been as smooth as I expected. I first wrote a function to move a vehicle’s two front motors, then another function to stop the front two motors. The test sample below (1) run the two motors non stop, (2) hold 4 seconds, (3) stop two motors.
# *** Vehicle Config ***
vehicleDict01 = {
'MOTOR_DRIVER_DICT_NUM': 2,
}
vehicleDictDict = {
'1': vehicleDict01,
'2': vehicleDict01,
}
# *** Vehicle and Wheel Functions ***
def setupVehicle(vehicleNum):
motorDriverDictNum = vehicleDictDict[str(vehicleNum)]['MOTOR_DRIVER_DICT_NUM']
frontLeftMotorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, 1)
frontRightMotorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, 2)
motorDictDict = {'FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR': frontLeftMotorDict, 'FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR': frontRightMotorDict}
return motorDictDict
def moveVehicleTwoFrontMotorsForwardNonStop(vehicleNum):
motorDictDict = setupVehicle(vehicleNum)
frontLeftMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
frontRightMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
moveMotorForwardNonStop(frontLeftMotorConfigDict)
moveMotorForwardNonStop(frontRightMotorConfigDict)
return
def stopVehicleTwoFrontMotors(vehicleNum):
motorDictDict = setupVehicle(vehicleNum)
frontLeftMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
frontRightMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
stopMotor(frontLeftMotorConfigDict)
stopMotor(frontRightMotorConfigDict)
return
def testMoveVehicleTwoFrontMotorsForwardNonStop():
moveVehicleTwoFrontMotorsForwardNonStop(vehicleNum = 1)
return
def testStopVehicleTwoFrontMotors():
stopVehicleTwoFrontMotors(vehicleNum = 1)
return
# *** Sample Test ***
# testMoveVehicleTwoFrontMotorsForwardNonStop()
# utime.sleep(4)
# testStopVehicleTwoFrontMotors()
Move vehicle forward and backward, turn vehicle left and right tested OK
Only four statements are need to move vehicle forward and backward, turn left and right, as listed below:
# test move vehicle forward and backward, turn vehicle left and right
testMoveVehicleMotorListForwardHoldTime() # move forward 4 seconds
testMoveVehicleMotorListBackwardHoldTime() # move backward 4 seconds
testTurnVehicleLeftHoldTime() # turn left 4 seconds
testTurnVehicleRightHoldTime() # turn right 4 seconds
Full listing below:
# Program Name
# spv5011_2021sep0504.py - tlfong01 2021sep05hkt1927
# Reference
# Pi-Top Forum - making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
# https://forum.pi-top.com/t/making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
#
# Configuration
# Acer Aspire XC-780 Intel CORE i5-6400 2.7GHz, 8GB, Chinese Windows 10 Home (64-bit, 2020nov15),
# Thonny 3.3.3, Python 3.7.9 (32-bit), Tk 8.6.9, USB COM Port #4
#
# Thonny MicroPython Intepreter
# Micropython (Rapsberry Pi Pico)
#
# DC Motor
# TT130 1:48 gear motor
# 9.0V = 350mA = 240uS = 70rpm
# 7.2V = 270mA = 300us = 55rpm
# 6.0V = 250mA = 340us = 49rpm
# 4.5V = 200mA = 400us = 42rpm
# 3.0V = 150mA = 660us = 25rpm
# N20 1:100 6V DC Gear Motor with quadrature encoder signals A, B
# N20 Gear Motor Spec (6V gear 1:100 no load speed = 300 rpm (https://www.pololu.com/search/compare/173)
#
# DC Motor Driver
# TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver
# Brief Description of Program Function
# 1. Move DC motor forward, backware, stop.
# 2. Use PWM to control motor speed
# 3. Use motor encoder to measure speed
# 4. Use encoder signals to help driving a 2WD to move in a straight line
# Digital Oscilloscope ATTEN ADS1102CAL+
# https://toolboom.com/en/digital-oscilloscope-atten-ads1102calplus/
# ATTEN ADS100 User Manual
# https://micromir.ucoz.ru/Oscil/Atten/ADS1000_User_Manual.pdf
import utime
from machine import Pin, PWM
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Motor Level Config and Functions ***
# *** Motor Dicts ***
motorDriverDict02 = {
'TITLE' : 'TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver Dictionary v0.2 tlfong01 2021aug23hkt1009',
'STANDBY' : 5,
'1': {'IN1': 10, 'IN2': 11, 'PWM' : 3, 'ENCODE': 14, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
'2': {'IN1': 12, 'IN2': 13, 'PWM' : 4, 'ENCODE': 15, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
'3': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0, 'ENCODE': 0, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
'4': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0, 'ENCODE': 0, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
}
motorDriverDictDict = {
'1': motorDriverDict02,
'2': motorDriverDict02,
}
# *** Motor Functions ***
def setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum):
motorDriverDict = motorDriverDictDict[str(motorDriverDictNum)] # Get driver dict
driverStandBy = Pin(motorDriverDict['STANDBY'], Pin.OUT) # create driverStandBy pin object
motorIn1 = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN1'], Pin.OUT) # Create Motor # motorNum In1 pin object
motorIn2 = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN2'], Pin.OUT) # Create Motor # motorNum In2 pin object
motorPwm = PWM(Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['PWM'])) # Create Motor # motorNum Pwm pin object
motorEncode = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['ENCODE'], Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN) # Create Motor # motorNum Encode pin object
motorPwmFreq = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ']
motorDutyCycle = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE']
motorEncIntCntRev = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION']
motorConfigDict = {'StdBy': driverStandBy, 'In1': motorIn1, 'In2': motorIn2, 'Pwm': motorPwm, 'Encode': motorEncode}
motorStateDict = {'PwmFreq': motorPwmFreq, 'DutyCycle': motorDutyCycle, 'EncodeIntCntRev': motorEncIntCntRev}
motorDict = {'MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT': motorConfigDict, 'MOTOR_STATE_DICT': motorStateDict}
motorConfigDict['StdBy'].high() # enable motor driver normal operation, (low = disable)
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].freq(motorStateDict['PwmFreq']) # setup frequency
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].duty_u16(int(65536 / 100) * motorStateDict['DutyCycle']) # and duty cycle
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return motorDict
def changeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycle(motorDict, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
motorStateDict = motorDict['MOTOR_STATE_DICT']
motorStateDict['PwmFreq'] = pwmFreq
motorStateDict['DutyCycle'] = dutyCycle
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].freq(motorStateDict['PwmFreq'])
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].duty_u16(int(65536 / 100) * motorStateDict['DutyCycle'])
return
def stopMotor(motorConfigDict):
motorConfigDict['In1'].low()
motorConfigDict['In2'].low()
return
def moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict):
motorConfigDict['In1'].low() # move motor
motorConfigDict['In2'].high() # backward
return
def moveMotorForwardSeconds(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds):
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def moveMotorForwardHoldTime(motorConfigDict, holdTime):
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(holdTime)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def moveMotorBackwardNonStop(motorConfigDict):
motorConfigDict['In1'].high() # move motor
motorConfigDict['In2'].low() # backward
return
def moveMotorBackwardSeconds(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds):
moveMotorBackwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Interrupt Related Functions ***
def encodeIntCallBack(pin):
global encodeIntCount
encodeIntCount = encodeIntCount + 1
return
def readEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle, moveSeconds):
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorStateDict = motorDict['MOTOR_STATE_DICT']
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
changeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycle(motorDict, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
motorConfigDict['Encode'].irq(encodeIntCallBack, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
global encodeIntCount
encodeIntCount = 0
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
totalEncodeIntCount = encodeIntCount
return totalEncodeIntCount
# *** Move revoloutions and distance ***
def moveMotorEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, encodeIntCount):
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
#intCountPerSecond = 983
intCountPerSecond = 750
print(' encodeIntCount =', encodeIntCount)
print(' intCountPerSecond =', intCountPerSecond)
moveSeconds = encodeIntCount / intCountPerSecond
print(' moveSeconds =', moveSeconds)
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def moveMotorRevolutions(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, revolutions):
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
intCountPerRevolution = 983
intCountPerSecond = 750
moveSeconds = (revolutions * intCountPerRevolution) / intCountPerSecond
print(' intCountPerRevolution =', intCountPerRevolution)
print(' intCountPerSecond =', intCountPerSecond)
print(' moveSeconds =', moveSeconds)
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
# *** Test Functions ***
def testMoveMotorForwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, moveSeconds):
print('\ntestmoveMotorForwardSeconds()')
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
moveMotorForwardSeconds(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def testMoveMotorBackwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, moveSeconds):
print('\ntestMoveMotorBackwardSeconds()')
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
moveMotorBackwardSeconds(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def testChangeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycleAndmoveMotorForwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle, moveSeconds):
print('\ntestChangeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycleAndmoveMotorForwardSeconds()')
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
changeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycle(motorDict, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
print('moveSeconds =', moveSeconds)
moveMotorForwardSeconds(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def testMeasureMotorSpeed(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
totalEncodeIntCount = readEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle, moveSeconds = 1)
print('motorNum =', motorNum, end = '')
print(' pwmFreq =', pwmFreq, end = '')
print(' dutyCycle =', dutyCycle, end = '')
print(' totalEncodeIntCount Per Second =', totalEncodeIntCount, end = '')
print(' motor speed rpm =', int(int(totalEncodeIntCount * 60)/100))
return
def testMoveMotorEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, encodeIntCount):
print('testMoveMotorEncodeIntCount(), ...')
moveMotorEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, encodeIntCount)
return
def testMoveMotorRevolutions(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, revolutions):
print('testMoveMotorRevolutions(), ...')
moveMotorRevolutions(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, revolutions)
return
def testMeasureEncodeIntCountMoveSeconds(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle, moveSeconds):
encodeIntCount = readEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle, moveSeconds)
print('MotorDriverDictNum =', motorDriverDictNum, ' ', end = '')
print('MotorNum =', motorNum, ' ', end = '')
print('PWM Freq =', pwmFreq, ' ', end = '')
print('DutyCycle =', dutyCycle, ' ', end = '')
print('MoveSeconds =,', moveSeconds, ' ', end = '')
print('encodeIntCount =', encodeIntCount)
return encodeIntCount
def testStopMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum):
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
# *** Old Main Tests ***
'''
testMoveMotorForwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, moveSeconds = 2)
testMoveMotorBackwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 2, moveSeconds = 4)
testChangeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycleAndmoveMotorForwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1 , \ pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 10, moveSeconds = 2)
testChangeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycleAndmoveMotorForwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1 , \
pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 90, moveSeconds = 1)
testMeasureMotorSpeed(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 80)
testMeasureMotorSpeed(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 10)
testMoveMotorEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, encodeIntCount = 1020)
testMoveMotorEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 2, encodeIntCount = 1920)
testMoveMotorRevolutions(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, revolutions = 1)
testMeasureEncodeIntCountMoveSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 100, moveSeconds = 4)
testStopMotor(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1)
'''
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
#
# *** Vehicle Level Config and Functions ***
vehicleDict01 = {
'MOTOR_DRIVER_DICT_NUM': 2,
}
vehicleDictDict = {
'1': vehicleDict01,
'2': vehicleDict01,
}
# *** Vehicle and Wheel Functions ***
def setupVehicle(vehicleNum):
motorDriverDictNum = vehicleDictDict[str(vehicleNum)]['MOTOR_DRIVER_DICT_NUM']
frontLeftMotorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, 1)
frontRightMotorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, 2)
motorDictDict = {'FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR': frontLeftMotorDict, 'FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR': frontRightMotorDict}
return motorDictDict
def moveVehicleMotorListForwardHoldTime(vehicleNum, holdTime):
motorDictDict = setupVehicle(vehicleNum)
frontLeftMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
frontRightMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
motorConfigDictList = [frontLeftMotorConfigDict, frontRightMotorConfigDict]
for motorConfigDict in motorConfigDictList:
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(holdTime)
for motorConfigDict in motorConfigDictList:
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def moveVehicleMotorListBackwardHoldTime(vehicleNum, holdTime):
motorDictDict = setupVehicle(vehicleNum)
frontLeftMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
frontRightMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
motorConfigDictList = [frontLeftMotorConfigDict, frontRightMotorConfigDict]
for motorConfigDict in motorConfigDictList:
moveMotorBackwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(holdTime)
for motorConfigDict in motorConfigDictList:
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def turnTwoMotorsLeftHoldTime(frontLeftMotorConfigDict, frontReghtConfigDict, holdTime):
moveMotorForwardNonStop(frontLeftMotorConfigDict)
moveMotorBackward(frontRightMotorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(holdTime)
stopMotor(frontLeftMotorConfigDict)
stopMotor(frontRightMotorConfigDict)
return
def turnVehicleLeftHoldTime(vehicleNum, holdTime):
motorDictDict = setupVehicle(vehicleNum)
frontLeftMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
frontRightMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
moveMotorForwardNonStop(frontLeftMotorConfigDict)
moveMotorBackwardNonStop(frontRightMotorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(holdTime)
stopMotor(frontLeftMotorConfigDict)
stopMotor(frontRightMotorConfigDict)
return
def turnVehicleRightHoldTime(vehicleNum, holdTime):
motorDictDict = setupVehicle(vehicleNum)
frontLeftMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
frontRightMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
moveMotorBackwardNonStop(frontLeftMotorConfigDict)
moveMotorForwardNonStop(frontRightMotorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(holdTime)
stopMotor(frontLeftMotorConfigDict)
stopMotor(frontRightMotorConfigDict)
return
# *** Test Functions ***
def testMoveVehicleMotorListForwardHoldTime():
moveVehicleMotorListForwardHoldTime(vehicleNum = 1, holdTime = 4)
return
def testMoveVehicleMotorListBackwardHoldTime():
moveVehicleMotorListBackwardHoldTime(vehicleNum = 1, holdTime = 4)
return
def testTurnVehicleLeftHoldTime():
turnVehicleLeftHoldTime(vehicleNum = 1, holdTime = 4)
return
def testTurnVehicleRightHoldTime():
turnVehicleRightHoldTime(vehicleNum = 1, holdTime = 4)
return
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Main Tests ***
# * test move vehicle forward and backward, turn vehicle left and right
testMoveVehicleMotorListForwardHoldTime() # move forward 4 seconds
testMoveVehicleMotorListBackwardHoldTime() # move backward 4 seconds
testTurnVehicleLeftHoldTime() # turn left 4 secopnds
testTurnVehicleRightHoldTime() # turn right 4 seconds
# End
Now the youtube.
How to sync the two motors
We can see that the two motors do not sync, in the sense that the two wheels, each with the white stripe (cable tie), should move at the same speed.
In other words, if they start being adjacent to each other, they should always stay adjacent after any number of revolutions, forward or backward. And for turning left and right, they should go opposite direction, but stay adjacent again (for a split second) after one revolution.
I have not yet any solid idea of how to do the sync. It would be nice if any interested readers can reply with suggestions.
My first version of interrupt function works OK, but only for one motor. Now I am trying to modify it for use in 2WD and 4WD. The first draft is listed below.
# *** Interrupt Functions - Draft v0.1 2021sep06hkt1632 ***
# Design Notes
# 1. I am drafting the interrupt functions for 2WD, scalable to 4WD
# 2. / to continue, ...
def setupMotorIntCallBacks(VehicleNum = 1):
# draft only!!!
#motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
#motorStateDict = motorDict['MOTOR_STATE_DICT']
#motorConfigDict['Encode'].irq(encodeIntCallBack, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
return
def motorEncodeIntCallBack1(pin):
global motorEncodeIntCount1
motorEncodeIntCount1 = motorEncodeIntCount1 + 1
return
def motorEncodeIntCallBack2(pin):
global motorEncodeIntCount2
motorEncodeIntCount2 = motorEncodeIntCount2 + 1
return
def motorEncodeIntCallBack3(pin):
global motorEncodeIntCount3
motorEncodeIntCount3 = motorEncodeIntCount3 + 1
return
def motorEncodeIntCallBack4(pin):
global motorEncodeInt4
motorEncodeIntCount4 = motorEncodeIntCount4 + 1
return
def readMotorEncodeIntEventCount1(motorDict, countTime):
global motorEncodeInt1
return motorEncodeInt1
def readMotorEncodeIntEventCount2(motorDict, countTime):
global motorEncodeInt2
return motorEncodeInt2
def readMotorEncodeIntEventCount3(motorDict, countTime):
global motorEncodeInt3
return motorEncodeInt3
def readMotorEncodeIntEventCount4(motorDict, countTime):
global motorEncodeInt4
return motorEncodeInt4
I am hitting the forum’s 32k limit. So I am making another reply to move on, …
/ to continue, …
I am drafting a test function to proving the concept of:
Using a list of two interrupt event counts of this 2WD (later 4 counts for 4WD).
Using only one callback function for 2WD’s two interrupt pins.
# *** Interrupt Functions ***
# *** Interrupt Event Variables and Service Routines ***
# *** Setup Motor and Vehicle ***
def setupMotorV2(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum):
motorDriverDict = motorDriverDictDict[str(motorDriverDictNum)] # Get driver dict
driverStandBy = Pin(motorDriverDict['STANDBY'], Pin.OUT) # create driverStandBy pin object
motorIn1 = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN1'], Pin.OUT) # Create Motor # motorNum In1 pin object
motorIn2 = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN2'], Pin.OUT) # Create Motor # motorNum In2 pin object
motorPwm = PWM(Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['PWM'])) # Create Motor # motorNum Pwm pin object
motorEncode = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['ENCODE'], Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN) # Create Motor # motorNum Encode pin object
motorPwmFreq = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ']
motorDutyCycle = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE']
motorEncodeIntCount = 0
motorConfigDict = {'StdBy': driverStandBy, 'In1': motorIn1, 'In2': motorIn2, 'Pwm': motorPwm, 'Encode': motorEncode}
motorConfigDict['StdBy'].high() # enable motor driver normal operation, (low = disable)
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].freq(motorPwmFreq) # setup frequency
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].duty_u16(int(65536 / 100) * motorDutyCycle) # and duty cycle
motorStateDict = {'PwmFreq': motorPwmFreq, 'DutyCycle': motorDutyCycle, 'MotorEncodeIntCount': motorEncodeIntCount}
motorDict = {'MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT': motorConfigDict, 'MOTOR_STATE_DICT': motorStateDict}
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return motorDict
def setupVehicleV2(vehicleNum):
print(' setupVehicle(), ...')
motorDriverDictNum = vehicleDictDict[str(vehicleNum)]['MOTOR_DRIVER_DICT_NUM']
frontLeftMotorDict = setupMotorV2(motorDriverDictNum, 1)
frontRightMotorDict = setupMotorV2(motorDriverDictNum, 2)
frontLeftMotorInterruptPin = frontLeftMotorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']['Encode']
frontRightMotorInterruptPin = frontRightMotorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']['Encode']
motorInterruptPinList = [frontLeftMotorInterruptPin, frontRightMotorInterruptPin]
vehicleDict = {'FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR': frontLeftMotorDict, 'FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR': frontRightMotorDict, 'INTERRUPT_PIN_LIST': motorInterruptPinList}
return vehicleDict
def testSyncTwoVehicleWheels():
print('testSyncTwoVehicleWheels(), ...')
# *** This function reads one of the interrupt count list ***
def readMotorEncodeIntCount(countNum):
return motorEncodeIntCount[countNum]
# *** motorEncodeCallBack ***
# Notes:
# This callback function is a bit too clever to understand. All motor interrupt pins will trigger this callback.
# The callback will find which interrupt pin interrupts, then increment the corresponding element of the int count list.
def motorEncodeIntCallBack(pin):
index = interruptPinList.index(pin)
motorEncodeIntCountList[index] += 1
return
vehicleDict = setupVehicleV2(vehicleNum = 1)
vehicleDict['INTERRUPT_PIN_LIST'][0].irq(motorEncodeIntCallBack, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
vehicleDict['INTERRUPT_PIN_LIST'][1].irq(motorEncodeIntCallBack, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
#print(' motorEncodeIntServiceRoutine[2] =', motorEncodeIntCountList[2])
return
# *** Main Tests ***
#testMoveVehicleForwardBackwardTurnLeftTurnRight()
testSyncTwoVehicleWheels()
# End
I was jealous that PiTop4 can use mpu6050 gesture to control a robot. This morning I read how to do it. So I might try later to use my smart phone to control my smart robot, to say, first walk in a straight line.
Raspberry Pi Pico Controls Robot with Smartphone Accelerometer - Ash Hill, 2021sep07
Raspberry Pi: Python Libraries for I2C, SPI, UART - Sebastian Günther, 2021sep06
I feel jealous that some smart guy has a smart 4WD, while mine is only a stupid looking 2WD, which should damage my reputation. So I am stalling my 2WD project and go build a smart 4WD. Stay tuned. See you later.
Scaling up 2WD to 4WD
So there you are, 2WD becomes 4WD!
# Program Name
# spv5013_2021sep0603.py - tlfong01 2021sep06hkt1802
# Reference
# Pi-Top Forum - making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
# https://forum.pi-top.com/t/making-a-rpi-pico-based-smart-vehicle/924
#
# Configuration
# Acer Aspire XC-780 Intel CORE i5-6400 2.7GHz, 8GB, Chinese Windows 10 Home (64-bit, 2020nov15),
# Thonny 3.3.3, Python 3.7.9 (32-bit), Tk 8.6.9, USB COM Port #4
#
# Thonny MicroPython Intepreter
# Micropython (Rapsberry Pi Pico)
#
# DC Motor
# TT130 1:48 gear motor
# 9.0V = 350mA = 240uS = 70rpm
# 7.2V = 270mA = 300us = 55rpm
# 6.0V = 250mA = 340us = 49rpm
# 4.5V = 200mA = 400us = 42rpm
# 3.0V = 150mA = 660us = 25rpm
# N20 1:100 6V DC Gear Motor with quadrature encoder signals A, B
# N20 Gear Motor Spec (6V gear 1:100 no load speed = 300 rpm (https://www.pololu.com/search/compare/173)
#
# DC Motor Driver
# TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver
# Brief Description of Program Function
# 1. Move DC motor forward, backware, stop.
# 2. Use PWM to control motor speed
# 3. Use motor encoder to measure speed
# 4. Use encoder signals to help driving a 2WD to move in a straight line
# Digital Oscilloscope ATTEN ADS1102CAL+
# https://toolboom.com/en/digital-oscilloscope-atten-ads1102calplus/
# ATTEN ADS100 User Manual
# https://micromir.ucoz.ru/Oscil/Atten/ADS1000_User_Manual.pdf
import utime
from machine import Pin, PWM
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Motor Level Config and Functions ***
# *** Motor Dicts ***
motorDriverDict02 = {
'TITLE' : 'TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver Dictionary v0.2 tlfong01 2021aug23hkt1009',
'STANDBY' : 5,
'1': {'IN1': 10, 'IN2': 11, 'PWM' : 3, 'ENCODE': 14, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
'2': {'IN1': 12, 'IN2': 13, 'PWM' : 4, 'ENCODE': 15, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
'3': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0, 'ENCODE': 0, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
'4': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0, 'ENCODE': 0, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
}
motorDriverDictDict = {
'1': motorDriverDict02,
'2': motorDriverDict02,
}
# *** Motor Functions ***
def setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum):
motorDriverDict = motorDriverDictDict[str(motorDriverDictNum)] # Get driver dict
driverStandBy = Pin(motorDriverDict['STANDBY'], Pin.OUT) # create driverStandBy pin object
motorIn1 = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN1'], Pin.OUT) # Create Motor # motorNum In1 pin object
motorIn2 = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['IN2'], Pin.OUT) # Create Motor # motorNum In2 pin object
motorPwm = PWM(Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['PWM'])) # Create Motor # motorNum Pwm pin object
motorEncode = Pin(motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['ENCODE'], Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN) # Create Motor # motorNum Encode pin object
motorPwmFreq = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ']
motorDutyCycle = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE']
motorEncIntCntRev = motorDriverDict[str(motorNum)]['DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION']
motorConfigDict = {'StdBy': driverStandBy, 'In1': motorIn1, 'In2': motorIn2, 'Pwm': motorPwm, 'Encode': motorEncode}
motorStateDict = {'PwmFreq': motorPwmFreq, 'DutyCycle': motorDutyCycle, 'EncodeIntCntRev': motorEncIntCntRev}
motorDict = {'MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT': motorConfigDict, 'MOTOR_STATE_DICT': motorStateDict}
motorConfigDict['StdBy'].high() # enable motor driver normal operation, (low = disable)
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].freq(motorStateDict['PwmFreq']) # setup frequency
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].duty_u16(int(65536 / 100) * motorStateDict['DutyCycle']) # and duty cycle
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return motorDict
def changeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycle(motorDict, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
motorStateDict = motorDict['MOTOR_STATE_DICT']
motorStateDict['PwmFreq'] = pwmFreq
motorStateDict['DutyCycle'] = dutyCycle
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].freq(motorStateDict['PwmFreq'])
motorConfigDict['Pwm'].duty_u16(int(65536 / 100) * motorStateDict['DutyCycle'])
return
def stopMotor(motorConfigDict):
motorConfigDict['In1'].low()
motorConfigDict['In2'].low()
return
def moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict):
motorConfigDict['In1'].low() # move motor
motorConfigDict['In2'].high() # backward
return
def moveMotorForwardSeconds(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds):
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def moveMotorForwardHoldTime(motorConfigDict, holdTime):
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(holdTime)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def moveMotorBackwardNonStop(motorConfigDict):
motorConfigDict['In1'].high() # move motor
motorConfigDict['In2'].low() # backward
return
def moveMotorBackwardSeconds(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds):
moveMotorBackwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Interrupt Related Functions ***
def encodeIntCallBack(pin):
global encodeIntCount
encodeIntCount = encodeIntCount + 1
return
def readEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle, moveSeconds):
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorStateDict = motorDict['MOTOR_STATE_DICT']
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
changeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycle(motorDict, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
motorConfigDict['Encode'].irq(encodeIntCallBack, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
global encodeIntCount
encodeIntCount = 0
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
totalEncodeIntCount = encodeIntCount
return totalEncodeIntCount
# *** Move revoloutions and distance ***
def moveMotorEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, encodeIntCount):
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
#intCountPerSecond = 983
intCountPerSecond = 750
print(' encodeIntCount =', encodeIntCount)
print(' intCountPerSecond =', intCountPerSecond)
moveSeconds = encodeIntCount / intCountPerSecond
print(' moveSeconds =', moveSeconds)
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def moveMotorRevolutions(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, revolutions):
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
intCountPerRevolution = 983
intCountPerSecond = 750
moveSeconds = (revolutions * intCountPerRevolution) / intCountPerSecond
print(' intCountPerRevolution =', intCountPerRevolution)
print(' intCountPerSecond =', intCountPerSecond)
print(' moveSeconds =', moveSeconds)
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
# *** Test Functions ***
def testMoveMotorForwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, moveSeconds):
print('\ntestmoveMotorForwardSeconds()')
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
moveMotorForwardSeconds(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def testMoveMotorBackwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, moveSeconds):
print('\ntestMoveMotorBackwardSeconds()')
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
moveMotorBackwardSeconds(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def testChangeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycleAndmoveMotorForwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle, moveSeconds):
print('\ntestChangeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycleAndmoveMotorForwardSeconds()')
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
changeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycle(motorDict, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
print('moveSeconds =', moveSeconds)
moveMotorForwardSeconds(motorConfigDict, moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def testMeasureMotorSpeed(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
totalEncodeIntCount = readEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle, moveSeconds = 1)
print('motorNum =', motorNum, end = '')
print(' pwmFreq =', pwmFreq, end = '')
print(' dutyCycle =', dutyCycle, end = '')
print(' totalEncodeIntCount Per Second =', totalEncodeIntCount, end = '')
print(' motor speed rpm =', int(int(totalEncodeIntCount * 60)/100))
return
def testMoveMotorEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, encodeIntCount):
print('testMoveMotorEncodeIntCount(), ...')
moveMotorEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, encodeIntCount)
return
def testMoveMotorRevolutions(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, revolutions):
print('testMoveMotorRevolutions(), ...')
moveMotorRevolutions(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, revolutions)
return
def testMeasureEncodeIntCountMoveSeconds(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle, moveSeconds):
encodeIntCount = readEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle, moveSeconds)
print('MotorDriverDictNum =', motorDriverDictNum, ' ', end = '')
print('MotorNum =', motorNum, ' ', end = '')
print('PWM Freq =', pwmFreq, ' ', end = '')
print('DutyCycle =', dutyCycle, ' ', end = '')
print('MoveSeconds =,', moveSeconds, ' ', end = '')
print('encodeIntCount =', encodeIntCount)
return encodeIntCount
def testStopMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum):
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
# *** Old Main Tests ***
'''
testMoveMotorForwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, moveSeconds = 2)
testMoveMotorBackwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 2, moveSeconds = 4)
testChangeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycleAndmoveMotorForwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1 , \ pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 10, moveSeconds = 2)
testChangeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycleAndmoveMotorForwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1 , \
pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 90, moveSeconds = 1)
testMeasureMotorSpeed(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 80)
testMeasureMotorSpeed(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 10)
testMoveMotorEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, encodeIntCount = 1020)
testMoveMotorEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 2, encodeIntCount = 1920)
testMoveMotorRevolutions(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, revolutions = 1)
testMeasureEncodeIntCountMoveSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, pwmFreq = 1000, dutyCycle = 100, moveSeconds = 4)
testStopMotor(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1)
'''
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
#
# *** Vehicle Level Config and Functions ***
vehicleDict01 = {
'MOTOR_DRIVER_DICT_NUM': 2,
}
vehicleDictDict = {
'1': vehicleDict01,
'2': vehicleDict01,
}
# *** Vehicle and Wheel Functions ***
'''
def encodeIntCallBack(pin):
global encodeIntCount
encodeIntCount = encodeIntCount + 1
return
def readEncodeIntCount(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle, moveSeconds):
motorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum)
motorStateDict = motorDict['MOTOR_STATE_DICT']
motorConfigDict = motorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
changeMotorPwmFreqAndDutyCycle(motorDict, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
motorConfigDict['Encode'].irq(encodeIntCallBack, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
global encodeIntCount
encodeIntCount = 0
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(moveSeconds)
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
totalEncodeIntCount = encodeIntCount
return totalEncodeIntCount
motorDriverDict02 = {
'TITLE' : 'TB6612FNG Dual DC Motor Driver Dictionary v0.2 tlfong01 2021aug23hkt1009',
'STANDBY' : 5,
'1': {'IN1': 10, 'IN2': 11, 'PWM' : 3, 'ENCODE': 14, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
'2': {'IN1': 12, 'IN2': 13, 'PWM' : 4, 'ENCODE': 15, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
'3': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0, 'ENCODE': 0, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
'4': {'IN1': 0, 'IN2': 0, 'PWM' : 0, 'ENCODE': 0, \
'DEFAULT_PWM_FREQ': 1000, 'DEFAULT_DUTY_CYCLE': 50, 'DEFAULT_ENCODE_INT_PULSE_PER_REVOLUTION': 980},
}
'''
def setupVehicle(vehicleNum):
motorDriverDictNum = vehicleDictDict[str(vehicleNum)]['MOTOR_DRIVER_DICT_NUM']
frontLeftMotorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, 1)
frontRightMotorDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, 2)
motorDictDict = {'FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR': frontLeftMotorDict, 'FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR': frontRightMotorDict}
return motorDictDict
def moveVehicleMotorListForwardHoldTime(vehicleNum, holdTime):
motorDictDict = setupVehicle(vehicleNum)
frontLeftMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
frontRightMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
motorConfigDictList = [frontLeftMotorConfigDict, frontRightMotorConfigDict]
for motorConfigDict in motorConfigDictList:
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(holdTime)
for motorConfigDict in motorConfigDictList:
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def moveVehicleMotorListBackwardHoldTime(vehicleNum, holdTime):
motorDictDict = setupVehicle(vehicleNum)
frontLeftMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
frontRightMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
motorConfigDictList = [frontLeftMotorConfigDict, frontRightMotorConfigDict]
for motorConfigDict in motorConfigDictList:
moveMotorBackwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(holdTime)
for motorConfigDict in motorConfigDictList:
stopMotor(motorConfigDict)
return
def turnTwoMotorsLeftHoldTime(frontLeftMotorConfigDict, frontReghtConfigDict, holdTime):
moveMotorForwardNonStop(frontLeftMotorConfigDict)
moveMotorBackward(frontRightMotorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(holdTime)
stopMotor(frontLeftMotorConfigDict)
stopMotor(frontRightMotorConfigDict)
return
def turnVehicleLeftHoldTime(vehicleNum, holdTime):
motorDictDict = setupVehicle(vehicleNum)
frontLeftMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
frontRightMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
moveMotorForwardNonStop(frontLeftMotorConfigDict)
moveMotorBackwardNonStop(frontRightMotorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(holdTime)
stopMotor(frontLeftMotorConfigDict)
stopMotor(frontRightMotorConfigDict)
return
def turnVehicleRightHoldTime(vehicleNum, holdTime):
motorDictDict = setupVehicle(vehicleNum)
frontLeftMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
frontRightMotorConfigDict = motorDictDict['FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR']['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']
moveMotorBackwardNonStop(frontLeftMotorConfigDict)
moveMotorForwardNonStop(frontRightMotorConfigDict)
utime.sleep(holdTime)
stopMotor(frontLeftMotorConfigDict)
stopMotor(frontRightMotorConfigDict)
return
snipped … to avoid 32k word limit
def setupVehicleV2(vehicleNum):
print(' setupVehicle(), ...')
motorDriverDictNum = vehicleDictDict[str(vehicleNum)]['MOTOR_DRIVER_DICT_NUM']
frontLeftMotorDict = setupMotorV2(motorDriverDictNum, 1)
frontRightMotorDict = setupMotorV2(motorDriverDictNum, 2)
frontLeftMotorInterruptPin = frontLeftMotorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']['Encode']
frontRightMotorInterruptPin = frontRightMotorDict['MOTOR_CONFIG_DICT']['Encode']
motorInterruptPinList = [frontLeftMotorInterruptPin, frontRightMotorInterruptPin]
vehicleDict = {'FRONT_LEFT_MOTOR': frontLeftMotorDict, 'FRONT_RIGHT_MOTOR': frontRightMotorDict, 'INTERRUPT_PIN_LIST': motorInterruptPinList}
return vehicleDict
def testSyncTwoVehicleWheels():
print('testSyncTwoVehicleWheels(), ...')
# *** This function reads one of the interrupt count list ***
def readMotorEncodeIntCount(countNum):
return motorEncodeIntCount[countNum]
# *** motorEncodeCallBack ***
# Notes:
# This callback function is a bit too clever to understand. All motor interrupt pins will trigger this callback.
# The callback will find which interrupt pin interrupts, then increment the corresponding element of the int count list.
def motorEncodeIntCallBack(pin):
index = interruptPinList.index(pin)
motorEncodeIntCountList[index] += 1
return
vehicleDict = setupVehicleV2(vehicleNum = 1)
vehicleDict['INTERRUPT_PIN_LIST'][0].irq(motorEncodeIntCallBack, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
vehicleDict['INTERRUPT_PIN_LIST'][1].irq(motorEncodeIntCallBack, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
#print(' motorEncodeIntServiceRoutine[2] =', motorEncodeIntCountList[2])
return
# *** Main Tests ***
#testMoveVehicleForwardBackwardTurnLeftTurnRight()
#testSyncTwoVehicleWheels()
#testTurnVehicleLeftHoldTime()
testMoveMotorForwardSeconds(motorDriverDictNum = 2, motorNum = 1, moveSeconds = 10)
TM310 DC Motor Calibration
TT DC Gear Reduced Motor with Encoder for Smart Car DIY - AliExpress US$5
Spec:
Rated voltage: DC 9V
No-load current: 100mA
Stall current: 1.2A
No-load speed: 8000 rpm
Suitable voltage: 6-12V
Reduction ratio: 1:48/1:90
TM310 Motor #1 and #2 Speed Discrepancy
So I calibrated the second motor. I found the speeds of the second motor is very close to the first one; both encoder signals measure almost “exactly” 300uS.
This is very good news, because it means that it is practical and easy to sync two motors (bought by same order, therefore very likely from the same production lot from the manufacturer), by adjusting PWM duty cycle.
The second motor’s encoder AB signals at 12V power are displayed below.
Adding WS2812b NeoPixels LEDs to my 4WD
Now I am thinking of adding NeoPixels to my smart 4WD.
This pico relay module looks good. I hope to get on and mount it on my smart pico.
MT310 Encoder Motor #3 Calibration Notes
So I checked out MT310 #3. It seems too good to be true that this third motor’s encoder A signal is also almost exactly 300uS. Now I need to display all 4 motor’s encoder A signals together, at the same time, and and see if there is any tiny difference of the A signal periods. I still think now it is too good to be true, or there are some critical mistake I have made in the calibrations.
MT310 Motor #4 12V power Speed Measurement
So I checked out Motor 4. I was glad to see the that that encoder Signal is now 290us, not 300us as other three. If all 4 motors were axactly 300us, than is was too good to be true. Now (300 - 290) / 300 ~= 0.3% speed difference. I guess it should be easy to adjust the duty cycle of either motor to get same speed. (Apology: it should not be called “in sync” which is about time, but should be called speed matching, which is about speed.
Note - I am hitting the forum’s 32k word limit again. So I need to make a new reply.
/ to continue, …
Speed measurement of 4 MT310 motors
The encoder A signal of Motor 4 has little glitches. I need to display all 4 A signals together, at the same time, to see if this switching noise/glitches is common to all 4 motors, or just Motor 4.
Now I am doing the following speed measurements.
All 4 MT310 motors powered by the same 12V DC.
All 4 MT310 motor encoder powered by the same 5VDC.
Use 30MHz 4 channel scope to display the 4 encoder A signals.
Check if the A signals have almost identical, say, 300uS period.
MT310 Encoder Motor x 4 powered by 12VDC moving at the same time
4WD TM310 1:90 Encoder 12ppr powered by 12VDC
I am happy to see my 4 channel scope displaying the 4 motors’ encoder A signals all showing roughly 300us period pulses. I am not going to take pulse period measurements by hand and then calculate the corresponding speeds, because my next step is to use Thonny micropython to detect the encoder A signals as interrupt events and count them to calculate very precise speed values.
WaveShare DC Motor x 4 Module
Now I am looking at the WaveShare Pico DC Motor x 4 Module, to see how the professionals are playing with Pico and 4WD. I am glad to see that WaveShare is using the TB6612FNG motor driver. But I am also jealous to find that they are using PCA9615 16 PWM channel to drive the PCA9615. In order not to damage */my reputation, I think I need to catch up and show off that I can also use PCA9615. 
TM310 Encoder Motor Current Measurements
*
Now I am measuring the motors’ no load free running currents. This is a summary:
M1 = 0.114A
M2 = 0.165A
M3 = 0.134A
M4 = 0.130A
M1 = 0.118A
M1 + M2 = 0.274A
M1 + M2 + M3 = 0.399A
M1 + M2 + M3 + M4 = 0.515A
So very roughly each motor takes 100mA to 170mA, all 4 motors together takes about 500mA in total.
Perhaps I should also check out the stall currents.
TM310 Stall Current
I check the stall current of only Motor #1, and found it around a scary 2.2A. I only held the motor wheel for 1 second or so. The motor uses metal gear, so I guess the metal gear box won’t crash, but the motor coil should heat up and burn out. Perhaps I should do a destructive motor burnt out test later.
Using Pico Thonny MicroPython to calculate TM310 motor speed by counting Encoder A pulses per second
Now let me do my dodgy calculations.
The Motor encoder A pulse period as displayed by the scope is 300us.
The TM310 spec says pulses per revolution is 12ppr.
So one revolution takes 12 pulses or 12 x 300us = 3600us.
So rps (revolutions per second) = 1 / 3600us = 1000000/3600 = 278rps
So shaft rotation speed without 1:90 gear ratio = 278 x 60 = 16680 rpm
So geared motor speed = 16680 / 90 = 185 rpm
This 185 rpm is what I am going to match or verify with pico micropython now.
Note1
TM310 spec say no load speed at 9V is 8000rpm. But so far I have been using 12V to drive to motor. So I need to test again at 9VDC.
TM310 motor speed at 9VDC
So I tested the same motor again, this time using 9V. I found the pulse period goes down from 300us to 400us.
So rpm should be 16680 x 9/12 = 12,510rpm, still much higher than the specified 8000rpm.
So I still need to use pico micropython to help finding out who is correct.
Using PCA9615 16 Channel PWM Driver to control TB6612FNG Motor Controller
Now I found a problem when scaling up from 2WD to 4WD: that I seem to have not enough GP pins to go round for controlling the motor, using TB6612FNG, sooner or later. One workaround is to use I2C PCA9615 16 channel controllers.
WaveShare’s module is looking good. So I am studying their documentation to see if there is anything I can borrow. Below is the references and demo code.
'''
Pico-Motor-Driver Demo Code - WaveShare
https://www.waveshare.com/w/upload/5/5c/Pico-Motor-Driver-code.7z
Pico-Motor-Driver Module Wiki - WasveShare
https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/Pico-Motor-Driver
Pico-Motor-Driver Schematic - WaveShare
https://www.waveshare.com/w/upload/b/b8/Pico_Motor_Driver_SCH.pdf
'''
import time
from machine import Pin, I2C
import math
class PCA9685:
# Registers/etc.
__SUBADR1 = 0x02
__SUBADR2 = 0x03
__SUBADR3 = 0x04
__MODE1 = 0x00
__PRESCALE = 0xFE
__LED0_ON_L = 0x06
__LED0_ON_H = 0x07
__LED0_OFF_L = 0x08
__LED0_OFF_H = 0x09
__ALLLED_ON_L = 0xFA
__ALLLED_ON_H = 0xFB
__ALLLED_OFF_L = 0xFC
__ALLLED_OFF_H = 0xFD
def __init__(self, address=0x40, debug=False):
self.i2c = I2C(0, scl=Pin(21), sda=Pin(20), freq=100000)
self.address = address
self.debug = debug
if (self.debug):
print("Reseting PCA9685")
self.write(self.__MODE1, 0x00)
def write(self, cmd, value):
"Writes an 8-bit value to the specified register/address"
self.i2c.writeto_mem(int(self.address), int(cmd), bytes([int(value)]))
if (self.debug):
print("I2C: Write 0x%02X to register 0x%02X" % (value, cmd))
def read(self, reg):
"Read an unsigned byte from the I2C device"
rdate = self.i2c.readfrom_mem(int(self.address), int(reg), 1)
if (self.debug):
print("I2C: Device 0x%02X returned 0x%02X from reg 0x%02X" % (self.address, int(reg), rdate[0]))
return rdate[0]
def setPWMFreq(self, freq):
"Sets the PWM frequency"
prescaleval = 25000000.0 # 25MHz
prescaleval /= 4096.0 # 12-bit
prescaleval /= float(freq)
prescaleval -= 1.0
if (self.debug):
print("Setting PWM frequency to %d Hz" % freq)
print("Estimated pre-scale: %d" % prescaleval)
prescale = math.floor(prescaleval + 0.5)
if (self.debug):
print("Final pre-scale: %d" % prescale)
oldmode = self.read(self.__MODE1)
#print("oldmode = 0x%02X" %oldmode)
newmode = (oldmode & 0x7F) | 0x10 # sleep
self.write(self.__MODE1, newmode) # go to sleep
self.write(self.__PRESCALE, int(math.floor(prescale)))
self.write(self.__MODE1, oldmode)
time.sleep(0.005)
self.write(self.__MODE1, oldmode | 0x80)
def setPWM(self, channel, on, off):
"Sets a single PWM channel"
self.write(self.__LED0_ON_L+4*channel, on & 0xFF)
self.write(self.__LED0_ON_H+4*channel, on >> 8)
self.write(self.__LED0_OFF_L+4*channel, off & 0xFF)
self.write(self.__LED0_OFF_H+4*channel, off >> 8)
if (self.debug):
print("channel: %d LED_ON: %d LED_OFF: %d" % (channel,on,off))
def setServoPulse(self, channel, pulse):
pulse = pulse * (4095 / 100)
self.setPWM(channel, 0, int(pulse))
def setLevel(self, channel, value):
if (value == 1):
self.setPWM(channel, 0, 4095)
else:
self.setPWM(channel, 0, 0)
class MotorDriver():
def __init__(self, debug=False):
self.debug = debug
self.pwm = PCA9685()
self.pwm.setPWMFreq(50)
self.MotorPin = ['MA', 0,1,2, 'MB',3,4,5, 'MC',6,7,8, 'MD',9,10,11]
self.MotorDir = ['forward', 0,1, 'backward',1,0]
def MotorRun(self, motor, mdir, speed, runtime):
if speed > 100:
return
mPin = self.MotorPin.index(motor)
mDir = self.MotorDir.index(mdir)
if (self.debug):
print("set PWM PIN %d, speed %d" %(self.MotorPin[mPin+1], speed))
print("set pin A %d , dir %d" %(self.MotorPin[mPin+2], self.MotorDir[mDir+1]))
print("set pin b %d , dir %d" %(self.MotorPin[mPin+3], self.MotorDir[mDir+2]))
self.pwm.setServoPulse(self.MotorPin[mPin+1], speed)
self.pwm.setLevel(self.MotorPin[mPin+2], self.MotorDir[mDir+1])
self.pwm.setLevel(self.MotorPin[mPin+3], self.MotorDir[mDir+2])
time.sleep(runtime)
self.pwm.setServoPulse(self.MotorPin[mPin+1], 0)
self.pwm.setLevel(self.MotorPin[mPin+2], 0)
self.pwm.setLevel(self.MotorPin[mPin+3], 0)
def MotorStop(self, motor):
mPin = self.MotorPin.index(motor)
self.pwm.setServoPulse(self.MotorPin[mPin+1], 0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
m = MotorDriver()
time.sleep(1)
print("ttest code")
try:
print("this is a motor driver test code")
#Parameter 1: motor select:'MA', 'MB', 'MC', 'MD'
#Parameter 2: turn dir:'forward', 'backward'
#Parameter 3: motor speed: 0-100
#Parameter 4: Running time: >0
print("motor A forward, speed 100%, Run for 2S, then stop")
m.MotorRun('MA', 'forward', 100, 2)
print("motor A backward, speed 100%, Run for 2S, then stop")
m.MotorRun('MA', 'backward', 100, 2)
print("motor B forward, speed 50%, Run for 4S, then stop")
m.MotorRun('MB', 'forward', 50, 4)
print("motor B forward, speed 50%, Run for 4S, then stop")
m.MotorRun('MB', 'backward', 50, 4)
time.sleep(2)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
exit()
# .END
Writing a python program to measure the TM310 encoder DC motor speed by counting the encoder A signal interrupts per second
TB6612FNG troubleshooting notes - Channel B bad
I found TB6612FNG Channel A driving Motor 1 working smoothly, but Channel B driving Motor 2 a bit “sticky” often I need to give the motor a “push” to start it moving. I swapped the AO1, 2 with the BO1,2 and found that Motor 1 now becomes sticky and Motor 2 becomes smooth. So I can safely conclude that the TB6612FNG’s Channel B is not working properly, perhaps damaged.
Grouping working functions as modules - blinkLedv076
The 4WD code is getting messy and complicated. So I am thinking of grouping some of the working functions as modules. The first candidate is blink_led_v076. But I don’t know how to load the python program into MicroPython’s /lib or /tlfong01_lib. I found the utility “rshell” not working in Windows Power Shell, or pip to out of date and could not be updated. So I am thinking of using Rpi4B instead of Win10 PC to host the Thonny IDE, to see if problem can be solved.
blink_led_v076 module
# Program Name
# blink_led_v77.py - tlfong01 2021sep13
#
# Reference
# Adding External Modules To MicroPythn With Raspberry Pi Pico - peppe80, 2021may31
# https://peppe8o.com/adding-external-modules-to-micropython-with-raspberry-pi-pico/
# sys.path.append('c:/pico_micropython_library')
# print('sys.path =', sys.path)
# sys.path = ['', '/lib', 'c:/pico_micropython_library']
#
# The Raspberry Pi Pico File Management System - (Ep. 0.1) 6,615 viewsMar 15, 2021
# https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G06tPDjZ3zM
# Using MicroPython and uploading libraries on Raspberry Pi Pico Using rshell to upload custom code - Martin Fitzpatrick
# https://www.mfitzp.com/tutorials/using-micropython-raspberry-pico/
#
# Configuration
# Acer Aspire XC-780 Intel CORE i5-6400 2.7GHz, 8GB, Chinese Windows 10 Home (64-bit, 2020nov15),
# Thonny 3.3.3, Python 3.7.9 (32-bit), Tk 8.6.9, USB COM Port #4
#
# Thonny MicroPython Intepreter
# Micropython (Rapsberry Pi Pico)
#
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
import utime
from machine import Pin, PWM, Timer
import sys
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Print Hello World - last update 2021sep13 ***
def printHelloWorld():
print(' Hello World')
return
def testPrintHelloWorld():
print('\ntestPrintHelloWorld(), ...')
printHelloWorld()
return
# *** Sample Test ***
#testPrintHelloWorld()
'''
Sample output - tlfong01 2021sep12hkt2032
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
testPrintHelloWorldV060(), ...
Hello World
'''
# *** Blink Led Using toggle pin function - Last update 2021sep13 ***
def loopBlinkLed(ledPinNum, onTime, offTime, blinkCount):
ledPin = Pin(ledPinNum, Pin.OUT)
for count in range(blinkCount):
ledPin.high()
utime.sleep(onTime)
ledPin.low()
utime.sleep(offTime)
return
def testLoopBlinkLed():
print('\nBegin testLoopBlinkLed(), ...')
print(' System LED at pin25 should blink now, ...')
loopBlinkLed(ledPinNum = 25, onTime = 0.1, offTime = 1, blinkCount = 4)
print('End testLoopBlinkLed(), ...')
return
# *** Sample Test ***
#testLoopBlinkLed()
'''
Sample output
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Begin testBlinkLed(), ...
System LED at pin25 should blink now, ...
End testBlinkLed(), ...
>>>
'''
# *** Blink System LED - Last update 2021spep13 ***
# Notes
# 1. Thie blink LED function uses the callback function blinkLed() with input parameter blinkLedTimer
# 2. To blink led, initialize timer blinkLedTimer which repeatedly at set frequency triggers callback function blinkLed()
# 3. A more newbie friendly blink Led version uses a loop of function toggleLed()
def callBackBlinkLed(blinkLedTimer):
global systemLedPin
systemLedPin.toggle()
return
def testCallBackBlinkLed():
global systemLedPin
systemLedPinNum = 25
systemLedPin = Pin(systemLedPinNum, Pin.OUT)
blinkLedTimer = Timer()
blinkLedTimer.init(freq = 2.0, mode = Timer.PERIODIC, callback = callBackBlinkLed)
print('\ntestBlinkLed(), ...')
print(' System LED at pin25 should blink now, ...')
return
# *** Sample test ***
#testCallBackBlinkLed()
''' Sample output ***
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
testBlinkLed(), ...
System LED at pin25 should blink now, ...
'''
# *** Main ***
print('Begin blink_led_v77, ...')
testPrintHelloWorld()
testLoopBlinkLed()
testCallBackBlinkLed()
print('End blink_led_v77, ...')
# End
TB6612FNG Module Capacitor Explosion
So I tested a new TB6612, hoping that it would replace the bad, one channel sticky guy.
But as soon as powered it up, there was “loud” explosion, following by “heavy” smoke that last about three minutes. I let the smoke settle down, and found that the pretty yellow capacitor was burnt out to become half yellow, half charcoal black!
I vaguely remember long time ago I read about old versions of TB6612 had the faulty capacitor problem. But I never thought that new versions still have problems. I guess the poor guy’s cap is for max 9V, but I powered it with 12V!
Anyway, I think I would replace the burned cap with a 30V 10uF or higher and try again, and see if there is any more explosion. 
I am confused about the problematic cap. So I go to Pololu to find the schematic.
TB6612FNG Replacement Cap 25V 470u
I don’t understand why Pololu uses 10uF cereamic cap. I guess it is for easy manufacturing. Anyway, I think it is safe to use a big electrolyte cap.
But I dare not to try it to night, in case there is another explosion and tripping off my flat’s MCB (Mini Circuit Breaker) and I could not find any electrician to come to rescue in time.
Rpi Pico TB6612FNG TM310 Testing Rig Notes
BLDC Motor 4WD (Aslong GM25-325S BLDC) Testing Notes
The motors I have been playing with, N20, TT130, MT310, are a bit too weak. So I now try to test stronger motors. My plan is to use the same Pico to drive all of them, with little or not modification of the motor driver hardware and software. The motors being tested is Aslong GM25-325S 1:260 gear motor.
TB6612FNG x 3 = 6WD
Now I am scaling up my 4WD to 6WD, by TB6612FNG x 3. I might not wire 6 motors for now, but 3 motor drivers with 6 channels for 4WD is helpful for swapping testing and troubleshooting. (For the modules with marking TB6612FNG, I have no confidence of the ceramic cap, because one of them had a big explosion. So I am replacing the original ceramic ones with electrolyte 25V 470uF/47uF. So far so good, no explosions, 
Standard Pico Module A Bit Bulky
I am finding the standard Pico board a bit bulky. So I am taking the opportunity of upgrading my 2WD to 4WD/6WD project to try out another Pico module.
Eleven RP2040 alternatives to the Raspberry Pi Pico #PiDay #RaspberryPiPico @MUO_official - 2021sep17
TM310 4WD Mark II
Now I am assembling TM310 Mark II for field testing. Also I found that when upscaling feom2Wd to 4WD, the wiring and singal routing complexity increases not just two fold but four or more folds, and the troubleshooting chore is becoming unmanageable. So with two almost identical cars make swap troubleshooting much easier than with only one car to tackle.
TB6612FNG 4WD wheels turning off center
It was difficult to fit the cheapy yellow wheel to the TM310 motor, with the result that the wheels are moving uglily off centre.
Testing 4WD TM310 Motor Encoder Signals
Now I am going to test the 4WD’s encoder signals. The setup is briefly described below.
All four motors are powered by the same 12V DC source Riden RD6006 DC
PSU
All four motors encoders are power by the same 5V DC.
All encoder’ encoder A signals are displayed by the Rigol DS1054 4 channel scope.
Scope display of the four encoder’s A signals
Testing TM310 Motor #1
Encoder output A scope display
Now I have assembled two TB6612FNGs and mounted the old Pico. I am testing the first TB6612FNG manually, offline, using only jumper wires. So far so good. My remaining test plas is summarized below:
Test 2nd TB6612FNG, also manually off line (ie, without Pico).
Calibrate all 4WD motor speeds, still offline, using external PWM sig gen.
Write a short micropython program, reading TM310 motor encoder interrupt signals, to verify scope displayed encoder signals match software read data and calculated speed.
TB6612FNG TM310 Motor Speed vs PWM (manual offline with PWM sig gen)
The photo below was taken when the four wheels are moving by two TB6612FNG motor driver. The control signals to the motor drivers are:
In1 = Low
In2 = Hign
PWM = High
Next step is to use an external PWM sig gen as input to the TB6612FNG’s PWM input, calibrating the speed (I mean, the encoder signal A)
PWM Sig Gen Reference
How can Rpi4B python UART talk to XY PWM Signal Generators?
PiTop Products Google Alert Update
This morning Google Alert has a paragraph on PiTop. So I went there to see if there is anything new, hoping to find something like PiTop [Pico] 
I also read The Pico Python Programming tutorial by MakeUseOf, and found it newbie friendly. I might use the PWM functions there to drive the TB6612FNG motor driver.
Pico PWM Pins
I skimmed a couple of pico tutorials on using PWM and found that pico PWM is more powerful and flexible than Rpi PWM. So I changed my mind not to use XY-PWM sig gen but use Pico PWM.
Raspberry Pi Pico Pinout, specifications, datasheet in detail - Etechnophiles
…
The Raspberry Pi Pico has 8 PWM blocks/slices(1-8) and each PWM block provides up to two PWM outputs(A-B).
This means each block can drive up to two PWM outputs.
Hence, there is a total of 16 PWM output channels available at a time and every GPIO pin on the pico is capable of generating PWM output.
So all GPIO pins can be configured to get PWM signal output when required but two GPIO pins with the same PWM designation cannot be used at once.
Now I have created 4 PWM pin objects with Pico pins GP0, GP1, GP2, and GP3, all with default frequency of 1kHz, and 50% duty cycle.
And this is the full program listing.
# *** pwm_test_2021sep2503.py tlfong01 2021sep25hkt1614 ***
from machine import Pin, PWM
from time import sleep
# *** Testing PWM fading in/out system LED 4 times ***
def fadeInFadeOutSystemLed():
systemLedPinNum = 25
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(systemLedPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(1000)
for count in range(4):
for dutyCycle in range(65025):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
sleep(0.0001)
for dutyCycle in range(65025, 0, -1):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
sleep(0.0001)
return
def testFadeInFadeOutSystemLed():
fadeInFadeOutSystemLed()
return
# *** Sample Test ***
#testFadeInFadeOutSystemLed()
# *** Test 4 PWM Pins ***
# *** Pwm Pin Numbers and List ***
pwmPinNum0 = 0
pwmPinNum1 = 1
pwmPinNum2 = 2
pwmPinNum3 = 3
pwmPinNumList = [pwmPinNum0, pwmPinNum1, pwmPinNum2, pwmPinNum3]
# *** Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
pwmPin0 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum0))
pwmPin1 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum1))
pwmPin2 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum2))
pwmPin3 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum3))
pwmPinList = [pwmPin0, pwmPin1, pwmPin2, pwmPin3]
# *** Defualt Frequency and Duty Cycle ***
defaultPwmFreq = 1000
defaultDutyCycle = 32767
# *** Initializing Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
for pwmPin in pwmPinList:
pwmPin.freq(defaultPwmFreq)
pwmPin.duty_u16(defaultDutyCycle)
# *** End ***
Four Pico PWM Pins Controlling the speeds of 4 TM310 motors
Now the four Pico PWM pins are inputting to the PWM pins of 4 TB6612FNG motor controller’s PWM pins. The PWM frequency is set to 16384 (25%) duty cycle, so the wheels are turning very slowly, as expected.
DC Geared Encoder Motor Speed Measurement - Part 1 Reading motor encoder interrupt signals
Now that I know how to control motor speed using PWM, next step to calibrate the PWM vs speed. And to find the speed, the first step is to find the encoder interrupt events per second. From interrupt events persecond, and also from pulses per revolution, gear ratio, I can find speed rpm.
…
Pico GP0, 1, 2, 3 set to PWM 1kHz, 50% duty cycle to control 4x TB6612FNG + tm310 1:90 motor, Vm 12VDC
Errata - don’t know why duty cycle does not show 50%, must be a bug somewhere.
Note - Hitting 32k words limit. So new reply.
/ to continue, …
4x TM310 1:90 12ppr Vm= 12VDC, 1kHz, 50%? Ducty Cycle
Now I am displaying the 4 motors’ encoder A signals, when driver pwm 1kHz, 50% duty cycle.
Errata - The program generating 1kHz 50% display duty cycle much smaller than 50%. Need to debug the program below.
# *** encoder interrupt event reading encode_int_2021sep2602.py tlfong01 2021sep26hkt1335 ***
from machine import Pin, PWM
#from time import sleep
import utime
# *** Testing PWM fading in/out system LED 4 times ***
def pwmSystemLed():
systemLedPinNum = 25
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(systemLedPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(1000)
for count in range(4):
for dutyCycle in range(65025):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
for dutyCycle in range(65025, 0, -1):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
return
def testPwmSystemLed():
print('testPwmSystemLed(), ...')
pwmSystemLed()
return
# *** Sample Test ***
#testPwmSystemLed()
# *** Test 4 PWM Pins ***
# *** Pwm Pin Numbers and List ***
pwmPinNum0 = 0
pwmPinNum1 = 1
pwmPinNum2 = 2
pwmPinNum3 = 3
pwmPinNumList = [pwmPinNum0, pwmPinNum1, pwmPinNum2, pwmPinNum3]
# *** Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
pwmPin0 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum0))
pwmPin1 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum1))
pwmPin2 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum2))
pwmPin3 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum3))
pwmPinList = [pwmPin0, pwmPin1, pwmPin2, pwmPin3]
# *** Defualt Frequency and Duty Cycle ***
defaultPwmFreq = 1000
defaultPwmDutyCycle = 50
#defaultDutyCycle = 25
# *** Initializing Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
def setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq):
pwmPin.freq(pwmFreq)
return
def setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, dutyCycle):
u16DutyCycle = dutyCycle * 65536
pwmPin.duty_u16(u16DutyCycle)
def setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList, pwmFreq, pwmDutyCycle):
print(' pwmDutyCycle =', pwmDutyCycle)
for pwmPin in pwmPinList:
setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq)
setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, pwmDutyCycle)
return
def testSetupPwmPinList(pwmPinList, pwmFreq, pwmDutyCycle):
#setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList = pwmPinList, pwmFreq = defaultPwmFreq, pwmDutyCycle = defaultPwmDutyCycle)
#utime.sleep(2)
#setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList = pwmPinList, pwmFreq = 1000, pwmDutyCycle = 90)
#utime.sleep(2)
#setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList = pwmPinList, pwmFreq = 1000, pwmDutyCycle = 50)
#utime.sleep(2)
#setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList = pwmPinList, pwmFreq = 1000, pwmDutyCycle = 25)
#utime.sleep(2)
#setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList = pwmPinList, pwmFreq = 1000, pwmDutyCycle = 10)
#utime.sleep(2)
setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList, pwmFreq, pwmDutyCycle)
utime.sleep(2)
return
# *** Read Endcoder Interrupts ***
motorEncode = Pin(driverDict[str(motorNum)]['ENCODE'], Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
def testReadMotorEncodeValue02(driverDictNum, motorNum):
# *** Setup Driver ***
setupDriver(driverDictNum)
# *** Move motor forward ***
moveMotorForward(driverDictNum, motorNum)
# *** Read motor encode value ***
print('Move motor by hand and read encode value every second, ...')
for secondCount in range(100):
encodeValue = readMotorEncodeValue(driverDictNum, motorNum)
print(' motor encode value =', encodeValue)
utime.sleep(1)
return
def testMeasureMotorSpeed01(driverDictNum, motorNum):
# *** Setup Driver ***
setupDriver(driverDictNum)
# *** Move motor forward ***
moveMotorForward(driverDictNum, motorNum)
# *** Measure Motor Speed ***
# *** Start counting 10 revolutions ***
usTicks1 = utime.ticks_us()
# *** Find lapse time of 100 revolutions ***
revCount = 0
while revCount < 10:
if readMotorEncodeValue(driverDictNum, motorNum) == 0:
revCount = revCount + 1
utime.sleep(0.000001)
usTicks2 = utime.ticks_us()
rev10Us = utime.ticks_diff(usTicks2, usTicks1)
revUs = int(rev10Us / 10)
rps = int(1000000 / revUs)
rpmRaw = int(rps * 60)
rpmGear100 = int(rpmRaw / 100)
print('revUs =', revUs)
print('rps =', rps)
print('rpm raw =', rpmRaw)
print('rpm 100 =', rpmGear100)
moveMotorStop(driverDictNum, motorNum)
return
def readEncoderInterrupts(pwmDutyCycle):
setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList = pwmPinList, pwmFreq = 1000, pwmDutyCycle = pwmDutyCycle)
sleep(2)
return
def testReadEncoderInterrupts(pwmDutyCycle):
print('testReadEncoderInterrupts()')
readEncoderInterrupts(pwmDutyCycle)
return
def testMeasureMotorSpeed(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle):
print('\ntestMeasureMotorSpeed(), ...')
# *** Setup motor and move motor forward ***
motorConfigDict = setupMotor(motorDriverDictNum, motorNum, pwmFreq, dutyCycle)
moveMotorForwardNonStop(motorConfigDict)
# *** Define callback funtion ***
def encodeIntCallBack(pin):
global encodeIntEventCount
encodeIntEventCount = encodeIntEventCount + 1
return
# *** Setup callback function ***
motorConfigDict['Encode'].irq(encodeIntCallBack, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
# *** Count Encode Interrupt Events Every Second ***
global encodeIntEventCount
encodeIntEventCount = 0
totalSecondCount = 4
#print('totalSecondCount =', totalSecondCount)
for secondCount in range(totalSecondCount):
#print('TotalEncodeIntEventCount =', encodeIntEventCount)
utime.sleep(1)
avgEncodeIntEventCount = int(encodeIntEventCount / totalSecondCount)
#print('pwmFreq =', motorConfigDict['PwmFreq'])
print('dutyCycle =', motorConfigDict['DutyCycle'])
#print('average encodeIntEventCount Per Second =', avgEncodeIntEventCount)
print('N20 rpm =', int((avgEncodeIntEventCount * 60)/100))
return
# ***Main ***
#testPwmSystemLed()
testSetupPwmPinList(pwmPinList = pwmPinList, pwmFreq = 1000, pwmDutyCycle = 50)
#testReadEncoderInterrupts(pwmDutyCycle = 90)
# *** End ***
Reading Four TM310 Motor Encoders’ Signal A connected to Pico GP4, 5, 6, 7 and calculate the motor speeds
Now that I have used Pico’s GP 0, 1, 2, 3 as PWM pins inputting 1kHz, 50% duty cycle to each of the 4 TB6612FNG DC motor driver channels.
The four motors connected to the output of the four motor driver channels moves with the encoder pulses about 430us. Earlier the encoder pulses for 12V no pwm have a period fo 300us.
Now I need to calculate the speeds in rpm, corresponding to the pulse periods 300us (100% duty cycle) and 430us (50% duty cycle).
The TM310 has a gear ratio of 1:90.
The AB phase is 12ppr.
For 1kHz, 50% duty cycle, the pulse period is about 430us.
So pulse frequency = 1 / 430us
= 1000000 / 430
= 2,325 pulses per second
= 2,325 / 12
= 193 revolutions per second
= 193 / 90
= 2.15 rps
= 2.15 * 60
= 130 rpm
Note: my dodgy calculation has not been verified!
The above 2,325 pulses per second is based on the scope display measurement.
Next step is to use the Pico interrupt pin to count the encoder signal A interrupts which should match the scope measurements.
Interrupt counts measurements
Now I am using Pcio PWM pins (GP0, 1, 2, 3) at 1kHz, 50% dc to drive the pwm pins of 4 TB6612FNG motor drivers.
I am using Pico input pins GP 4, 5, 6, 7 to detect the motor encoders’ Signal C output signal. The signals at GP3 GP7 are shown below.
PWM duty cycle debugging notes
I found the bug in my set duty cycle function. The following is a debugged full listing.
# *** wpm_int_03_2021sep2805 - pwm motor speed control and encoder interrupt detection, tlfong01, 2021sep28hkt1415 ***
from machine import Pin, PWM
import utime
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Testing PWM fading in/out system LED 4 times ***
def pwmSystemLed():
systemLedPinNum = 25
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(systemLedPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(1000)
for count in range(4):
for dutyCycle in range(65025):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
for dutyCycle in range(65025, 0, -1):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
return
def testPwmSystemLed():
print('testPwmSystemLed(), ...')
pwmSystemLed()
return
# *** Sample Test ***
#testPwmSystemLed()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Setup 4 PWM Pins ***
# *** Pwm Pin Numbers and List ***
pwmPinNum0 = 0
pwmPinNum1 = 1
pwmPinNum2 = 2
pwmPinNum3 = 3
pwmPinNumList = [pwmPinNum0, pwmPinNum1, pwmPinNum2, pwmPinNum3]
# *** Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
pwmPin0 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum0))
pwmPin1 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum1))
pwmPin2 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum2))
pwmPin3 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum3))
pwmPinList01 = [pwmPin0, pwmPin1, pwmPin2, pwmPin3]
# *** Defualt Frequency and Duty Cycle ***
defaultPwmFreq = 1000
defaultPwmDutyCycle = 50
# *** Initializing Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
def setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq):
pwmPin.freq(pwmFreq)
return
def setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, dutyCycle):
u16DutyCycle = int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536)
pwmPin.duty_u16(u16DutyCycle)
return
def setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList, pwmFreq, pwmDutyCycle):
print(' pwmFreq =', pwmFreq)
print(' pwmDutyCycle =', pwmDutyCycle)
for pwmPin in pwmPinList:
setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq)
setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, pwmDutyCycle)
return
def testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle):
setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList = pwmPinList01, pwmFreq = 1000, pwmDutyCycle = pwmDutyCycle)
return
# Sample test ***
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 0)
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 50)
testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 50)
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Read Interrupt Pins ***
intPinNum0 = 4
intPinNum1 = 5
intPinNum2 = 6
intPinNum3 = 7
intPinNumList = [intPinNum0, intPinNum1, intPinNum2, intPinNum3]
# *** Interrupt input pin Objects and List ***
intPin0 = Pin(Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin1 = Pin(Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin2 = Pin(Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin3 = Pin(Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinList = [intPin0, intPin1, intPin2, intPin3]
global encodeIntCount0
global encodeIntCount1
global encodeIntCount2
global encodeIntCount3
encodeIntCount0 = 7
encodeIntCount1 = 8
encodeIntCount2 = 9
encodeIntCount3 = 10
# *** Define interrupt callback functions ***
def encodeIntCallBack0(pin):
global encodeIntCount0
encodeIntCount0 = encodeIntCount0 + 1
return
def encodeIntCallBack1(pin):
global encodeIntCount1
encodeIntCount1 = encodeIntCount1 + 1
return
def encodeIntCallBack2(pin):
global encodeIntCount2
encodeIntCount2 = encodeIntCount2 + 1
return
def encodeIntCallBack3(pin):
global encodeIntCount3
encodeIntCount3 = encodeIntCount3 + 1
return
def testReadencodeInterrupts():
print(' testReadencodeInterrupts(), ...')
print(' Read encode value every second, while moving motor/wheel by hand, ...')
global encodeIntCount0
global encodeIntCount1
global encodeIntCount2
global encodeIntCount3
for second in range(100):
newIntCount0 = encodeIntCount0
newIntCount1 = encodeIntCount1
newIntCount2 = encodeIntCount2
newIntCount3 = encodeIntCount3
print('\n newIntCount0 =', newIntCount0)
print(' newIntCount1 =', newIntCount1)
print(' newIntCount2 =', newIntCount2)
print(' newIntCount3 =', newIntCount3)
utime.sleep(1)
return
# **** Setup Callback Functions ***
intPin0.irq(encodeIntCallBack0, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin1.irq(encodeIntCallBack1, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin2.irq(encodeIntCallBack2, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin3.irq(encodeIntCallBack3, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
# Sample Test ***
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 50)
#testReadencodeInterrupts()
# ***Main ***
#testPwmSystemLed()
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 0)
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 50)
# *** End ***
Using Rpi Pico GP 4, 5, 6, 7 to detect/count TM310 Motor Encode A signals and calculate motor speeds
Using Pico GP 4, 5, 6, 7 to measure encoder interrupts per second
Pico GP pins 4, 5, 6, 7 measure the encoder signals from Motors 1, 2, 3, 4 as listed below:
GP4 Interrupts per second = 2968
GP5 Interrupts per second = 2743
GP6 Interrupts per second = 2994
GP7 Interrupts per second = 2923
So far so good. Now I am going to refactor the code.
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Interrupt functions for single interrupt pin GP4 ***
intPinGp4 = Pin(4, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinGp5 = Pin(5, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinGp6 = Pin(6, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinGp7 = Pin(7, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
global intCountGp4
global intCountGp5
global intCountGp6
global intCountGp7
intCountGp4 = 0
intCountGp5 = 0
intCountGp6 = 0
intCountGp7 = 0
def intCallBackGp4(pin):
global intCountGp4
intCountGp4 = intCountGp4 + 1
return
def intCallBackGp5(pin):
global intCountGp5
intCountGp5 = intCountGp5 + 1
return
def intCallBackGp6(pin):
global intCountGp6
intCountGp6 = intCountGp6 + 1
return
def intCallBackGp7(pin):
global intCountGp7
intCountGp7 = intCountGp7 + 1
return
intPinGp4.irq(intCallBackGp4, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPinGp5.irq(intCallBackGp5, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPinGp6.irq(intCallBackGp6, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPinGp7.irq(intCallBackGp7, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
def measureGp4IntPerSecond():
global intCountGp4
intCountGp4 = 0
utime.sleep(1)
newIntCount = intCountGp4
return newIntCount
def measureGp5IntPerSecond():
global intCountGp5
intCountGp5 = 0
utime.sleep(1)
newIntCount = intCountGp5
return newIntCount
def measureGp6IntPerSecond():
global intCountGp6
intCountGp6 = 0
utime.sleep(1)
newIntCount = intCountGp6
return newIntCount
def measureGp7IntPerSecond():
global intCountGp7
intCountGp7 = 0
utime.sleep(1)
newIntCount = intCountGp7
return newIntCount
def testMeasureGp4IntPerSecond():
print('\ntestMeasureGP4IntPerSecond(), ...')
newIntCount = measureGp4IntPerSecond()
print(' GP4 Interrupts per second =', newIntCount, end = '')
return
def testMeasureGp5IntPerSecond():
print('\ntestMeasureGP5IntPerSecond(), ...')
newIntCount = measureGp5IntPerSecond()
print(' GP5 Interrupts per second =', newIntCount, end = '')
return
def testMeasureGp6IntPerSecond():
print('\ntestMeasureGP6IntPerSecond(), ...')
newIntCount = measureGp6IntPerSecond()
print(' GP6 Interrupts per second =', newIntCount, end = '')
return
def testMeasureGp7IntPerSecond():
print('\ntestMeasureGP7IntPerSecond(), ...')
newIntCount = measureGp4IntPerSecond()
print(' GP7 Interrupts per second =', newIntCount, end = '')
return
# *** Sample tests ***
testMeasureGp4IntPerSecond()
testMeasureGp5IntPerSecond()
testMeasureGp6IntPerSecond()
testMeasureGp7IntPerSecond()
# Sample output - tlfong01 2021oct01hkt1502***
testMeasureGP4IntPerSecond(), ...
GP4 Interrupts per second = 2968
testMeasureGP5IntPerSecond(), ...
GP5 Interrupts per second = 2743
testMeasureGP6IntPerSecond(), ...
GP6 Interrupts per second = 2994
testMeasureGP7IntPerSecond(), ...
GP7 Interrupts per second = 2923
Read Quad Interrupts Sutble Bug
I wrote 4 read single interrupts at GP 4, 5, 6, 7 and found them OK. But when I use list functions to combine the four reads and found the functions for GP 6, 7 always return 0. I tried to swap things but could not locate the bug. Need to work harder later.
# *** pwm_int_17.py - pwm and interrupt testing, tlfong01, 2021oct01hkt1650 ***
from machine import Pin, PWM
import utime
# *** Contents ***
# testPwmSystemLed()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Testing PWM fading in/out system LED 4 times ***
# Notes:
# 1. Just a short demo/test program to make use the pwm hardware software is working properly
def pwmSystemLed():
systemLedPinNum = 25
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(systemLedPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(1000)
for count in range(4):
for dutyCycle in range(65025):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
for dutyCycle in range(65025, 0, -1):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
return
def testPwmSystemLed():
print('testPwmSystemLed(), ...')
print(' System LED now fades in and out a couple of times')
pwmSystemLed()
print(' End of test.')
return
# *** Sample Test ***
#testPwmSystemLed()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Setup 4 PWM Pins ***
# Notes:
# 1. Setting up GP 0, 1, 2, 3 as pwm pins at 1 kHz, 50% duty cycle
# 2. Connecting the pwm pins to the pwm inputs of TB6612FNG move the DC motor TM310.
# *** Pwm Pin Numbers and List ***
pwmPinNum0 = 0
pwmPinNum1 = 1
pwmPinNum2 = 2
pwmPinNum3 = 3
pwmPinNumList = [pwmPinNum0, pwmPinNum1, pwmPinNum2, pwmPinNum3]
# *** Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
pwmPin0 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum0))
pwmPin1 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum1))
pwmPin2 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum2))
pwmPin3 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum3))
pwmPinList01 = [pwmPin0, pwmPin1, pwmPin2, pwmPin3]
# *** Defualt Frequency and Duty Cycle ***
defaultPwmFreq = 1000
defaultPwmDutyCycle = 50
# *** Initializing Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
def setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq):
pwmPin.freq(pwmFreq)
return
def setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, dutyCycle):
u16DutyCycle = int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536)
pwmPin.duty_u16(u16DutyCycle)
return
def setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList, pwmFreq, pwmDutyCycle):
print(' pwmFreq =', pwmFreq)
print(' pwmDutyCycle =', pwmDutyCycle)
for pwmPin in pwmPinList:
setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq)
setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, pwmDutyCycle)
return
def testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle):
setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList = pwmPinList01, pwmFreq = 1000, pwmDutyCycle = pwmDutyCycle)
return
# Sample test ***
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 0)
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 50)
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Interrupt functions for single interrupt pin GP4 ***
intPinGp4 = Pin(4, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinGp5 = Pin(5, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinGp6 = Pin(6, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinGp7 = Pin(7, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
global intCountGp4
global intCountGp5
global intCountGp6
global intCountGp7
intCountGp4 = 0
intCountGp5 = 0
intCountGp6 = 0
intCountGp7 = 0
def intCallBackGp4(pin):
global intCountGp4
intCountGp4 = intCountGp4 + 1
return
def intCallBackGp5(pin):
global intCountGp5
intCountGp5 = intCountGp5 + 1
return
def intCallBackGp6(pin):
global intCountGp6
intCountGp6 = intCountGp6 + 1
return
def intCallBackGp7(pin):
global intCountGp7
intCountGp7 = intCountGp7 + 1
return
intPinGp4.irq(intCallBackGp4, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPinGp5.irq(intCallBackGp5, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPinGp6.irq(intCallBackGp6, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPinGp7.irq(intCallBackGp7, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
def measureGp4IntPerSecond():
global intCountGp4
intCountGp4 = 0
utime.sleep(1)
newIntCount = intCountGp4
return newIntCount
def measureGp5IntPerSecond():
global intCountGp5
intCountGp5 = 0
utime.sleep(1)
newIntCount = intCountGp5
return newIntCount
def measureGp6IntPerSecond():
global intCountGp6
intCountGp6 = 0
utime.sleep(1)
newIntCount = intCountGp6
return newIntCount
def measureGp7IntPerSecond():
global intCountGp7
intCountGp7 = 0
utime.sleep(1)
newIntCount = intCountGp7
return newIntCount
def testMeasureGp4IntPerSecond():
print('\ntestMeasureGP4IntPerSecond(), ...')
newIntCount = measureGp4IntPerSecond()
print(' GP4 Interrupts per second =', newIntCount, end = '')
return
def testMeasureGp5IntPerSecond():
print('\ntestMeasureGP5IntPerSecond(), ...')
newIntCount = measureGp5IntPerSecond()
print(' GP5 Interrupts per second =', newIntCount, end = '')
return
def testMeasureGp6IntPerSecond():
print('\ntestMeasureGP6IntPerSecond(), ...')
newIntCount = measureGp6IntPerSecond()
print(' GP6 Interrupts per second =', newIntCount, end = '')
return
def testMeasureGp7IntPerSecond():
print('\ntestMeasureGP7IntPerSecond(), ...')
newIntCount = measureGp4IntPerSecond()
print(' GP7 Interrupts per second =', newIntCount, end = '')
return
# *** Sample tests ***
#testMeasureGp4IntPerSecond()
#testMeasureGp5IntPerSecond()
#testMeasureGp6IntPerSecond()
#testMeasureGp7IntPerSecond()
# Sample output - tlfong01 2021oct01hkt1502***
'''
testMeasureGP4IntPerSecond(), ...
GP4 Interrupts per second = 2968
testMeasureGP5IntPerSecond(), ...
GP5 Interrupts per second = 2743
testMeasureGP6IntPerSecond(), ...
GP6 Interrupts per second = 2994
testMeasureGP7IntPerSecond(), ...
GP7 Interrupts per second = 2923
'''
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Interrupt functions for multiple (4) interrupt pins GP 4, 5, 6, 7 ***
intPinNum0 = 4
intPinNum1 = 5
intPinNum2 = 6
intPinNum3 = 7
intPin0 = Pin(intPinNum0, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin1 = Pin(intPinNum1, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin2 = Pin(intPinNum2, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin3 = Pin(intPinNum3, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinDict = {
'0': intPin0,
'1': intPin1,
'2': intPin2,
'3': intPin3,
}
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
intCountDict = {
'0': intCount0,
'1': intCount1,
'2': intCount2,
'3': intCount3,
}
def intCallBack0(pin):
global intCount0
intCount0 = intCount0 + 1
return
def intCallBack1(pin):
global intCount1
intCount1 = intCount1 + 1
return
def intCallBack2(pin):
global intCount2
intCount = intCount2 + 1
return
def intCallBack3(pin):
global intCount3
intCount = intCount3 + 1
return
intCallBackDict = {
'0': intCallBack0,
'1': intCallBack1,
'2': intCallBack2,
'3': intCallBack3,
}
def measureIntPinIntPerSecond(intPinNum):
intPin = intPinDict[str(intPinNum)]
intPin.irq(intCallBackDict[str(intPinNum)], Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
utime.sleep(1)
if intPinNum == 0:
newIntCount = intCount0
elif intPinNum == 1:
newIntCount = intCount1
elif intPinNum == 2:
newIntCount = intCount2
else:
newIntCount = intCount3
return newIntCount
def testMeasureIntPinIntPerSecond(intPinNum):
newIntCount = measureIntPinIntPerSecond(intPinNum)
print(' intPinNum =', intPinNum, end = '')
print(' Interrupts per second =', newIntCount)
return
# *** Test functions ***
def testMeasureQuadInterrupts():
print('\ntestMeasureQuadInterrupts(), ...')
testMeasureIntPinIntPerSecond(intPinNum = 0)
testMeasureIntPinIntPerSecond(intPinNum = 1)
testMeasureIntPinIntPerSecond(intPinNum = 2)
testMeasureIntPinIntPerSecond(intPinNum = 3)
return
# *** Main Tests ***
testMeasureGp4IntPerSecond()
testMeasureGp5IntPerSecond()
testMeasureGp6IntPerSecond()
testMeasureGp7IntPerSecond()
testMeasureQuadInterrupts()
# *** End ***
# *** Sample Output tlfong01 2021oct0101 ***
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
testMeasureGP4IntPerSecond(), ...
GP4 Interrupts per second = 2966
testMeasureGP5IntPerSecond(), ...
GP5 Interrupts per second = 2726
testMeasureGP6IntPerSecond(), ...
GP6 Interrupts per second = 3086
testMeasureGP7IntPerSecond(), ...
GP7 Interrupts per second = 2990
testMeasureQuadInterrupts(), ...
intPinNum = 0 Interrupts per second = 2945
intPinNum = 1 Interrupts per second = 2662
intPinNum = 2 Interrupts per second = 0
intPinNum = 3 Interrupts per second = 0
Debugged Quad Motor Interrupt Counter and Speed Measurement
I found a careless typo, corectected it, made some pretty printing formatting, and got the results below:
testMeasureQuadInterrupts(), ...
intPinNum = 0
Interrupts per second = 2929
No gear revolutions per second = 244.08
Geared revolutions per second (rps) = 2.71
Geared revolutions per minute (rpm) = 162.72
intPinNum = 1
Interrupts per second = 2782
No gear revolutions per second = 231.83
Geared revolutions per second (rps) = 2.58
Geared revolutions per minute (rpm) = 154.56
intPinNum = 2
Interrupts per second = 3036
No gear revolutions per second = 253.00
Geared revolutions per second (rps) = 2.81
Geared revolutions per minute (rpm) = 168.67
intPinNum = 3
Interrupts per second = 2694
No gear revolutions per second = 224.50
Geared revolutions per second (rps) = 2.49
Geared revolutions per minute (rpm) = 149.67
Next step is to “sync” the 4 motors.
Note - Hitting 32k words limit again. So next reply.
/ to continue, …
The pretty print results
'''
testMeasureQuadInterrupts(), ...
------------------------------------------------------------------
intPinNum pps 1:1 rps 1:90 rps rpm
------------------------------------------------------------------
0 3041 253.42 2.82 168.94
1 2849 237.42 2.64 158.28
2 3044 253.67 2.82 169.11
3 2837 236.42 2.63 157.61
------------------------------------------------------------------
>>>
'''
Now I am using python’s list function to scale up single interrupt to multiple (four interrupts). To save words, I am not listing the TLDR code. The final printout is shown below:
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
ppsList = [2912, 2774, 2888, 2956]
minimum = 2774
maximum = 2956
average = 2882
rpmList = [161, 154, 160, 164]
minimum = 154
maximum = 164
average = 159
Measuring motor speeds at Vmotor = 12V, 9V, 6V, 4.5V, and 3.0V
Now I am checking out the pps and rpm with varying Vmotor, and 100% PWM frequency (actually just High Level) with the follow rssults summary:
12V = 3036pps 55rpm
9V = 2282pps 42rpm
6V = 1408pps 28rpm
4.5V = 972pps 18rpm
3.0V = 527pps 10rpm (Motor 1 actually not moving at all!)
And the program listing with sample outputs:
# *** pwm_int_35.py - pwm and interrupt testing, tlfong01, 2021oct03hkt1638 ***
from machine import Pin, PWM
import utime
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Conents
#
# Part 1 - PWM Functions
# 1.1 Using PWM pin to fade in and fade out the system LED
# 1.2 Using GP 0, 1, 2, 3 pins' PWM signalsto control the speed of TB6612FNG driving TM310 DC motor
# Part 2 - Interrupt Functions
# 2.1 Using GP4, 5, 6, 7 input pins to detect and count mtor encoder A signals and calculate motor speed
# *** Part 1 - PWM Functions
def pwmSystemLed():
systemLedPinNum = 25
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(systemLedPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(1000)
for count in range(4):
for dutyCycle in range(65025):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
for dutyCycle in range(65025, 0, -1):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
return
def testPwmSystemLed():
print('testPwmSystemLed(), ...')
print(' System LED now fades in and out a couple of times')
pwmSystemLed()
print(' End of test.')
return
# *** Sample Test ***
#testPwmSystemLed()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Setup 4 PWM Pins ***
# Notes:
# 1. Setting up GP 0, 1, 2, 3 as pwm pins at 1 kHz, 50% duty cycle
# 2. Connecting the pwm pins to the pwm inputs of TB6612FNG move the DC motor TM310.
# *** Pwm Pin Numbers and List ***
pwmPinNum0 = 0
pwmPinNum1 = 1
pwmPinNum2 = 2
pwmPinNum3 = 3
pwmPinNumList = [pwmPinNum0, pwmPinNum1, pwmPinNum2, pwmPinNum3]
# *** Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
pwmPin0 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum0))
pwmPin1 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum1))
pwmPin2 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum2))
pwmPin3 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum3))
pwmPinList01 = [pwmPin0, pwmPin1, pwmPin2, pwmPin3]
# *** Defualt Frequency and Duty Cycle ***
defaultPwmFreq = 1000
defaultPwmDutyCycle = 50
# *** Initializing Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
def setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq):
pwmPin.freq(pwmFreq)
return
def setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, dutyCycle):
u16DutyCycle = int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536)
pwmPin.duty_u16(u16DutyCycle)
return
def setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList, pwmFreq, pwmDutyCycle):
print(' pwmFreq =', pwmFreq)
print(' pwmDutyCycle =', pwmDutyCycle)
for pwmPin in pwmPinList:
setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq)
setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, pwmDutyCycle)
return
def testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle):
setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList = pwmPinList01, pwmFreq = 1000, pwmDutyCycle = pwmDutyCycle)
return
# Sample test ***
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 0)
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 50)
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Interrupt functions for multiple (4) interrupt pins GP 4, 5, 6, 7 ***
intPinNum0 = 4
intPinNum1 = 5
intPinNum2 = 6
intPinNum3 = 7
intPinNumList = [intPinNum0, intPinNum1, intPinNum2, intPinNum3]
intPin0 = Pin(intPinNum0, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin1 = Pin(intPinNum1, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin2 = Pin(intPinNum2, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin3 = Pin(intPinNum3, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinDict = {
'0': intPin0,
'1': intPin1,
'2': intPin2,
'3': intPin3,
}
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
intCountDict = {
'0': intCount0,
'1': intCount1,
'2': intCount2,
'3': intCount3,
}
def intCallBack0(pin):
global intCount0
intCount0 = intCount0 + 1
return
def intCallBack1(pin):
global intCount1
intCount1 = intCount1 + 1
return
def intCallBack2(pin):
global intCount2
intCount2 = intCount2 + 1
return
def intCallBack3(pin):
global intCount3
intCount3 = intCount3 + 1
return
intCallBackDict = {
'0': intCallBack0,
'1': intCallBack1,
'2': intCallBack2,
'3': intCallBack3,
}
intPin0.irq(intCallBack0, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin1.irq(intCallBack1, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin2.irq(intCallBack2, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin3.irq(intCallBack3, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
def measureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum, seconds):
#intPin = intPinDict[str(intPinNum)]
#intPin.irq(intCallBackDict[str(intPinNum)], Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
utime.sleep(seconds)
if intPinNum == 0:
newIntCount = intCount0
elif intPinNum == 1:
newIntCount = intCount1
elif intPinNum == 2:
newIntCount = intCount2
else:
newIntCount = intCount3
return newIntCount
def testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum, seconds):
newIntCount = measureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum, seconds)
print('\n', intPinNum, ' ', end = '')
print(newIntCount, ' ', end = '')
print('{:.2f}'.format(newIntCount / 12), ' ', end = '')
print('{:.2f}'.format((newIntCount / 12) / 90), ' ', end = '')
print('{:.2f}'.format(((newIntCount / 12) / 90) * 60), ' ', end = '')
return
def measureFourIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNumList):
intCountList = [0, 0, 0, 0]
for count in range(len(intPinNumList)):
intCountList[count] = measureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNumList[count], 1)
return intCountList
# *** Test functions ***
def testMeasureQuadInterrupts():
print('\ntestMeasureQuadInterrupts(), ...')
print('\n ------------------------------------------------------------------', end = '')
print('\n intPinNum pps 1:1 rps 1:90 rps rpm', end = '')
print('\n ------------------------------------------------------------------', end = '')
testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum = 0, seconds = 1)
testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum = 1, seconds = 1)
testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum = 2, seconds = 1)
testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum = 3, seconds = 1)
print('\n ------------------------------------------------------------------', end = '')
return
def testMeasureFourInterrupts(intPinNumList):
ppsList = measureFourIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNumList)
print('ppsList =', ppsList)
print('minimum =', min(ppsList))
print('maximum =', max(ppsList))
print('average =', int(sum(ppsList) / len(ppsList)))
rpmList = ppsList.copy()
for count in range(len(rpmList)):
rpmList[count] = int(((rpmList[count] / 12) / 90) * 60)
print('\nrpmList =', rpmList)
print('minimum =', min(rpmList))
print('maximum =', max(rpmList))
print('average =', int(sum(rpmList) / len(rpmList)))
dpsList = ppsList.copy()
for count in range(len(dpsList)):
dpsList[count] = float(((dpsList[count] / 12) / 90) * 3.14 * 6.3)
print('\ndpsList =', (dpsList))
print('minimum =', '{:.2f}'.format(min(dpsList)))
print('maximum =', '{:.2f}'.format(max(dpsList)))
print('average =', '{:.2f}'.format(float(sum(dpsList) / len(dpsList))))
return
# *** Main Tests ***
testMeasureFourInterrupts([4, 5, 6, 7])
# *** End ***
# *** Sample Output tlfong01 2021oct0201 ***
'''
Summary tlfong01 2021oct03hkt1636
12V = 3036pps 55rpm
9V = 2282pps 42rpm
6V = 1408pps 28rpm
4.5V = 972pps 18rpm
3.0V = 527pps 10rpm (Motor 1 actually not moving at all!)
Vmotor = 12V (no TB6612FNG, PWM = 100% (just High level 3V3)
test testMeasureFourInterrupts([4, 5, 6, 7])
First run
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
ppsList = [3030, 3026, 3042, 3046]
minimum = 3026
maximum = 3046
average = 3036
rpmList = [168, 168, 169, 169]
minimum = 168
maximum = 169
average = 168
dpsList = [55.4995, 55.42624, 55.7193, 55.79257]
minimum = 55.43
maximum = 55.79
average = 55.61
>>>
Second run
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
ppsList = [3050, 3058, 3047, 3051]
minimum = 3047
maximum = 3058
average = 3051
rpmList = [169, 169, 169, 169]
minimum = 169
maximum = 169
average = 169
dpsList = [55.86584, 56.01237, 55.81089, 55.88416]
minimum = 55.81
maximum = 56.01
average = 55.89
>>>
Vmotor = 9V
First Run
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
ppsList = [2283, 2284, 2282, 2280]
minimum = 2280
maximum = 2284
average = 2282
rpmList = [126, 126, 126, 126]
minimum = 126
maximum = 126
average = 126
dpsList = [41.81695, 41.83527, 41.79864, 41.762]
minimum = 41.76
maximum = 41.84
average = 41.80
Second Run
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
ppsList = [2278, 2278, 2292, 2275]
minimum = 2275
maximum = 2292
average = 2280
rpmList = [126, 126, 127, 126]
minimum = 126
maximum = 127
average = 126
dpsList = [41.72537, 41.72537, 41.9818, 41.67042]
minimum = 41.67
maximum = 41.98
average = 41.78
>>>
---
Vmotor = 6V
First Run
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
ppsList = [1411, 1407, 1408, 1408]
minimum = 1407
maximum = 1411
average = 1408
rpmList = [78, 78, 78, 78]
minimum = 78
maximum = 78
average = 78
dpsList = [25.84482, 25.77155, 25.78987, 25.78987]
minimum = 25.77
maximum = 25.84
average = 25.80
Second Run
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
ppsList = [1404, 1400, 1404, 1403]
minimum = 1400
maximum = 1404
average = 1402
rpmList = [78, 77, 78, 77]
minimum = 77
maximum = 78
average = 77
dpsList = [25.7166, 25.64333, 25.7166, 25.69829]
minimum = 25.64
maximum = 25.72
average = 25.69
>>>
4.5V
First Run
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
ppsList = [973, 969, 974, 973]
minimum = 969
maximum = 974
average = 972
rpmList = [54, 53, 54, 54]
minimum = 53
maximum = 54
average = 53
dpsList = [17.82212, 17.74885, 17.84043, 17.82212]
minimum = 17.75
maximum = 17.84
average = 17.81
Second Run
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
ppsList = [977, 977, 981, 983]
minimum = 977
maximum = 983
average = 979
rpmList = [54, 54, 54, 54]
minimum = 54
maximum = 54
average = 54
dpsList = [17.89538, 17.89538, 17.96865, 18.00528]
minimum = 17.90
maximum = 18.01
average = 17.94
3.0V
First Run
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
ppsList = [524, 522, 536, 526]
minimum = 522
maximum = 536
average = 527
rpmList = [29, 29, 29, 29]
minimum = 29
maximum = 29
average = 29
dpsList = [9.597935, 9.5613, 9.817735, 9.634567]
minimum = 9.56
maximum = 9.82
average = 9.65
Second Run
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
ppsList = [538, 536, 530, 544]
minimum = 530
maximum = 544
average = 537
rpmList = [29, 29, 29, 30]
minimum = 29
maximum = 30
average = 29
dpsList = [9.854367, 9.817735, 9.707834, 9.964268]
minimum = 9.71
maximum = 9.96
average = 9.84
>>>
'''
# *** End of Sample Output ***
---
Resuming PWM Control of Motor Speed
Just before now, I have not been using the two TB6612FNG drivers at all. I only use the external Riden PSU to drive the motors directly, with 12VDC, and later 9, 6, 4.5 and 3.0V. I also only use 4 Pico GP pins, 4, 5, 6, 7 as interrupt pins to detect and count interrupts. This way I focus only on the motor encoder signals A and how the pico is reading it and calculate the speeds. This as simple as possible wiring/interface should have the least noise effect on the interrupt signals.
Now I am moving on using Pico’s 4 GP pins to output 4 PWM signals to the TB6612FNG drivers to change the speed and do some measurements. I still do not use other GP pins to do the direction, stop, standaby control. In other words, I will be using only 4 GP pins, 4, 5, 6, 7 (B in the picture below) to read interrupt signals, and another four pins GP 0, 1, 2, 3 (A in the pic below) to be the PWM pins. The wiring is shown below. Only four PWM control pins of the two TB6612FNG drivers and connected to the Pico. Other TB6612 control pins © are wired manually by jumpers to Vcc and Gnd.
This is a new chapter of the 4WD testing. So I am moving to the new reply.
/ to continue, …
Calibrating TM310 motors speed vs PWM duty cycle
Now I am using pico’s GP0, 1, 2, 3 to output 4 PWM signals to the two TB6612FNG motor drivers’s 4 motor driving channels, and check out the corresponding motor speed by detecting the encoder’s A signals and do the pps (pulse per second) to rpm calculation by using Pico.
Notes:
C = GP 0, 1, 2, 3 PWM output pins
D = GP 4, 5, 6, 7 Interrupt input pins
E = 4 x TM301 motor encoder A signals
F = 4 x TB6612FNG PWM input control signals
A, B = 2 x TB6612FNG’s other control signals manually jumpered to Vcc and Gnd.
G, H = 2 x TB6612 motor driver modules
Testing PWM Duty Cycle 50%, 10%, 90% OK
I am using the following function calls to generate signals of duty cycle 50%, 10%, and 90% and found all is well. Next step is to calibrate duty cycle vs motor speed.
# testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 50)
# testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 10)
# testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 90)
The full listing of code.
# *** pwm_int_37.py - pwm and interrupt testing, tlfong01, 2021oct03hkt2110 ***
from machine import Pin, PWM
import utime
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Conents
#
# Part 1 - PWM Functions
# 1.1 Using PWM pin to fade in and fade out the system LED
# 1.2 Using GP 0, 1, 2, 3 pins' PWM signalsto control the speed of TB6612FNG driving TM310 DC motor
# Part 2 - Interrupt Functions
# 2.1 Using GP4, 5, 6, 7 input pins to detect and count mtor encoder A signals and calculate motor speed
# *** Part 1 - PWM Functions ***
def pwmSystemLed():
systemLedPinNum = 25
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(systemLedPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(1000)
for count in range(4):
for dutyCycle in range(65025):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
for dutyCycle in range(65025, 0, -1):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
return
def testPwmSystemLed():
print('testPwmSystemLed(), ...')
print(' System LED now fades in and out a couple of times')
pwmSystemLed()
print(' End of test.')
return
# *** Sample Test ***
#testPwmSystemLed()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Setup 4 PWM Pins ***
# Notes:
# 1. Setting up GP 0, 1, 2, 3 as pwm pins at 1 kHz, 50% duty cycle
# 2. Connecting the pwm pins to the pwm inputs of TB6612FNG move the DC motor TM310.
# *** Pwm Pin Numbers and List ***
pwmPinNum0 = 0
pwmPinNum1 = 1
pwmPinNum2 = 2
pwmPinNum3 = 3
pwmPinNumList = [pwmPinNum0, pwmPinNum1, pwmPinNum2, pwmPinNum3]
# *** Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
pwmPin0 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum0))
pwmPin1 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum1))
pwmPin2 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum2))
pwmPin3 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum3))
pwmPinList01 = [pwmPin0, pwmPin1, pwmPin2, pwmPin3]
# *** Defualt Frequency and Duty Cycle ***
defaultPwmFreq = 1000
defaultPwmDutyCycle = 50
# *** Initializing Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
def setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq):
pwmPin.freq(pwmFreq)
return
def setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, dutyCycle):
u16DutyCycle = int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536)
pwmPin.duty_u16(u16DutyCycle)
return
def setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList, pwmFreq, pwmDutyCycle):
print(' pwmFreq =', pwmFreq)
print(' pwmDutyCycle =', pwmDutyCycle)
for pwmPin in pwmPinList:
setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq)
setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, pwmDutyCycle)
return
def testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle):
setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList = pwmPinList01, pwmFreq = 1000, pwmDutyCycle = pwmDutyCycle)
return
# Sample test ***
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 50)
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 10)
testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 90)
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Interrupt functions for multiple (4) interrupt pins GP 4, 5, 6, 7 ***
intPinNum0 = 4
intPinNum1 = 5
intPinNum2 = 6
intPinNum3 = 7
intPinNumList = [intPinNum0, intPinNum1, intPinNum2, intPinNum3]
intPin0 = Pin(intPinNum0, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin1 = Pin(intPinNum1, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin2 = Pin(intPinNum2, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin3 = Pin(intPinNum3, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinDict = {
'0': intPin0,
'1': intPin1,
'2': intPin2,
'3': intPin3,
}
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
intCountDict = {
'0': intCount0,
'1': intCount1,
'2': intCount2,
'3': intCount3,
}
def intCallBack0(pin):
global intCount0
intCount0 = intCount0 + 1
return
def intCallBack1(pin):
global intCount1
intCount1 = intCount1 + 1
return
def intCallBack2(pin):
global intCount2
intCount2 = intCount2 + 1
return
def intCallBack3(pin):
global intCount3
intCount3 = intCount3 + 1
return
intCallBackDict = {
'0': intCallBack0,
'1': intCallBack1,
'2': intCallBack2,
'3': intCallBack3,
}
intPin0.irq(intCallBack0, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin1.irq(intCallBack1, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin2.irq(intCallBack2, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin3.irq(intCallBack3, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
def measureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum, seconds):
#intPin = intPinDict[str(intPinNum)]
#intPin.irq(intCallBackDict[str(intPinNum)], Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
utime.sleep(seconds)
if intPinNum == 0:
newIntCount = intCount0
elif intPinNum == 1:
newIntCount = intCount1
elif intPinNum == 2:
newIntCount = intCount2
else:
newIntCount = intCount3
return newIntCount
def testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum, seconds):
newIntCount = measureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum, seconds)
print('\n', intPinNum, ' ', end = '')
print(newIntCount, ' ', end = '')
print('{:.2f}'.format(newIntCount / 12), ' ', end = '')
print('{:.2f}'.format((newIntCount / 12) / 90), ' ', end = '')
print('{:.2f}'.format(((newIntCount / 12) / 90) * 60), ' ', end = '')
return
def measureFourIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNumList):
intCountList = [0, 0, 0, 0]
for count in range(len(intPinNumList)):
intCountList[count] = measureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNumList[count], 1)
return intCountList
# *** Test functions ***
def testMeasureQuadInterrupts():
print('\ntestMeasureQuadInterrupts(), ...')
print('\n ------------------------------------------------------------------', end = '')
print('\n intPinNum pps 1:1 rps 1:90 rps rpm', end = '')
print('\n ------------------------------------------------------------------', end = '')
testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum = 0, seconds = 1)
testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum = 1, seconds = 1)
testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum = 2, seconds = 1)
testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum = 3, seconds = 1)
print('\n ------------------------------------------------------------------', end = '')
return
def testMeasureFourInterrupts(intPinNumList):
ppsList = measureFourIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNumList)
print('ppsList =', ppsList)
print('minimum =', min(ppsList))
print('maximum =', max(ppsList))
print('average =', int(sum(ppsList) / len(ppsList)))
rpmList = ppsList.copy()
for count in range(len(rpmList)):
rpmList[count] = int(((rpmList[count] / 12) / 90) * 60)
print('\nrpmList =', rpmList)
print('minimum =', min(rpmList))
print('maximum =', max(rpmList))
print('average =', int(sum(rpmList) / len(rpmList)))
dpsList = ppsList.copy()
for count in range(len(dpsList)):
dpsList[count] = float(((dpsList[count] / 12) / 90) * 3.14 * 6.3)
print('\ndpsList =', (dpsList))
print('minimum =', '{:.2f}'.format(min(dpsList)))
print('maximum =', '{:.2f}'.format(max(dpsList)))
print('average =', '{:.2f}'.format(float(sum(dpsList) / len(dpsList))))
return
# *** Main Tests ***
#testMeasureFourInterrupts([4, 5, 6, 7])
# *** End ***
# *** Sample Output tlfong01 2021oct0201 ***
'''
'''
# *** End of Sample Output ***
Measuring 4 PWMs vs 4 Speeds OK
Now I am using the setPWM and MeasureInterrupts to do PWM vs Speed and found things more or less OK, except minor things such as one wheel does not turn at duty cycle at 10%. So 20% dc seems to be the smallest to do practical experiments.
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 50)
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 90)
testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 20)
testMeasureFourInterrupts([4, 5, 6, 7])
Below is a summary of the results. Full result and code listing is shown after that.
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
testSetupPwmPinList(), ... tlfong01 2021oct04hkt1025
pwmFreq = 1000
pwmDutyCycle = 50
ppsList = [2391, 2401, 2391, 2396]
rpmList = [132, 133, 132, 133]
dpsList = [43.79516, 43.97832, 43.79516, 43.88674]
pwmDutyCycle = 90
ppsList = [2796, 2874, 2883, 2859]
rpmList = [155, 159, 160, 158]
dpsList = [51.2134, 52.64211, 52.80696, 52.36735]
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
pwmDutyCycle = 20
ppsList = [1631, 1505, 1631, 1613]
rpmList = [90, 83, 90, 89]
dpsList = [29.87449, 27.56658, 29.87449, 29.54479]
pwmDutyCycle = 10
ppsList = [1295, 1019, 941, 967]
rpmList = [71, 56, 52, 53]
dpsList = [23.72008, 18.66468, 17.23598, 17.71222]
# *** pwm_int_40.py - pwm and interrupt testing, tlfong01, 2021oct04hkt1037 ***
from machine import Pin, PWM
import utime
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Conents
#
# Part 1 - Interrupt Functions
# 1.1 Using GP4, 5, 6, 7 input pins to detect and count mtor encoder A signals and calculate motor speed
# Part 2 - PWM Functions
# 2.1 Using PWM pin to fade in and fade out the system LED
# 2.2 Using GP 0, 1, 2, 3 pins' PWM signalsto control the speed of TB6612FNG driving TM310 DC motor
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Interrupt functions for multiple (4) interrupt pins GP 4, 5, 6, 7 ***
intPinNum0 = 4
intPinNum1 = 5
intPinNum2 = 6
intPinNum3 = 7
intPinNumList = [intPinNum0, intPinNum1, intPinNum2, intPinNum3]
intPin0 = Pin(intPinNum0, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin1 = Pin(intPinNum1, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin2 = Pin(intPinNum2, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin3 = Pin(intPinNum3, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinDict = {
'0': intPin0,
'1': intPin1,
'2': intPin2,
'3': intPin3,
}
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
intCountDict = {
'0': intCount0,
'1': intCount1,
'2': intCount2,
'3': intCount3,
}
def intCallBack0(pin):
global intCount0
intCount0 = intCount0 + 1
return
def intCallBack1(pin):
global intCount1
intCount1 = intCount1 + 1
return
def intCallBack2(pin):
global intCount2
intCount2 = intCount2 + 1
return
def intCallBack3(pin):
global intCount3
intCount3 = intCount3 + 1
return
intCallBackDict = {
'0': intCallBack0,
'1': intCallBack1,
'2': intCallBack2,
'3': intCallBack3,
}
intPin0.irq(intCallBack0, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin1.irq(intCallBack1, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin2.irq(intCallBack2, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin3.irq(intCallBack3, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
def measureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum, seconds):
#intPin = intPinDict[str(intPinNum)]
#intPin.irq(intCallBackDict[str(intPinNum)], Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
utime.sleep(seconds)
if intPinNum == 0:
newIntCount = intCount0
elif intPinNum == 1:
newIntCount = intCount1
elif intPinNum == 2:
newIntCount = intCount2
else:
newIntCount = intCount3
return newIntCount
def testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum, seconds):
newIntCount = measureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum, seconds)
print('\n', intPinNum, ' ', end = '')
print(newIntCount, ' ', end = '')
print('{:.2f}'.format(newIntCount / 12), ' ', end = '')
print('{:.2f}'.format((newIntCount / 12) / 90), ' ', end = '')
print('{:.2f}'.format(((newIntCount / 12) / 90) * 60), ' ', end = '')
return
def measureFourIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNumList):
intCountList = [0, 0, 0, 0]
for count in range(len(intPinNumList)):
intCountList[count] = measureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNumList[count], 1)
return intCountList
# *** Test functions ***
def testMeasureQuadInterrupts():
print('\ntestMeasureQuadInterrupts(), ...')
print('\n ------------------------------------------------------------------', end = '')
print('\n intPinNum pps 1:1 rps 1:90 rps rpm', end = '')
print('\n ------------------------------------------------------------------', end = '')
testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum = 0, seconds = 1)
testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum = 1, seconds = 1)
testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum = 2, seconds = 1)
testMeasureIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNum = 3, seconds = 1)
print('\n ------------------------------------------------------------------', end = '')
return
def testMeasureFourInterrupts(intPinNumList):
ppsList = measureFourIntPinIntSeconds(intPinNumList)
print('ppsList =', ppsList)
print('minimum =', min(ppsList))
print('maximum =', max(ppsList))
print('average =', int(sum(ppsList) / len(ppsList)))
rpmList = ppsList.copy()
for count in range(len(rpmList)):
rpmList[count] = int(((rpmList[count] / 12) / 90) * 60)
print('\nrpmList =', rpmList)
print('minimum =', min(rpmList))
print('maximum =', max(rpmList))
print('average =', int(sum(rpmList) / len(rpmList)))
dpsList = ppsList.copy()
for count in range(len(dpsList)):
dpsList[count] = float(((dpsList[count] / 12) / 90) * 3.14 * 6.3)
print('\ndpsList =', (dpsList))
print('minimum =', '{:.2f}'.format(min(dpsList)))
print('maximum =', '{:.2f}'.format(max(dpsList)))
print('average =', '{:.2f}'.format(float(sum(dpsList) / len(dpsList))))
return
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Part 2 - PWM Functions ***
def pwmSystemLed():
systemLedPinNum = 25
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(systemLedPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(1000)
for count in range(4):
for dutyCycle in range(65025):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
for dutyCycle in range(65025, 0, -1):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
return
def testPwmSystemLed():
print('testPwmSystemLed(), ...')
print(' System LED now fades in and out a couple of times')
pwmSystemLed()
print(' End of test.')
return
# *** Sample Test ***
#testPwmSystemLed()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Setup 4 PWM Pins ***
# Notes:
# 1. Setting up GP 0, 1, 2, 3 as pwm pins at 1 kHz, 50% duty cycle
# 2. Connecting the pwm pins to the pwm inputs of TB6612FNG move the DC motor TM310.
# *** Pwm Pin Numbers and List ***
pwmPinNum0 = 0
pwmPinNum1 = 1
pwmPinNum2 = 2
pwmPinNum3 = 3
pwmPinNumList = [pwmPinNum0, pwmPinNum1, pwmPinNum2, pwmPinNum3]
# *** Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
pwmPin0 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum0))
pwmPin1 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum1))
pwmPin2 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum2))
pwmPin3 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum3))
pwmPinList01 = [pwmPin0, pwmPin1, pwmPin2, pwmPin3]
# *** Defualt Frequency and Duty Cycle ***
defaultPwmFreq = 1000
defaultPwmDutyCycle = 50
# *** Initializing Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
def setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq):
pwmPin.freq(pwmFreq)
return
def setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, dutyCycle):
u16DutyCycle = int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536)
pwmPin.duty_u16(u16DutyCycle)
return
def setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList, pwmFreq, pwmDutyCycle):
print(' pwmFreq =', pwmFreq)
print(' pwmDutyCycle =', pwmDutyCycle)
for pwmPin in pwmPinList:
setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq)
setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, pwmDutyCycle)
return
def testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle):
print(' testSetupPwmPinList(), ... tlfong01 2021oct04hkt1025')
setupPwmPinList(pwmPinList = pwmPinList01, pwmFreq = 1000, pwmDutyCycle = pwmDutyCycle)
return
# Sample test ***
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 50)
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 10)
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 90)
# *** Main Tests ***
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 50)
#testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 90)
testSetupPwmPinList(pwmDutyCycle = 20)
testMeasureFourInterrupts([4, 5, 6, 7])
# *** End ***
# *** Sample Output tlfong01 2021oct0201 ***
'''
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
testSetupPwmPinList(), ... tlfong01 2021oct04hkt1025
pwmFreq = 1000
pwmDutyCycle = 50
ppsList = [0, 0, 0, 0]
minimum = 0
maximum = 0
average = 0
rpmList = [0, 0, 0, 0]
minimum = 0
maximum = 0
average = 0
dpsList = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
minimum = 0.00
maximum = 0.00
average = 0.00
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
testSetupPwmPinList(), ... tlfong01 2021oct04hkt1025
pwmFreq = 1000
pwmDutyCycle = 50
ppsList = [2391, 2401, 2391, 2396]
minimum = 2391
maximum = 2401
average = 2394
rpmList = [132, 133, 132, 133]
minimum = 132
maximum = 133
average = 132
dpsList = [43.79516, 43.97832, 43.79516, 43.88674]
minimum = 43.80
maximum = 43.98
average = 43.86
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
testSetupPwmPinList(), ... tlfong01 2021oct04hkt1025
pwmFreq = 1000
pwmDutyCycle = 90
ppsList = [2796, 2874, 2883, 2859]
minimum = 2796
maximum = 2883
average = 2853
rpmList = [155, 159, 160, 158]
minimum = 155
maximum = 160
average = 158
dpsList = [51.2134, 52.64211, 52.80696, 52.36735]
minimum = 51.21
maximum = 52.81
average = 52.26
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
testSetupPwmPinList(), ... tlfong01 2021oct04hkt1025
pwmFreq = 1000
pwmDutyCycle = 10
ppsList = [1295, 1019, 941, 967]
minimum = 941
maximum = 1295
average = 1055
rpmList = [71, 56, 52, 53]
minimum = 52
maximum = 71
average = 58
dpsList = [23.72008, 18.66468, 17.23598, 17.71222]
minimum = 17.24
maximum = 23.72
average = 19.33
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
testSetupPwmPinList(), ... tlfong01 2021oct04hkt1025
pwmFreq = 1000
pwmDutyCycle = 20
ppsList = [1631, 1505, 1631, 1613]
minimum = 1505
maximum = 1631
average = 1595
rpmList = [90, 83, 90, 89]
minimum = 83
maximum = 90
average = 88
dpsList = [29.87449, 27.56658, 29.87449, 29.54479]
minimum = 27.57
maximum = 29.87
average = 29.22
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
testSetupPwmPinList(), ... tlfong01 2021oct04hkt1025
pwmFreq = 1000
pwmDutyCycle = 20
ppsList = [1572, 1620, 1614, 1665]
minimum = 1572
maximum = 1665
average = 1617
rpmList = [87, 90, 89, 92]
minimum = 87
maximum = 92
average = 89
dpsList = [28.7938, 29.673, 29.5631, 30.49725]
minimum = 28.79
maximum = 30.50
average = 29.63
>>>
'''
# *** End of Sample Output ***
A shorter summary is this:
DutyCycle 90%, pps = 2853, rpm = 158
DutyCycle 50%, pps = 2394, rpm = 132
DutyCycle 20%, pps = 1595, rpm = 88
DutyCycle 10%, pps = 1055, rpm = 58
Excel shows that duty cycle vs rpm is more or less linear:
Actually it is not important for duty cycle vs speed to be linear, because to sync speeds, Pico will be adjusting duty cycles in real time.
The time has come to do the real thing: synchronizing the wheel speeds, which is necessary to move the 4WD in straight line, in a circle, in a square etc. Stay tuned. 
Setting up PWM and measuring motor speed as a list of 4 motors/pins
Now I have modified the code to process the four motors as a list. The code is again too long, hitting the 32k limit, so I am not listing it here. A summary of the tests is show below:
# *** Main Tests ***
setupPwmPinListV2(pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3], pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000],
pwmDutyCycleList = [90, 90, 90, 90])
testMeasureIntPinNumListInt100Ms([0, 1, 2, 3])
# *** End ***
# *** Sample Output tlfong01 2021oct04hkt1657 ***
'''
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
testSetupPwmPinNumListV2(), ...
pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3]
pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000]
pwmDutyCycleList = [90, 90, 90, 90]
testMeasureIntPinNumListInt100Ms()
ppsList = [36, 34, 26, 33] , min = 26 , max = 36 , avg = 32
rpmList = [20, 18, 14, 18] , min = 14 , max = 20 , avg = 17
>>>
'''
# *** End of Sample Output ***
Cross Calibrating Speed of Four 4WD Motors
Now I have modified the program to do the following:
Setup PWM frequency and PWM duty cycle of the list of 4 motors.
Repeat count the interrupts (pps) and calculate the speed (rpm)
The following results shows how reliable or consistent are the speed of four motors at the same pwm frequency and duty cycle.
Next step is to try to adjust individual duty cycle to each motor so that they move the “same” speed.
# *** Sample Output tlfong01 2021oct04hkt1657 ***
'''
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
setupPwmPinNumList(), ...
pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3]
pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000]
pwmDutyCycleList = [50, 50, 50, 50]
testCountIntPinNumListIntOneTenthSecond()
ppsList = [32, 28, 26, 24] , min 24 , max 32 , avg 27 rpmList = [17, 15, 14, 13] , min 13 , max 17 , avg 14
ppsList = [27, 24, 31, 34] , min 24 , max 34 , avg 29 rpmList = [15, 13, 17, 18] , min 13 , max 18 , avg 15
ppsList = [31, 28, 27, 21] , min 21 , max 31 , avg 26 rpmList = [17, 15, 15, 11] , min 11 , max 17 , avg 14
ppsList = [27, 27, 28, 30] , min 27 , max 30 , avg 28 rpmList = [15, 15, 15, 16] , min 15 , max 16 , avg 15
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
setupPwmPinNumList(), ...
pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3]
pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000]
pwmDutyCycleList = [25, 25, 25, 25]
testCountIntPinNumListIntOneTenthSecond()
ppsList = [32, 22, 24, 20] , min 20 , max 32 , avg 24 rpmList = [17, 12, 13, 11] , min 11 , max 17 , avg 13
ppsList = [17, 16, 24, 20] , min 16 , max 24 , avg 19 rpmList = [9, 8, 13, 11] , min 8 , max 13 , avg 10
ppsList = [21, 21, 22, 21] , min 21 , max 22 , avg 21 rpmList = [11, 11, 12, 11] , min 11 , max 12 , avg 11
ppsList = [24, 22, 17, 27] , min 17 , max 27 , avg 22 rpmList = [13, 12, 9, 15] , min 9 , max 15 , avg 12
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
setupPwmPinNumList(), ...
pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3]
pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000]
pwmDutyCycleList = [20, 20, 20, 20]
testCountIntPinNumListIntOneTenthSecond()
ppsList = [21, 23, 19, 21] , min 19 , max 23 , avg 21 rpmList = [11, 12, 10, 11] , min 10 , max 12 , avg 11
ppsList = [20, 19, 16, 18] , min 16 , max 20 , avg 18 rpmList = [11, 10, 8, 10] , min 8 , max 11 , avg 9
ppsList = [21, 22, 14, 20] , min 14 , max 22 , avg 19 rpmList = [11, 12, 7, 11] , min 7 , max 12 , avg 10
ppsList = [21, 23, 20, 15] , min 15 , max 23 , avg 19 rpmList = [11, 12, 11, 8] , min 8 , max 12 , avg 10
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
setupPwmPinNumList(), ...
pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3]
pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000]
pwmDutyCycleList = [90, 90, 90, 90]
testCountIntPinNumListIntOneTenthSecond()
ppsList = [71, 24, 21, 21] , min 21 , max 71 , avg 34 rpmList = [39, 13, 11, 11] , min 11 , max 39 , avg 18
ppsList = [25, 41, 26, 31] , min 25 , max 41 , avg 30 rpmList = [13, 22, 14, 17] , min 13 , max 22 , avg 16
ppsList = [29, 41, 24, 29] , min 24 , max 41 , avg 30 rpmList = [16, 22, 13, 16] , min 13 , max 22 , avg 16
ppsList = [37, 37, 0, 35] , min 0 , max 37 , avg 27 rpmList = [20, 20, 0, 19] , min 0 , max 20 , avg 14
>>>
'''
Unreliable/unrepeatable speeds at duty cylcle 90%. Duty cycles in the range of 20% to 50% are more reliable.
So I will start experimenting with duty cycle 25%.
This reply is approaching the forum;s 32k words limit. So I will start a new reply.
/ to continue, …
Choosing an optimum duty cycle for calibration/benchmarking
I found low duty cycles like 20% and 25% not satisfactory, because one of the four motors sometimes gets stuck. A 50% duty cycle is more smooth and repeatable. A 50% measurement is shown below:
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
setupPwmPinNumList(), ...
pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3]
pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000]
pwmDutyCycleList = [50, 50, 50, 50]
testCountIntPinNumListIntOneTenthSecond()
ppsList = [32, 24, 28, 25] , min 24 , max 32 , dif 8 , avg 27
ppsList = [39, 26, 29, 23] , min 23 , max 39 , dif 16 , avg 29
ppsList = [31, 28, 28, 21] , min 21 , max 31 , dif 10 , avg 27
ppsList = [31, 28, 26, 16] , min 16 , max 31 , dif 15 , avg 25
ppsList = [31, 26, 34, 22] , min 22 , max 34 , dif 12 , avg 28
ppsList = [29, 26, 27, 19] , min 19 , max 29 , dif 10 , avg 25
ppsList = [28, 28, 24, 20] , min 20 , max 28 , dif 8 , avg 25
ppsList = [30, 24, 24, 28] , min 24 , max 30 , dif 6 , avg 26
ppsList = [33, 27, 18, 22] , min 18 , max 33 , dif 15 , avg 25
ppsList = [31, 26, 24, 19] , min 19 , max 31 , dif 12 , avg 25
ppsList = [28, 22, 25, 22] , min 22 , max 28 , dif 6 , avg 24
ppsList = [32, 21, 27, 32] , min 21 , max 32 , dif 11 , avg 28
ppsList = [34, 23, 27, 22] , min 22 , max 34 , dif 12 , avg 26
ppsList = [28, 24, 25, 20] , min 20 , max 28 , dif 8 , avg 24
ppsList = [36, 23, 31, 21] , min 21 , max 36 , dif 15 , avg 27
ppsList = [32, 26, 26, 23] , min 23 , max 32 , dif 9 , avg 26
ppsList = [32, 27, 23, 23] , min 23 , max 32 , dif 9 , avg 26
ppsList = [32, 24, 26, 23] , min 23 , max 32 , dif 9 , avg 26
ppsList = [30, 23, 30, 27] , min 23 , max 30 , dif 7 , avg 27
ppsList = [33, 26, 28, 23] , min 23 , max 33 , dif 10 , avg 27
>>>
'''
This is a full listing of the code, with sample results.
# *** pwm_int_48.py - pwm and interrupt testing, tlfong01, 2021oct05hkt2031 ***
from machine import Pin, PWM
import utime
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Conents
#
# Part 1 - Interrupt Functions
# 1.1 Using GP4, 5, 6, 7 input pins to detect and count mtor encoder A signals and calculate motor speed
# Part 2 - PWM Functions
# 2.1 Using PWM pin to fade in and fade out the system LED
# 2.2 Using GP 0, 1, 2, 3 pins' PWM signals to control the speed of TB6612FNG driving TM310 DC motor
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Interrupt functions for multiple (4) interrupt pins GP 4, 5, 6, 7 ***
intPinNum0 = 4 #GP4
intPinNum1 = 5 #GP5
intPinNum2 = 6 #GP6
intPinNum3 = 7 #GP7
intPinNumDict = {'0': 4,
'1': 5,
'2': 6,
'3': 7,
}
intPinNumList = [intPinNum0, intPinNum1, intPinNum2, intPinNum3]
intPin0 = Pin(intPinNum0, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin1 = Pin(intPinNum1, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin2 = Pin(intPinNum2, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin3 = Pin(intPinNum3, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinDict = {
'0': intPin0,
'1': intPin1,
'2': intPin2,
'3': intPin3,
}
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
intCountDict = {
'0': intCount0,
'1': intCount1,
'2': intCount2,
'3': intCount3,
}
def intCallBack0(pin):
global intCount0
intCount0 = intCount0 + 1
return
def intCallBack1(pin):
global intCount1
intCount1 = intCount1 + 1
return
def intCallBack2(pin):
global intCount2
intCount2 = intCount2 + 1
return
def intCallBack3(pin):
global intCount3
intCount3 = intCount3 + 1
return
intCallBackDict = {
'0': intCallBack0,
'1': intCallBack1,
'2': intCallBack2,
'3': intCallBack3,
}
intPin0.irq(intCallBack0, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin1.irq(intCallBack1, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin2.irq(intCallBack2, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin3.irq(intCallBack3, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
def countIntPinIntCountTime(intPinNum, countTime):
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
utime.sleep(countTime)
if intPinNum == 0:
intCount = intCount0
elif intPinNum == 1:
intCount = intCount1
elif intPinNum == 2:
intCount = intCount2
else:
intCount = intCount3
return intCount
def countIntPinIntOneTenthSecond(intPinNum):
intCount = countIntPinIntCountTime(intPinNum = intPinNum, countTime = 0.01)
return intCount
def countIntPinNumListIntOneTenthSecond(intPinNumList):
intCountList = [0] * len(intPinNumList)
for index in range(len(intPinNumList)):
intCountList[index] = countIntPinIntOneTenthSecond(intPinNumList[index])
return intCountList
# *** Test functions ***
def repeatCountIntPinNumListIntOneTenthSecond(intPinNumList, repeatTimes, pauseTime):
print('\n testCountIntPinNumListIntOneTenthSecond()')
for count in range(repeatTimes):
ppsList = countIntPinNumListIntOneTenthSecond(intPinNumList)
print(' ppsList =', ppsList, end = '')
print(' , min ', min(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , max ', max(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , dif ', max(ppsList) - min(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , avg ', int(sum(ppsList) / len(ppsList)))
'''
rpmList = ppsList.copy()
for index in range(len(rpmList)):
rpmList[index] = int(((rpmList[index] / 12) / 90) * 10 * 60)
print(' rpmList =', rpmList, end = '')
print(' , min ', min(rpmList), end = '')
print(' , max ', max(rpmList), end = '')
print(' , avg ', int(sum(rpmList) / len(rpmList)))
'''
utime.sleep(pauseTime)
return
# *** Sample Test ***
#repeatCountIntPinNumListIntOneTenthSecond(intPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3], repeatTimes = 4, pauseTime = 0.5)
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Part 2 - PWM Functions ***
def pwmSystemLed():
systemLedPinNum = 25
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(systemLedPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(1000)
for count in range(4):
for dutyCycle in range(65025):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
for dutyCycle in range(65025, 0, -1):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
return
def testPwmSystemLed():
print('testPwmSystemLed(), ...')
print(' System LED now fades in and out a couple of times')
pwmSystemLed()
print(' End of test.')
return
# *** Sample Test ***
#testPwmSystemLed()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Setup 4 PWM Pins ***
# Notes:
# 1. Setting up GP 0, 1, 2, 3 as pwm pins at 1 kHz, 50% duty cycle
# 2. Connecting the pwm pins to the pwm inputs of TB6612FNG move the DC motor TM310.
# *** Pwm Pin Numbers and List ***
pwmPinNum0 = 0 #GP0
pwmPinNum1 = 1 #GP1
pwmPinNum2 = 2 #GP2
pwmPinNum3 = 3 #GP3
pwmPinNumList = [pwmPinNum0, pwmPinNum1, pwmPinNum2, pwmPinNum3]
pwmPinNumDict = {
'0': 0,
'1': 1,
'2': 2,
'3': 3,
}
# *** Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
pwmPin0 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum0))
pwmPin1 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum1))
pwmPin2 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum2))
pwmPin3 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum3))
pwmPinList01 = [pwmPin0, pwmPin1, pwmPin2, pwmPin3]
pwmPinDict = {'0': pwmPin0,
'1': pwmPin1,
'2': pwmPin2,
'3': pwmPin3,
}
# *** Defualt Frequency and Duty Cycle ***
defaultPwmFreq = 1000
defaultPwmDutyCycle = 50
# *** Initializing Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
def setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq):
pwmPin.freq(pwmFreq)
return
def setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, dutyCycle):
u16DutyCycle = int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536)
pwmPin.duty_u16(u16DutyCycle)
return
def setupPwmPinNumList(pwmPinNumList, pwmFreqList, pwmDutyCycleList):
print(' setupPwmPinNumList(), ...')
print(' pwmPinNumList =', pwmPinNumList)
print(' pwmFreqList =', pwmFreqList)
print(' pwmDutyCycleList =', pwmDutyCycleList)
for index in range(len(pwmPinNumList)):
pwmPin = pwmPinDict[str(index)]
setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreqList[index])
setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, pwmDutyCycleList[index])
return
def testSetupPwmPinNumList():
setupPwmPinNumList(pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3], pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000],
pwmDutyCycleList = [90, 90, 90, 90])
return
# Sample test ***
#testSetupPwmPinNumList()
# *** Main Tests ***
setupPwmPinNumList(pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3],
pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000],
pwmDutyCycleList = [50, 50, 50, 50])
repeatCountIntPinNumListIntOneTenthSecond(intPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3], repeatTimes = 20, pauseTime = 0.2)
# *** End ***
# *** Sample Output tlfong01 2021oct04hkt1657 ***
'''
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
setupPwmPinNumList(), ...
pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3]
pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000]
pwmDutyCycleList = [50, 50, 50, 50]
testCountIntPinNumListIntOneTenthSecond()
ppsList = [32, 24, 28, 25] , min 24 , max 32 , dif 8 , avg 27
ppsList = [39, 26, 29, 23] , min 23 , max 39 , dif 16 , avg 29
ppsList = [31, 28, 28, 21] , min 21 , max 31 , dif 10 , avg 27
ppsList = [31, 28, 26, 16] , min 16 , max 31 , dif 15 , avg 25
ppsList = [31, 26, 34, 22] , min 22 , max 34 , dif 12 , avg 28
ppsList = [29, 26, 27, 19] , min 19 , max 29 , dif 10 , avg 25
ppsList = [28, 28, 24, 20] , min 20 , max 28 , dif 8 , avg 25
ppsList = [30, 24, 24, 28] , min 24 , max 30 , dif 6 , avg 26
ppsList = [33, 27, 18, 22] , min 18 , max 33 , dif 15 , avg 25
ppsList = [31, 26, 24, 19] , min 19 , max 31 , dif 12 , avg 25
ppsList = [28, 22, 25, 22] , min 22 , max 28 , dif 6 , avg 24
ppsList = [32, 21, 27, 32] , min 21 , max 32 , dif 11 , avg 28
ppsList = [34, 23, 27, 22] , min 22 , max 34 , dif 12 , avg 26
ppsList = [28, 24, 25, 20] , min 20 , max 28 , dif 8 , avg 24
ppsList = [36, 23, 31, 21] , min 21 , max 36 , dif 15 , avg 27
ppsList = [32, 26, 26, 23] , min 23 , max 32 , dif 9 , avg 26
ppsList = [32, 27, 23, 23] , min 23 , max 32 , dif 9 , avg 26
ppsList = [32, 24, 26, 23] , min 23 , max 32 , dif 9 , avg 26
ppsList = [30, 23, 30, 27] , min 23 , max 30 , dif 7 , avg 27
ppsList = [33, 26, 28, 23] , min 23 , max 33 , dif 10 , avg 27
>>>
'''
# *** End of Sample Output ***
Pico Running Out of Pins
Pico is now running out of pins. I need to consider using GPIO Extenders, such as MCP23017, MCP23s17 etc.
pwmPinNum0 = 0 #GP0
pwmPinNum1 = 1 #GP1
pwmPinNum2 = 2 #GP2
pwmPinNum3 = 3 #GP3
intPinNum0 = 4 #GP4
intPinNum1 = 5 #GP5
intPinNum2 = 6 #GP6
intPinNum3 = 7 #GP7
picoMotorDriverGpPinNumDict = { \
'0': {'StdByPinNum1': 8, #GP 8
'StdByPinNum2': 9, #GP 9
'AinPinNum1' : 10, #GP 10
'AinPinNum2' : 11, #GP 11
'PwmPinNum1' : 12, #GP 12
'BinPinNum1' : 13, #GP 13
'BinPinNum2' : 14, #GP 14
'PwmPinNum2' : 15, #GP 15
}
'1': {'StdByPinNum1': 16, #GP 16
'StdByPinNum2': 17, #GP 17
'AinPinNum1' : 18, #GP 18
'AinPinNum2' : 19, #GP 19
'PwmPinNum1' : 20, #GP 20
'BinPinNum1' : 21, #GP 21
'BinPinNum2' : 22, #GP 22
'PwmPinNum2' : 26, #GP 23
},
}
Complete Program Listing
# *** pwm_int_49.py - pwm and interrupt testing, tlfong01, 2021oct07hkt1542 ***
from machine import Pin, PWM
import utime
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Conents
#
# Part 1 - Interrupt Functions
# 1.1 Using GP4, 5, 6, 7 input pins to detect and count mtor encoder A signals and calculate motor speed
# Part 2 - PWM Functions
# 2.1 Using PWM pin to fade in and fade out the system LED
# 2.2 Using GP 0, 1, 2, 3 pins' PWM signals to control the speed of TB6612FNG driving TM310 DC motor
# Part 3 - TB6612FNG MotorDriver Functions
# 3.1 Setting up TB6612FNG motor drivers
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Part 1 - Interrupt Functions ***
# Interrupt functions for multiple (4) interrupt pins GP 4, 5, 6, 7 ***
intPinNum0 = 4 #GP4
intPinNum1 = 5 #GP5
intPinNum2 = 6 #GP6
intPinNum3 = 7 #GP7
picoIntGpPinNumDict = {'0': 4, # GP4
'1': 5, # GP5
'2': 6, # GP6
'3': 7, # GP7
}
intPinNumList = [intPinNum0, intPinNum1, intPinNum2, intPinNum3]
intPin0 = Pin(intPinNum0, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin1 = Pin(intPinNum1, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin2 = Pin(intPinNum2, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin3 = Pin(intPinNum3, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinDict = {
'0': intPin0,
'1': intPin1,
'2': intPin2,
'3': intPin3,
}
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
intCountDict = {
'0': intCount0,
'1': intCount1,
'2': intCount2,
'3': intCount3,
}
def intCallBack0(pin):
global intCount0
intCount0 = intCount0 + 1
return
def intCallBack1(pin):
global intCount1
intCount1 = intCount1 + 1
return
def intCallBack2(pin):
global intCount2
intCount2 = intCount2 + 1
return
def intCallBack3(pin):
global intCount3
intCount3 = intCount3 + 1
return
intCallBackDict = {
'0': intCallBack0,
'1': intCallBack1,
'2': intCallBack2,
'3': intCallBack3,
}
intPin0.irq(intCallBack0, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin1.irq(intCallBack1, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin2.irq(intCallBack2, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin3.irq(intCallBack3, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
def countIntPinIntPeriod(intPinNum, countPeriod):
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
utime.sleep(countPeriod)
if intPinNum == 0:
intCount = intCount0
elif intPinNum == 1:
intCount = intCount1
elif intPinNum == 2:
intCount = intCount2
else:
intCount = intCount3
return intCount
def countIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod):
intCountList = [0] * len(intPinNumList)
for index in range(len(intPinNumList)):
intCountList[index] = countIntPinIntPeriod(intPinNumList[index], countPeriod)
return intCountList
# *** Test functions ***
def repeatCountIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod, pauseTime, repeatTimes):
print('\n countIntPinNumListIntPeriod()')
picoIntGpPinNumList = [0] * len(intPinNumList)
for index in range(len(picoIntGpPinNumList)):
picoIntGpPinNumList[index] = picoIntGpPinNumDict[str(index)]
print(' intPinNumList =', intPinNumList)
print(' picoIntGpPinNumList =', picoIntGpPinNumList)
print(' countPeriod (seconds) =', countPeriod)
print(' pauseTime (seconds) =', pauseTime)
print(' repeat count times =', repeatTimes)
print('')
for count in range(repeatTimes):
ppsList = countIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod)
print(' ppsList =', ppsList, end = '')
print(' , min ', min(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , max ', max(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , dif ', max(ppsList) - min(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , avg ', int(sum(ppsList) / len(ppsList)))
'''
rpmList = ppsList.copy()
for index in range(len(rpmList)):
rpmList[index] = int(((rpmList[index] / 12) / 90) * 10 * 60)
print(' rpmList =', rpmList, end = '')
print(' , min ', min(rpmList), end = '')
print(' , max ', max(rpmList), end = '')
print(' , avg ', int(sum(rpmList) / len(rpmList)))
'''
utime.sleep(pauseTime)
return
# *** Sample Test ***
# ...
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Part 2 - PWM Functions ***
def pwmSystemLed():
systemLedPinNum = 25
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(systemLedPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(1000)
for count in range(4):
for dutyCycle in range(65025):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
for dutyCycle in range(65025, 0, -1):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
return
def testPwmSystemLed():
print('testPwmSystemLed(), ...')
print(' System LED now fades in and out a couple of times')
pwmSystemLed()
print(' End of test.')
return
# *** Sample Test ***
#testPwmSystemLed()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Setup 4 PWM Pins ***
# Notes:
# 1. Setting up GP 0, 1, 2, 3 as pwm pins at 1 kHz, 50% duty cycle
# 2. Connecting the pwm pins to the pwm inputs of TB6612FNG move the DC motor TM310.
# *** Pwm Pin Numbers and List ***
pwmPinNum0 = 0 #GP0
pwmPinNum1 = 1 #GP1
pwmPinNum2 = 2 #GP2
pwmPinNum3 = 3 #GP3
pwmPinNumList = [pwmPinNum0, pwmPinNum1, pwmPinNum2, pwmPinNum3]
picoPwmGpPinNumDict = {
'0': 0,
'1': 1,
'2': 2,
'3': 3,
}
# *** Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
pwmPin0 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum0))
pwmPin1 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum1))
pwmPin2 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum2))
pwmPin3 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum3))
pwmPinList01 = [pwmPin0, pwmPin1, pwmPin2, pwmPin3]
pwmPinDict = {'0': pwmPin0,
'1': pwmPin1,
'2': pwmPin2,
'3': pwmPin3,
}
# *** Defualt Frequency and Duty Cycle ***
defaultPwmFreq = 1000
defaultPwmDutyCycle = 50
# *** Initializing Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
def setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq):
pwmPin.freq(pwmFreq)
return
def setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, dutyCycle):
u16DutyCycle = int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536)
pwmPin.duty_u16(u16DutyCycle)
return
def setupPwmPinNumList(pwmPinNumList, pwmFreqList, pwmDutyCycleList):
picoPwmGpPinNumList = [0] * len(pwmPinNumList)
for index in range(len(picoPwmGpPinNumList)):
picoPwmGpPinNumList[index] = picoPwmGpPinNumDict[str(index)]
print(' setupPwmPinNumList(), ...')
print(' pwmPinNumList =', pwmPinNumList)
print(' Pico GP pin num list =', picoPwmGpPinNumList)
print(' pwmFreqList =', pwmFreqList)
print(' pwmDutyCycleList =', pwmDutyCycleList)
for index in range(len(pwmPinNumList)):
pwmPin = pwmPinDict[str(index)]
setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreqList[index])
setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, pwmDutyCycleList[index])
return
def testSetupPwmPinNumList():
setupPwmPinNumList(pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3], pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000],
pwmDutyCycleList = [90, 90, 90, 90])
return
# Sample test ***
#testSetupPwmPinNumList()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Part 3 - TB6612FNG Motor Driver Functions ***
picoMotorDriverGpPinNumDict = { \
'0': {'StdByPinNum1': 8, #GP 8
'StdByPinNum2': 9, #GP 9
'AinPinNum1' : 10, #GP 10
'AinPinNum2' : 11, #GP 11
'PwmPinNum1' : 12, #GP 12
'BinPinNum1' : 13, #GP 13
'BinPinNum2' : 14, #GP 14
'PwmPinNum2' : 15, #GP 15
}
'1': {'StdByPinNum1': 16, #GP 16
'StdByPinNum2': 17, #GP 17
'AinPinNum1' : 18, #GP 18
'AinPinNum2' : 19, #GP 19
'PwmPinNum1' : 20, #GP 20
'BinPinNum1' : 21, #GP 21
'BinPinNum2' : 22, #GP 22
'PwmPinNum2' : 26, #GP 23
},
}
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Old Main Tests ***
# *** Old Tests V1 2021oct07hkt1545 ***
def moveFourMotorsV1():
setupPwmPinNumList(pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3],
pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000],
pwmDutyCycleList = [50, 50, 50, 50])
return
def checkFourMotorsV1():
repeatCountIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3],
countPeriod = 0.1,
pauseTime = 0.2,
repeatTimes = 4,)
return
# ***Old tests ***
moveFourMotorsV1()
checkFourMotorsV1()
# *** Main Tests ***
#testSetupMotorDriverList(motorDriverNumList)
# *** End ***
# *** Sample Output tlfong01 2021oct04hkt1657 ***
# *** End of Sample Output ***
Moving and Stopping 4 Motors
Now I have written functions to move and start 4 motors.
def testStartAndStopMovingFourMotors():
print('Start moving 4 motors, ...')
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 0)
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 1)
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 0)
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 1)
utime.sleep(4)
print('Stop moving 4 motors.')
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 0)
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 1)
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 0)
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 1)
return
And this is the partial listing of the code.
# *** pico_4wd_v61.py - tlfong01, 2021oct09hkt1534 ***
from machine import Pin, PWM
import utime
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Conents
#
# Part 1 - Measure 4WD Motor Speeds
# 1.1 Using GP4, 5, 6, 7 input pins to detect and count mtor encoder A signals and calculate motor speed
# Part 2 - Change 4WD Speed and Direction
# 2.1 Using PWM pin to fade in and fade out the system LED
# 2.2 Using GP 0, 1, 2, 3 pins' PWM signals to control the speed of TB6612FNG driving TM310 DC motor
# Part 3 - Setup 4WD Motor Drivers
# 3.1 Setting up TB6612FNG motor drivers
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Part 3 - TB6612FNG Motor Driver Functions ***
stdByPinNum0 = 8
stdByPinNum1 = 9
aIn1PinNum0 = 10
aIn2PinNum0 = 11
aPwmPinNum0 = 0
bIn1PinNum0 = 12
bIn2PinNum0 = 13
bPwmPinNum0 = 1
aIn1PinNum1 = 14
aIn2PinNum1 = 15
aPwmPinNum1 = 2
bIn1PinNum1 = 16
bIn2PinNum1 = 17
bPwmPinNum1 = 3
motorDriverGpPinNumDict = { \
'0': {'StdByPinNum' : stdByPinNum0,
'0' : {'In1PinNum' : aIn1PinNum0,
'In2PinNum' : aIn2PinNum0,
'PwmPinNum' : aPwmPinNum0,
},
'1' : {'In1PinNum' : bIn1PinNum0,
'In2PinNum' : bIn2PinNum0,
'PwmPinNum' : bPwmPinNum0,
},
},
'1': {'StdByPinNum' : stdByPinNum1,
'0' : {'In1PinNum' : aIn1PinNum1,
'In2PinNum' : aIn2PinNum1,
'PwmPinNum' : aPwmPinNum1,
},
'1' : {'In1PinNum' : bIn1PinNum1,
'In2PinNum' : bIn2PinNum1,
'PwmPinNum' : bPwmPinNum1,
},
},
}
def setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum, channelNum):
stdByPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['StdByPinNum']
in1PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In1PinNum']
in2PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In2PinNum']
pwmPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['PwmPinNum']
stdByPin = Pin(stdByPinNum, Pin.OUT)
in1Pin = Pin(in1PinNum, Pin.OUT)
in2Pin = Pin(in2PinNum, Pin.OUT)
pwmPin = Pin(pwmPinNum, Pin.OUT)
stdByPin.high()
in1Pin.low()
in2Pin.high()
pwmPin.high()
return
def stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum, channelNum):
stdByPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['StdByPinNum']
in1PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In1PinNum']
in2PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In2PinNum']
pwmPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['PwmPinNum']
stdByPin = Pin(stdByPinNum, Pin.OUT)
in1Pin = Pin(in1PinNum, Pin.OUT)
in2Pin = Pin(in2PinNum, Pin.OUT)
pwmPin = Pin(pwmPinNum, Pin.OUT)
stdByPin.high()
in1Pin.high()
in2Pin.high()
pwmPin.high()
return
def testStartAndStopMovingFourMotors():
print('Start moving 4 motors, ...')
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 0)
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 1)
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 0)
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 1)
utime.sleep(4)
print('Stop moving 4 motors.')
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 0)
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 1)
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 0)
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 1)
return
# ***
testStartAndStopMovingFourMotors()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Old Main Tests ***
# *** Old Tests V1 2021oct07hkt1545 ***
def pwmChange4MotorSpeeds():
setupPwmPinNumList(pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3],
pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000],
pwmDutyCycleList = [50, 50, 50, 50])
return
def intMeasure4MotorSpeeds():
repeatCountIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3],
countPeriod = 0.1,
pauseTime = 0.2,
repeatTimes = 4,)
return
# ***Sample Tests ***
#pwmChange4MotorSpeeds()
#intMeasure4MotorSpeeds()
# *** Main Tests ***
testStartAndStopMovingFourMotors()
#utime.sleep(2)
# *** End ***
# *** Sample Output tlfong01 2021oct04hkt1657 ***
# *** End of Sample Output ***
/ to continue, …
I am hitting the forum’s 32k words limit, therefore another reply.
My code can do something like this.
def testStartAndStopMovingFourMotors():
print('Start moving 4 motors, ...')
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 0)
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 1)
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 0)
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 1)
utime.sleep(4)
print('Stop moving 4 motors.')
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 0)
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 1)
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 0)
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 1)
return
The video
The coomplete listing
# *** pico_4wd_v61.py - tlfong01, 2021oct09hkt1534 ***
from machine import Pin, PWM
import utime
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Conents
#
# Part 1 - Measure 4WD Motor Speeds
# 1.1 Using GP4, 5, 6, 7 input pins to detect and count mtor encoder A signals and calculate motor speed
# Part 2 - Change 4WD Speed and Direction
# 2.1 Using PWM pin to fade in and fade out the system LED
# 2.2 Using GP 0, 1, 2, 3 pins' PWM signals to control the speed of TB6612FNG driving TM310 DC motor
# Part 3 - Setup 4WD Motor Drivers
# 3.1 Setting up TB6612FNG motor drivers
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Part 1 - Measure 4WD Motor Speeds ***
intPinNum0 = 4 #GP4
intPinNum1 = 5 #GP5
intPinNum2 = 6 #GP6
intPinNum3 = 7 #GP7
intGpPinNumDict = {'0': 4, # GP4
'1': 5, # GP5
'2': 6, # GP6
'3': 7, # GP7
}
intPinNumList = [intPinNum0, intPinNum1, intPinNum2, intPinNum3]
intPin0 = Pin(intPinNum0, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin1 = Pin(intPinNum1, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin2 = Pin(intPinNum2, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin3 = Pin(intPinNum3, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinDict = {
'0': intPin0,
'1': intPin1,
'2': intPin2,
'3': intPin3,
}
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
intCountDict = {
'0': intCount0,
'1': intCount1,
'2': intCount2,
'3': intCount3,
}
def intCallBack0(pin):
global intCount0
intCount0 = intCount0 + 1
return
def intCallBack1(pin):
global intCount1
intCount1 = intCount1 + 1
return
def intCallBack2(pin):
global intCount2
intCount2 = intCount2 + 1
return
def intCallBack3(pin):
global intCount3
intCount3 = intCount3 + 1
return
intCallBackDict = {
'0': intCallBack0,
'1': intCallBack1,
'2': intCallBack2,
'3': intCallBack3,
}
intPin0.irq(intCallBack0, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin1.irq(intCallBack1, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin2.irq(intCallBack2, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin3.irq(intCallBack3, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
def countIntPinIntPeriod(intPinNum, countPeriod):
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
utime.sleep(countPeriod)
if intPinNum == 0:
intCount = intCount0
elif intPinNum == 1:
intCount = intCount1
elif intPinNum == 2:
intCount = intCount2
else:
intCount = intCount3
return intCount
def countIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod):
intCountList = [0] * len(intPinNumList)
for index in range(len(intPinNumList)):
intCountList[index] = countIntPinIntPeriod(intPinNumList[index], countPeriod)
return intCountList
# *** Test functions ***
def repeatCountIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod, pauseTime, repeatTimes):
print('\n countIntPinNumListIntPeriod()')
intGpPinNumList = [0] * len(intPinNumList)
for index in range(len(intGpPinNumList)):
intGpPinNumList[index] = intGpPinNumDict[str(index)]
print(' intPinNumList =', intPinNumList)
print(' intGpPinNumList =', intGpPinNumList)
print(' countPeriod (seconds) =', countPeriod)
print(' pauseTime (seconds) =', pauseTime)
print(' repeat count times =', repeatTimes)
print('')
for count in range(repeatTimes):
ppsList = countIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod)
print(' ppsList =', ppsList, end = '')
print(' , min ', min(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , max ', max(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , dif ', max(ppsList) - min(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , avg ', int(sum(ppsList) / len(ppsList)))
'''
rpmList = ppsList.copy()
for index in range(len(rpmList)):
rpmList[index] = int(((rpmList[index] / 12) / 90) * 10 * 60)
print(' rpmList =', rpmList, end = '')
print(' , min ', min(rpmList), end = '')
print(' , max ', max(rpmList), end = '')
print(' , avg ', int(sum(rpmList) / len(rpmList)))
'''
utime.sleep(pauseTime)
return
# *** Sample Test ***
# ...
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Part 2 - PWM Functions ***
def pwmSystemLed():
systemLedPinNum = 25
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(systemLedPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(1000)
for count in range(4):
for dutyCycle in range(65025):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
for dutyCycle in range(65025, 0, -1):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
return
def testPwmSystemLed():
print('testPwmSystemLed(), ...')
print(' System LED now fades in and out a couple of times')
pwmSystemLed()
print(' End of test.')
return
# *** Sample Test ***
#testPwmSystemLed()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Setup 4 PWM Pins ***
# Notes:
# 1. Setting up GP 0, 1, 2, 3 as pwm pins at 1 kHz, 50% duty cycle
# 2. Connecting the pwm pins to the pwm inputs of TB6612FNG move the DC motor TM310.
# *** Pwm Pin Numbers and List ***
pwmPinNum0 = 0 #GP0
pwmPinNum1 = 1 #GP1
pwmPinNum2 = 2 #GP2
pwmPinNum3 = 3 #GP3
pwmPinNumList = [pwmPinNum0, pwmPinNum1, pwmPinNum2, pwmPinNum3]
picoPwmGpPinNumDict = {
'0': 0,
'1': 1,
'2': 2,
'3': 3,
}
# *** Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
pwmPin0 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum0))
pwmPin1 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum1))
pwmPin2 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum2))
pwmPin3 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum3))
pwmPinList01 = [pwmPin0, pwmPin1, pwmPin2, pwmPin3]
pwmPinDict = {'0': pwmPin0,
'1': pwmPin1,
'2': pwmPin2,
'3': pwmPin3,
}
# *** Defualt Frequency and Duty Cycle ***
defaultPwmFreq = 1000
defaultPwmDutyCycle = 50
# *** Initializing Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
def setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq):
pwmPin.freq(pwmFreq)
return
def setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, dutyCycle):
u16DutyCycle = int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536)
pwmPin.duty_u16(u16DutyCycle)
return
def setupPwmPinNumList(pwmPinNumList, pwmFreqList, pwmDutyCycleList):
picoPwmGpPinNumList = [0] * len(pwmPinNumList)
for index in range(len(picoPwmGpPinNumList)):
picoPwmGpPinNumList[index] = picoPwmGpPinNumDict[str(index)]
print(' setupPwmPinNumList(), ...')
print(' pwmPinNumList =', pwmPinNumList)
print(' Pico GP pin num list =', picoPwmGpPinNumList)
print(' pwmFreqList =', pwmFreqList)
print(' pwmDutyCycleList =', pwmDutyCycleList)
for index in range(len(pwmPinNumList)):
pwmPin = pwmPinDict[str(index)]
setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreqList[index])
setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, pwmDutyCycleList[index])
return
def testSetupPwmPinNumList():
setupPwmPinNumList(pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3], pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000],
pwmDutyCycleList = [90, 90, 90, 90])
return
# Sample test ***
#testSetupPwmPinNumList()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Part 3 - TB6612FNG Motor Driver Functions ***
stdByPinNum0 = 8
stdByPinNum1 = 9
aIn1PinNum0 = 10
aIn2PinNum0 = 11
aPwmPinNum0 = 0
bIn1PinNum0 = 12
bIn2PinNum0 = 13
bPwmPinNum0 = 1
aIn1PinNum1 = 14
aIn2PinNum1 = 15
aPwmPinNum1 = 2
bIn1PinNum1 = 16
bIn2PinNum1 = 17
bPwmPinNum1 = 3
motorDriverGpPinNumDict = { \
'0': {'StdByPinNum' : stdByPinNum0,
'0' : {'In1PinNum' : aIn1PinNum0,
'In2PinNum' : aIn2PinNum0,
'PwmPinNum' : aPwmPinNum0,
},
'1' : {'In1PinNum' : bIn1PinNum0,
'In2PinNum' : bIn2PinNum0,
'PwmPinNum' : bPwmPinNum0,
},
},
'1': {'StdByPinNum' : stdByPinNum1,
'0' : {'In1PinNum' : aIn1PinNum1,
'In2PinNum' : aIn2PinNum1,
'PwmPinNum' : aPwmPinNum1,
},
'1' : {'In1PinNum' : bIn1PinNum1,
'In2PinNum' : bIn2PinNum1,
'PwmPinNum' : bPwmPinNum1,
},
},
}
def setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum, channelNum):
stdByPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['StdByPinNum']
in1PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In1PinNum']
in2PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In2PinNum']
pwmPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['PwmPinNum']
stdByPin = Pin(stdByPinNum, Pin.OUT)
in1Pin = Pin(in1PinNum, Pin.OUT)
in2Pin = Pin(in2PinNum, Pin.OUT)
pwmPin = Pin(pwmPinNum, Pin.OUT)
stdByPin.high()
in1Pin.low()
in2Pin.high()
pwmPin.high()
return
def stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum, channelNum):
stdByPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['StdByPinNum']
in1PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In1PinNum']
in2PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In2PinNum']
pwmPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['PwmPinNum']
stdByPin = Pin(stdByPinNum, Pin.OUT)
in1Pin = Pin(in1PinNum, Pin.OUT)
in2Pin = Pin(in2PinNum, Pin.OUT)
pwmPin = Pin(pwmPinNum, Pin.OUT)
stdByPin.high()
in1Pin.high()
in2Pin.high()
pwmPin.high()
return
def testStartAndStopMovingFourMotors():
print('Start moving 4 motors, ...')
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 0)
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 1)
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 0)
setupMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 1)
utime.sleep(4)
print('Stop moving 4 motors.')
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 0)
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 0, channelNum = 1)
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 0)
stopMotorDriverChannel(motorDriverNum = 1, channelNum = 1)
return
# ***
testStartAndStopMovingFourMotors()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Old Main Tests ***
# *** Old Tests V1 2021oct07hkt1545 ***
def pwmChange4MotorSpeeds():
setupPwmPinNumList(pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3],
pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000],
pwmDutyCycleList = [50, 50, 50, 50])
return
def intMeasure4MotorSpeeds():
repeatCountIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3],
countPeriod = 0.1,
pauseTime = 0.2,
repeatTimes = 4,)
return
# ***Sample Tests ***
#pwmChange4MotorSpeeds()
#intMeasure4MotorSpeeds()
# *** Main Tests ***
testStartAndStopMovingFourMotors()
#utime.sleep(2)
# *** End ***
# *** Sample Output tlfong01 2021oct04hkt1657 ***
# *** End of Sample Output ***
Setup and move a list of 4 motors
Now I have modified the 4WD program to do list processing. For example:
def testSetupMoveMotorList(motorConfigDictList):
motorControlDictList = setupMotorList(motorConfigDictList)
moveMotorList(motorControlDictList)
utime.sleep(2)
stopMotorList(motorControlDictList)
return
testSetupMoveMotorList(motorConfigDictList_00_01_10_11)
Below is the complete code listing.
# *** pico_4wd_v66.py - tlfong01, 2021oct10hkt1644 ***
from machine import Pin, PWM
import utime
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# Conents
#
# Part 1 - Measure 4WD Motor Speeds
# 1.1 Using GP4, 5, 6, 7 input pins to detect and count mtor encoder A signals and calculate motor speed
# Part 2 - Change 4WD Speed and Direction
# 2.1 Using PWM pin to fade in and fade out the system LED
# 2.2 Using GP 0, 1, 2, 3 pins' PWM signals to control the speed of TB6612FNG driving TM310 DC motor
# Part 3 - Setup 4WD Motor Drivers
# 3.1 Setting up TB6612FNG motor drivers
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Part 1 - Measure 4WD Motor Speeds ***
intPinNum0 = 4 #GP4
intPinNum1 = 5 #GP5
intPinNum2 = 6 #GP6
intPinNum3 = 7 #GP7
intGpPinNumDict = {'0': 4, # GP4
'1': 5, # GP5
'2': 6, # GP6
'3': 7, # GP7
}
intPinNumList = [intPinNum0, intPinNum1, intPinNum2, intPinNum3]
intPin0 = Pin(intPinNum0, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin1 = Pin(intPinNum1, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin2 = Pin(intPinNum2, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin3 = Pin(intPinNum3, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinDict = {
'0': intPin0,
'1': intPin1,
'2': intPin2,
'3': intPin3,
}
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
intCountDict = {
'0': intCount0,
'1': intCount1,
'2': intCount2,
'3': intCount3,
}
def intCallBack0(pin):
global intCount0
intCount0 = intCount0 + 1
return
def intCallBack1(pin):
global intCount1
intCount1 = intCount1 + 1
return
def intCallBack2(pin):
global intCount2
intCount2 = intCount2 + 1
return
def intCallBack3(pin):
global intCount3
intCount3 = intCount3 + 1
return
intCallBackDict = {
'0': intCallBack0,
'1': intCallBack1,
'2': intCallBack2,
'3': intCallBack3,
}
intPin0.irq(intCallBack0, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin1.irq(intCallBack1, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin2.irq(intCallBack2, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin3.irq(intCallBack3, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
def countIntPinIntPeriod(intPinNum, countPeriod):
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
utime.sleep(countPeriod)
if intPinNum == 0:
intCount = intCount0
elif intPinNum == 1:
intCount = intCount1
elif intPinNum == 2:
intCount = intCount2
else:
intCount = intCount3
return intCount
def countIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod):
intCountList = [0] * len(intPinNumList)
for index in range(len(intPinNumList)):
intCountList[index] = countIntPinIntPeriod(intPinNumList[index], countPeriod)
return intCountList
# *** Test functions ***
def repeatCountIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod, pauseTime, repeatTimes):
print('\n countIntPinNumListIntPeriod()')
intGpPinNumList = [0] * len(intPinNumList)
for index in range(len(intGpPinNumList)):
intGpPinNumList[index] = intGpPinNumDict[str(index)]
print(' intPinNumList =', intPinNumList)
print(' intGpPinNumList =', intGpPinNumList)
print(' countPeriod (seconds) =', countPeriod)
print(' pauseTime (seconds) =', pauseTime)
print(' repeat count times =', repeatTimes)
print('')
for count in range(repeatTimes):
ppsList = countIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod)
print(' ppsList =', ppsList, end = '')
print(' , min ', min(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , max ', max(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , dif ', max(ppsList) - min(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , avg ', int(sum(ppsList) / len(ppsList)))
'''
rpmList = ppsList.copy()
for index in range(len(rpmList)):
rpmList[index] = int(((rpmList[index] / 12) / 90) * 10 * 60)
print(' rpmList =', rpmList, end = '')
print(' , min ', min(rpmList), end = '')
print(' , max ', max(rpmList), end = '')
print(' , avg ', int(sum(rpmList) / len(rpmList)))
'''
utime.sleep(pauseTime)
return
# *** Sample Test ***
# ...
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Part 2 - PWM Functions ***
def pwmSystemLed():
systemLedPinNum = 25
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(systemLedPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(1000)
for count in range(4):
for dutyCycle in range(65025):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
for dutyCycle in range(65025, 0, -1):
pwmPin.duty_u16(dutyCycle)
utime.sleep(0.0001)
return
def testPwmSystemLed():
print('testPwmSystemLed(), ...')
print(' System LED now fades in and out a couple of times')
pwmSystemLed()
print(' End of test.')
return
# *** Sample Test ***
#testPwmSystemLed()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Setup 4 PWM Pins ***
# Notes:
# 1. Setting up GP 0, 1, 2, 3 as pwm pins at 1 kHz, 50% duty cycle
# 2. Connecting the pwm pins to the pwm inputs of TB6612FNG move the DC motor TM310.
# *** Pwm Pin Numbers and List ***
pwmPinNum0 = 0 #GP0
pwmPinNum1 = 1 #GP1
pwmPinNum2 = 2 #GP2
pwmPinNum3 = 3 #GP3
pwmPinNumList = [pwmPinNum0, pwmPinNum1, pwmPinNum2, pwmPinNum3]
picoPwmGpPinNumDict = {
'0': 0,
'1': 1,
'2': 2,
'3': 3,
}
# *** Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
pwmPin0 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum0))
pwmPin1 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum1))
pwmPin2 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum2))
pwmPin3 = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum3))
pwmPinList01 = [pwmPin0, pwmPin1, pwmPin2, pwmPin3]
pwmPinDict = {'0': pwmPin0,
'1': pwmPin1,
'2': pwmPin2,
'3': pwmPin3,
}
# *** Defualt Frequency and Duty Cycle ***
defaultPwmFreq = 1000
defaultPwmDutyCycle = 50
# *** Initializing Pwm Pin Objects and List ***
def setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreq):
pwmPin.freq(pwmFreq)
return
def setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, dutyCycle):
u16DutyCycle = int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536)
pwmPin.duty_u16(u16DutyCycle)
return
def setupPwmPinNumList(pwmPinNumList, pwmFreqList, pwmDutyCycleList):
picoPwmGpPinNumList = [0] * len(pwmPinNumList)
for index in range(len(picoPwmGpPinNumList)):
picoPwmGpPinNumList[index] = picoPwmGpPinNumDict[str(index)]
print(' setupPwmPinNumList(), ...')
print(' pwmPinNumList =', pwmPinNumList)
print(' Pico GP pin num list =', picoPwmGpPinNumList)
print(' pwmFreqList =', pwmFreqList)
print(' pwmDutyCycleList =', pwmDutyCycleList)
for index in range(len(pwmPinNumList)):
pwmPin = pwmPinDict[str(index)]
setPwmFreq(pwmPin, pwmFreqList[index])
setPwmDutyCycle(pwmPin, pwmDutyCycleList[index])
return
def testSetupPwmPinNumList():
setupPwmPinNumList(pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3], pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000],
pwmDutyCycleList = [90, 90, 90, 90])
return
# Sample test ***
#testSetupPwmPinNumList()
def pwmChange4MotorSpeeds():
setupPwmPinNumList(pwmPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3],
pwmFreqList = [1000, 1000, 1000, 1000],
pwmDutyCycleList = [50, 50, 50, 50])
return
def intMeasure4MotorSpeeds():
repeatCountIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3],
countPeriod = 0.1,
pauseTime = 0.2,
repeatTimes = 4,)
return
# ***Sample Tests ***
#pwmChange4MotorSpeeds()
#intMeasure4MotorSpeeds()
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Part 3 - TB6612FNG Motor Driver Functions ***
stdByPinNum0 = 8
stdByPinNum1 = 9
aIn1PinNum0 = 10
aIn2PinNum0 = 11
aPwmPinNum0 = 0
bIn1PinNum0 = 12
bIn2PinNum0 = 13
bPwmPinNum0 = 1
aIn1PinNum1 = 14
aIn2PinNum1 = 15
aPwmPinNum1 = 2
bIn1PinNum1 = 16
bIn2PinNum1 = 17
bPwmPinNum1 = 3
motorConfigDict00 = {'MotorDriverNum': 0, 'ChannelNum': 0}
motorConfigDict01 = {'MotorDriverNum': 0, 'ChannelNum': 1}
motorConfigDict10 = {'MotorDriverNum': 1, 'ChannelNum': 0}
motorConfigDict11 = {'MotorDriverNum': 1, 'ChannelNum': 1}
motorConfigDictList_00_01_10_11 = [motorConfigDict00, motorConfigDict01, motorConfigDict10, motorConfigDict11]
motorDriverGpPinNumDict = { \
'0': {'StdByPinNum' : stdByPinNum0,
'0' : {'In1PinNum' : aIn1PinNum0,
'In2PinNum' : aIn2PinNum0,
'PwmPinNum' : aPwmPinNum0,
},
'1' : {'In1PinNum' : bIn1PinNum0,
'In2PinNum' : bIn2PinNum0,
'PwmPinNum' : bPwmPinNum0,
},
},
'1': {'StdByPinNum' : stdByPinNum1,
'0' : {'In1PinNum' : aIn1PinNum1,
'In2PinNum' : aIn2PinNum1,
'PwmPinNum' : aPwmPinNum1,
},
'1' : {'In1PinNum' : bIn1PinNum1,
'In2PinNum' : bIn2PinNum1,
'PwmPinNum' : bPwmPinNum1,
},
},
}
def setupMotor(motorConfigDict):
motorDriverNum = motorConfigDict['MotorDriverNum']
channelNum = motorConfigDict['ChannelNum']
stdByPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['StdByPinNum']
in1PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In1PinNum']
in2PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In2PinNum']
pwmPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['PwmPinNum']
stdByPin = Pin(stdByPinNum, Pin.OUT)
in1Pin = Pin(in1PinNum, Pin.OUT)
in2Pin = Pin(in2PinNum, Pin.OUT)
pwmPin = Pin(pwmPinNum, Pin.OUT)
motorControlDict = {'StdByPin': stdByPin,
'In1Pin' : in1Pin,
'In2Pin' : in2Pin,
'PwmPin' : pwmPin,
}
return motorControlDict
def setupMotorList(motorConfigDictList):
motorControlDictList = [0] * len(motorConfigDictList)
for index in range(len(motorConfigDictList)):
motorControlDict = setupMotor(motorConfigDictList[index])
motorControlDictList[index] = motorControlDict
return motorControlDictList
def moveMotor(motorControlDict):
motorControlDict['StdByPin'].high()
motorControlDict['In1Pin'].low()
motorControlDict['In2Pin'].high()
motorControlDict['PwmPin'].high()
return
def moveMotorList(motorControlDictList):
for motorControlDict in motorControlDictList:
moveMotor(motorControlDict)
return
def stopMotor(motorControlDict):
motorControlDict['In1Pin'].low()
motorControlDict['In2Pin'].low()
return
def stopMotorList(motorControlDictList):
for motorControlDict in motorControlDictList:
stopMotor(motorControlDict)
return
def testSetupMoveMotorList(motorConfigDictList):
motorControlDictList = setupMotorList(motorConfigDictList)
moveMotorList(motorControlDictList)
utime.sleep(2)
stopMotorList(motorControlDictList)
return
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
testSetupMoveMotorList(motorConfigDictList_00_01_10_11)
# *** End ***
Newbie friendly version of this Pico 4WD program
Now I have written some higher abstract level functions to make using the program user friendly. Below is an example of how to use the high level functions as two commands to setup and move 4 motors.
testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList(‘FourMotorsList’, ‘Forward’, ‘VerySlow’, ‘TwoSeconds’)
testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList(‘FourMotorsList’, ‘Backward’, ‘VeryFast’, ‘FourSeconds’)
I am hitting the 32k words limit again. So I am making a new reply to list the TLDR program.
/ to continue, …
Example commands to move 4 motors
testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList(‘FourMotorsList’, ‘Forward’, ‘VerySlow’, ‘TwoSeconds’)
testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList(‘FourMotorsList’, ‘Backward’, ‘VeryFast’, ‘FourSeconds’)
A complete listing of the previous 4WD program.
# *** pico_4wd_v70.py - tlfong01, 2021oct10hkt2039 ***
from machine import Pin, PWM
import utime
secondsDict = {'TwoSeconds': 2,
'FourSeconds': 4,
}
# *** Part 1 - Measure 4WD Motor Speeds ***
intPinNum0 = 4 #GP4
intPinNum1 = 5 #GP5
intPinNum2 = 6 #GP6
intPinNum3 = 7 #GP7
intGpPinNumDict = {'0': 4, # GP4
'1': 5, # GP5
'2': 6, # GP6
'3': 7, # GP7
}
intPinNumList = [intPinNum0, intPinNum1, intPinNum2, intPinNum3]
intPin0 = Pin(intPinNum0, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin1 = Pin(intPinNum1, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin2 = Pin(intPinNum2, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPin3 = Pin(intPinNum3, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
intPinDict = {
'0': intPin0,
'1': intPin1,
'2': intPin2,
'3': intPin3,
}
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
intCountDict = {
'0': intCount0,
'1': intCount1,
'2': intCount2,
'3': intCount3,
}
def intCallBack0(pin):
global intCount0
intCount0 = intCount0 + 1
return
def intCallBack1(pin):
global intCount1
intCount1 = intCount1 + 1
return
def intCallBack2(pin):
global intCount2
intCount2 = intCount2 + 1
return
def intCallBack3(pin):
global intCount3
intCount3 = intCount3 + 1
return
intCallBackDict = {
'0': intCallBack0,
'1': intCallBack1,
'2': intCallBack2,
'3': intCallBack3,
}
intPin0.irq(intCallBack0, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin1.irq(intCallBack1, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin2.irq(intCallBack2, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
intPin3.irq(intCallBack3, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
def countIntPinIntPeriod(intPinNum, countPeriod):
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
utime.sleep(countPeriod)
if intPinNum == 0:
intCount = intCount0
elif intPinNum == 1:
intCount = intCount1
elif intPinNum == 2:
intCount = intCount2
else:
intCount = intCount3
return intCount
def countIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod):
intCountList = [0] * len(intPinNumList)
for index in range(len(intPinNumList)):
intCountList[index] = countIntPinIntPeriod(intPinNumList[index], countPeriod)
return intCountList
# *** Test functions ***
def repeatCountIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod, pauseTime, repeatTimes):
print('\n countIntPinNumListIntPeriod()')
intGpPinNumList = [0] * len(intPinNumList)
for index in range(len(intGpPinNumList)):
intGpPinNumList[index] = intGpPinNumDict[str(index)]
print(' intPinNumList =', intPinNumList)
print(' intGpPinNumList =', intGpPinNumList)
print(' countPeriod (seconds) =', countPeriod)
print(' pauseTime (seconds) =', pauseTime)
print(' repeat count times =', repeatTimes)
print('')
for count in range(repeatTimes):
ppsList = countIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod)
print(' ppsList =', ppsList, end = '')
print(' , min ', min(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , max ', max(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , dif ', max(ppsList) - min(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , avg ', int(sum(ppsList) / len(ppsList)))
'''
rpmList = ppsList.copy()
for index in range(len(rpmList)):
rpmList[index] = int(((rpmList[index] / 12) / 90) * 10 * 60)
print(' rpmList =', rpmList, end = '')
print(' , min ', min(rpmList), end = '')
print(' , max ', max(rpmList), end = '')
print(' , avg ', int(sum(rpmList) / len(rpmList)))
'''
utime.sleep(pauseTime)
return
# *** Part 3 - TB6612FNG Motor Driver Functions ***
stdByPinNum0 = 8
stdByPinNum1 = 9
aIn1PinNum0 = 10
aIn2PinNum0 = 11
aPwmPinNum0 = 0
bIn1PinNum0 = 12
bIn2PinNum0 = 13
bPwmPinNum0 = 1
aIn1PinNum1 = 14
aIn2PinNum1 = 15
aPwmPinNum1 = 2
bIn1PinNum1 = 16
bIn2PinNum1 = 17
bPwmPinNum1 = 3
motorConfigDict00 = {'MotorDriverNum': 0, 'ChannelNum': 0}
motorConfigDict01 = {'MotorDriverNum': 0, 'ChannelNum': 1}
motorConfigDict10 = {'MotorDriverNum': 1, 'ChannelNum': 0}
motorConfigDict11 = {'MotorDriverNum': 1, 'ChannelNum': 1}
motorConfigDictList_00_01_10_11 = [motorConfigDict00, motorConfigDict01, motorConfigDict10, motorConfigDict11]
motorConfigDictList01 = motorConfigDictList_00_01_10_11
motorConfigDictListDict = {'FourMotorsList' : motorConfigDictList01,
}
motorDriverGpPinNumDict = { \
'0': {'StdByPinNum' : stdByPinNum0,
'0' : {'In1PinNum' : aIn1PinNum0,
'In2PinNum' : aIn2PinNum0,
'PwmPinNum' : aPwmPinNum0,
'PwmFreq' : 1000,
'DutyCycle' : 20,
},
'1' : {'In1PinNum' : bIn1PinNum0,
'In2PinNum' : bIn2PinNum0,
'PwmPinNum' : bPwmPinNum0,
'PwmFreq' : 1000,
'DutyCycle' : 20,
},
},
'1': {'StdByPinNum' : stdByPinNum1,
'0' : {'In1PinNum' : aIn1PinNum1,
'In2PinNum' : aIn2PinNum1,
'PwmPinNum' : aPwmPinNum1,
'PwmFreq' : 1000,
'DutyCycle' : 20,
},
'1' : {'In1PinNum' : bIn1PinNum1,
'In2PinNum' : bIn2PinNum1,
'PwmPinNum' : bPwmPinNum1,
'PwmFreq' : 1000,
'DutyCycle' : 20,
},
},
}
def setupMotorBasic(motorConfigDict):
motorDriverNum = motorConfigDict['MotorDriverNum']
channelNum = motorConfigDict['ChannelNum']
stdByPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['StdByPinNum']
in1PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In1PinNum']
in2PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In2PinNum']
stdByPin = Pin(stdByPinNum, Pin.OUT)
in1Pin = Pin(in1PinNum, Pin.OUT)
in2Pin = Pin(in2PinNum, Pin.OUT)
pwmPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['PwmPinNum']
pwmFreq = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['PwmFreq']
dutyCycle = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['DutyCycle']
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(pwmFreq)
u16DutyCycle = int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536)
pwmPin.duty_u16(u16DutyCycle)
motorControlDict = {'StdByPin': stdByPin,
'In1Pin' : in1Pin,
'In2Pin' : in2Pin,
'PwmPin' : pwmPin,
}
return motorControlDict
dutyCycleDict = {
'VeryVerySlow' : 95,
'VeryFast' : 90,
'Fast' : 80,
'Normal' : 50,
'Slow' : 40,
'VerySlow' : 30,
'VeryVerySlow' : 25,
}
def setupMotorList(motorConfigDictList):
motorControlDictList = [0] * len(motorConfigDictList)
for index in range(len(motorConfigDictList)):
motorControlDict = setupMotorBasic(motorConfigDictList[index])
motorControlDictList[index] = motorControlDict
return motorControlDictList
def moveMotorDirectionSpeedList(motorControlDictList, directionName, speedName):
for motorControlDict in motorControlDictList:
moveMotorDirectionSpeed(motorControlDict, directionName, speedName)
return
def moveMotorDirectionSpeed(motorControlDict, directionName, speedName):
moveMotorDirection(motorControlDict, directionName)
moveMotorSpeed(motorControlDict, speedName)
return
def moveMotorDirection(motorControlDict, directionName):
if directionName =='Forward':
motorControlDict['In1Pin'].low()
motorControlDict['In2Pin'].high()
elif directionName == 'Backward':
motorControlDict['In1Pin'].high()
motorControlDict['In2Pin'].low()
return
def moveMotorSpeed(motorControlDict, speedName):
pwmPin = motorControlDict['PwmPin']
dutyCycle = dutyCycleDict[speedName]
pwmPin.duty_u16(int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536) )
return
def stopMotor(motorControlDict):
motorControlDict['In1Pin'].low()
motorControlDict['In2Pin'].low()
return
def stopMotorList(motorControlDictList):
for motorControlDict in motorControlDictList:
stopMotor(motorControlDict)
return
def testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList(motorConfigDictListName, directionName, speedName, secondsName):
print('Begin testSetupMoveMotorList(), ...')
motorConfigDictList = motorConfigDictListDict[motorConfigDictListName]
motorControlDictList1 = setupMotorList(motorConfigDictList)
moveMotorDirectionSpeedList(motorControlDictList1, directionName, speedName)
utime.sleep(secondsDict[secondsName])
stopMotorList(motorControlDictList1)
print('End testSetupMoveMotorList(), ...')
return
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Main ***
testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList('FourMotorsList', 'Forward', 'VerySlow', 'TwoSeconds')
testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList('FourMotorsList', 'Backward', 'VeryFast', 'FourSeconds')
# *** End ***
Merging PWM and Interrupt Functions into Main Motor Control Functions
PWM functions have been merged and tested OK. Interrupt functions are to be tested.
Penzu complete listing of code: https://penzu.com/p/56eb8c7c
Interrupt count measuring OK (https://penzu.com/p/b176e88b)
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Begin testSetupMoveMotorList(), ...
After 2 seconds, ...
countIntPinNumListIntPeriod()
intPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3]
intGpPinNumList = [4, 5, 6, 7]
countPeriod (seconds) = 0.1
pauseTime (seconds) = 0.1
repeat count times = 10
countList = [294, 220, 300, 215] , min 215 , max 300 , dif 85 , avg 257
countList = [267, 226, 300, 210] , min 210 , max 300 , dif 90 , avg 250
countList = [284, 231, 301, 214] , min 214 , max 301 , dif 87 , avg 257
countList = [273, 229, 299, 213] , min 213 , max 299 , dif 86 , avg 253
countList = [290, 219, 301, 218] , min 218 , max 301 , dif 83 , avg 257
countList = [280, 224, 298, 217] , min 217 , max 298 , dif 81 , avg 254
countList = [302, 231, 298, 212] , min 212 , max 302 , dif 90 , avg 260
countList = [276, 216, 304, 216] , min 216 , max 304 , dif 88 , avg 253
countList = [295, 215, 298, 203] , min 203 , max 298 , dif 95 , avg 252
countList = [292, 214, 293, 210] , min 210 , max 293 , dif 83 , avg 252
End testSetupMoveMotorList(), ...
>>>
Scaling up 4WD with DC Motor x 4 to 6WD with BLDC Motor x 6
Now I am thinking of upgrading my 4WD to 6WD with BLDC motors. The BLDC motor has built in controllers, so there is no need to use any motor controllers. Some newbie is asking a question of testing BLDC motors, and I took the opportunity to do a little research and found it easy to expand the dictionaries for BLDC motors.
Brushless DC motor with built in controller - EESE, Asked 2021oct13
Part 5 - Using Rpi Pico and MicroPython to PWM control BLDC motor speed
Video = https://youtu.be/-omE34cMXj4
Test function =
```
def testBldcMotorV1():
print(' Begin testBldcMotor(), ...')
motorConfigDict = {'MotorDriverNum': 2, 'ChannelNum': 0}
motorControlDict = setupBldcMotor(motorConfigDict)
print(' Now start fast, ...')
hold('FourSeconds')
changeBldcMotorSpeed(motorControlDict, 'Normal')
print(' Now normal, ...')
hold('FourSeconds')
changeBldcMotorSpeed(motorControlDict, 'Slow')
print(' Now slow, ...')
hold('FourSeconds')
changeBldcMotorSpeed(motorControlDict, 'Fast')
print(' Now fast again, ...')
hold('FourSeconds')
changeBldcMotorSpeed(motorControlDict, 'Slow')
print(' Now slow again, ...')
hold('FourSeconds')
print(' End testSetupMotor(), ...')
return
```
Program listing and sample output = https://penzu.com/p/95b30513
Pico 6WD using BLDC motors
I found it easy to expand my 4WD DC motor project to 6WD using BLDC motor. So I am starting off with an A4 size acrylic plate as car body, and Aslong 2535 BLDC motors.
I read my post of the result of careless wiring of BLDC motors, just to remind myself.
Brushless DC motor with built in controller - Asked 2021Oct13
Part 6 - Aslong BLDC Postmortem
There you go, BLDC 6WD
Testing 4WD, to be scaled up to 6WD
For prototyping, I am testing just 4 motors, instead of 6, so maximum risk is frying 4 motors, instead of 6.
The testing video: https://youtu.be/fKe3huM2Qqc
4WD BLDC motors encoder signals (FG)
Now I am checking out the encoder signals (FG) of the 4 BLDC motors. I powered the four motor with the same 12V PSU and use my quad channel scope to display the encoder output waveforms, as show below. I know the motor speed is 107 rpm. I need to work back the pulses per revolution.
Calibrating 4WD BLDC - Speed vs PWM duty cycle
Notes
4 motors with only power, no PWM, tested OK.
Now going to test PWM duty cycle vs speed, for one motor only.
IEEE Spectrum Smart Cars Than Think
I have been reading the above IEEE Spectrum articles for a couple of years, thinking that I might borrow ideas from them.
IEEE Cars That Think - IEEE Spectrum
Big Aslong BLDC Motor Control Signals and PWM vs Speed Calibration
Aslong BLDC JGB37-2525 Spec
Now I am studying the BLDC spec, before calibrating things.
Calibrating PWM duty cycle vs mot speed (FG (encoder) pulses per second)
Now I am using PWM 1kHz 90% duty cycle to measure the speed of 19 pulses per second
Range of duty cycle when controlling Aslong BLDC motor speed
I found the range is approximately 37% to 100%. I think 99% or 100% should be the same as DC without PWM (to verify later). I also found that the motor slows down as duty cycle goes low.
At around 40%, the motor moves very slowly, and at 37%, the motor comes to stand still.
Again, I need to read the FG (encoder pulses) to get the precise motor speed.
433MHz RF Communication among Pico 4WDs
Now I am thinking of letting the Pico 4WDs to talk to each other using 433MHz transmitter (FS1000A) and receivers (MX05V) The feasibility study is satisfactory. The Pico sends a text message through GP0 (uart0 TxD) and received from GP1 (uart0 RxD). The hardware setup is shown below:
4WD 433MHz FS1000A/MX05V RF Communication References
Transmitting and Receiving messages through RF433 using Raspberry Pico - RpiSE, Asked 2021oct21
Chat: https://chat.stackexchange.com/rooms/130758/discussion-between-tlfong01-and-antifa
HC12 UART 433MHz transceiver testing notes
JBtek Windows 8 Supported Debug Cable for Raspberry Pi USB Programming USB to TTL Serial Cable - Amazon US$7
PL2303XHD Datasheet - Prolific 2023
http://www.prolific.com.tw/UserFiles/files/ds_pl2303HXD_v1_4_4.pdf
The power pin provides 500mA directly from the USB port and the RX/TX pins are 3.3V level for interfacing with the most common 3.3V logic level chipsets
Windows XP/Vista/7 & Windows 8 supported, MacOS X; PL2303 TA. drivers on your computer and connect with a terminal program at 115200 baud
Red cable : +5V
Black cable : GND
Green cable : TXD
White cable : RXD
Yellow cable : RTS
Blue cable : CTS
RealTerm Configuring HC12 433MHz Transceiver Record
Pico 4WD BLDC Quad HC12 433MHz RF Transceiver Setup Notes
Dual HC12 RF transceiver setup notes
HC12 at RealTerm COM10 transceiving to/from HC12 at RealTerm COM9 Tested OK
Testing HC12 #1 at Pico 1’s uart0 transceiving HC12 #2 at same Pico 1’s uart1
Now I am going to test if two HC12’s (on the same bread board, separated by 1 cm), controlled by two UART’s (uart0, uart1) of the same Pico can transmit/receive at RF 433MHz without any problem.
Testing Plan
1. I first use RealTerm to check out that the two HC12's are set up with the same configuration as summarized below:
RealTerm COM10
AT+RX
OK+B9600
OK+RC001
OK+RP:+20dBm
OK+FU3
---
RealTerm COM9
AT+RX
OK+B9600
OK+RC001
OK+RP:+20dBm
OK+FU3
Then I will disconnect the two Windows UART to TTL adaptors (at COM10, COM9) from the two HC12’s.
I will now connect the same Pico’s uart0, uart1 wires to the two HC12s.
I will first test if Pico microPython can also setup/config the HC12’s
Then I will send “Hello World” from HC12 #0 at uart0 and see if this message can transmit in air at 433MHz to HC #2 at uart1.
HC12 Testing Program v22 Complete Listing
# hc12_test_v22.py tlfong01 2021nov04hkt1705
#
# Pico GP Pin Assignment
# GP0 = UART0 TxD - connect to HC12 #0 RxD
# GP1 = UART0 RxD - connect to HC12 #0 TxD
# GP4 = UART0 TxD - connect to HC12 #1 RxD
# GP5 = UART0 RxD - connect to HC12 #1 TxD
# GP2 = TC12 #0 set pin - connect to HC12 #0 setPin
# GP3 = TC12 #1 set pin - connect to HC12 #1 setPin
# Setup notes
# 1. To test UART serialloop back, short TxD pin to RxD pin
# 2. To test HC12 #0, (1) Connect uart0 TxD to HC12 RxD, (2) Connect uart0 RxD to HC12 #0 TxD
# 3. To set TC12 partmeters, connect SET pin to Low,
# 4. To perform normal transmit/receive half duplex communcation, connect SET pin to High
# References
# 1. MicroPython Class UART – duplex serial communication bus
# https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/library/machine.UART.html
# 2. General information about the RP2xxx port
# https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/rp2/general.html
# 3. Understanding and Implementing the HC-12 Wireless Transceiver Module - Mark Hughes, AllAboutCircuits, 2016nov02
# https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/projects/understanding-and-implementing-the-hc-12-wireless-transceiver-module/
# 4. HC-12 vs nRF24L01 modules - Robin66, AllAboutCircuits, 2019may08
# https://forum.allaboutcircuits.com/threads/hc-12-vs-nrf24l01-modules.159540/
# 5. HC-12 433MHz Transceiver 1km serial (Si4438) (Product Sheet, Tutorial) - ¥34
# https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=a1z1r.7974869.0.0.269c3ad4pAu1MO&id=636694630080
# 6. HC Tech (汇承) Official Web Site - HC Tech
# http://www.hc01.com/home
# 7. HC12 Datasheet/User Manual v2.6 - HCTech 2018jul11
# http://www.hc01.com/downloads/HC-12%20english%20datasheets.pdf
# 8. HC-12 433MHz RF Transciver Module (SI4438, 433MHZ, 1KM) - SmartPrototyping, US$12
# https://www.smart-prototyping.com/HC-12-Wireless-Transceiver-Module-SI4438-433MHz-1km - US$12
# 9. Si4438 Transceiver Datasheet - Silicon Labs
# https://www.silabs.com/documents/public/data-sheets/Si4438.pdf
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
from machine import UART, Pin
import utime
uart0 = UART(0, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(0), rx=Pin(1))
uart1 = UART(1, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(4), rx=Pin(5))
uartPortDict = \
{
'0': uart0,
'1': uart1,
}
def uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
uartPort.write(writeBytes)
return
def uartReadOld(uartPortNum, lengthReadBytes):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
readBytes = uartPort.read(lengthReadBytes)
return readBytes
def uartRead(uartPortNum):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
readBytes = uartPort.read()
return readBytes
def testUartLoopBackV09(uartPortNum):
print(' Begin testUartLoopBackV09(), ...')
print(' Remember to short TxD and RxD!!!')
print(' uartPortNum =', uartPortNum)
writeBytes = 'Hello World'
uartPortNum = 0
uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print(' writeBytes =', writeBytes)
utime.sleep(0.5)
readBytes = uartRead(uartPortNum)
print(' readBytes =', readBytes)
print(' End testUartLoopBackV09().')
return
def testUartListLoopBackV09(uartPortNumList):
print(' Begin testUartLoopBackV09(), ...')
print(' Remember to short TxD and RxD!!!')
for uartPortNum in uartPortNumList:
print(' uartPortNum =', uartPortNum)
writeBytes = 'Hello World'
uartPortNum = 0
uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print(' writeBytes =', writeBytes)
utime.sleep(0.5)
readBytes = uartRead(uartPortNum)
print(' readBytes =', readBytes)
print(' End testUartLoopBackV09().')
return
def testHc12ConfigV09(uartPortNum):
print('Begin testHc12ConfigV09(), ...')
testUartLoopBackV09(uartPortNum)
print('End testHc12ConfigV09(), ...')
return
def testHc12ListConfigV09(uartPortNumList):
print('Begin testHc12ListConfigV09(), ...')
testUartListLoopBackV09(uartPortNumList)
print('End testHc12ListConfigV09(), ...')
return
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Main ***
#testUartListLoopBackV09([0, 1])
testHc12ListConfigV09([0, 1])
# .END
''' *** Sample output tlfong01 2021nov04hkt1704 ***
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Begin testHc12ListConfigV09(), ...
Begin testUartLoopBackV09(), ...
Remember to short TxD and RxD!!!
uartPortNum = 0
writeBytes = Hello World
readBytes = b'Hello World'
uartPortNum = 1
writeBytes = Hello World
readBytes = b'Hello World'
End testUartLoopBackV09().
End testHc12ListConfigV09(), ...
>>>
'''
# *** End of sample output **
HC12 Parameter Setting Troubleshooting Notes
So I wrote the I thought a simple microPython program to test the following:
Surprisingly, I always read ‘None’ from GP1. I thought the input format was wrong. So I tried things like b’AT’, ‘AT’, bytes(‘AT’, utf_8) etc, but no luck. After spending a couple of hours trials and errors, reading manuals, I gave up, and decide to return to RealTerm which did smoothly write ‘AT’, and get back ‘OK’. So I recorded the RealTerm procedure and capture the one shot scope captures, as shown below:
Looking at the scope displays, I think one thing I missed is that I was not aware the there was a time lag between ‘AT’ and ‘OK’, so perhaps that is the reason the program missed the ‘OK’ return message.
/ to continue, …
Exceeding forum’s 32k work limit, therefore another reply.
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
from machine import Pin, UART
import utime
# *** UART GP pin assignment and setup/configuration ***
uart0 = UART(0, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(0), rx=Pin(1))
uart1 = UART(1, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(8), rx=Pin(9)) # Warning: GP 4, 5 seem broken
uartPortDict = \
{
'0': uart0,
'1': uart1,
}
# HC12 GP pin assignment and setup/configuration ***
hc12SetPinNum0 = 2
hc12SetPinNum1 = 3
hc12SetPin0 = Pin(hc12SetPinNum0, Pin.OUT)
hc12SetPin1 = Pin(hc12SetPinNum1, Pin.OUT)
def uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
uartPort.write(writeBytes)
return
def uartRead(uartPortNum):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
readBytes = uartPort.read()
return readBytes
def testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
print('\n Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...')
print(' uartPortNum =', uartPortNum)
uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print(' writeBytes =', writeBytes)
utime.sleep(0.5)
readBytes = uartRead(uartPortNum)
print(' readBytes =', readBytes)
print(' End testUartLoopBack().')
return
def testUartListLoopBack(uartPortNumList, writeBytes):
print(' Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...')
print(' Remember to short TxD and RxD!!!')
for uartPortNum in uartPortNumList:
testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print(' End testUartLoopBack().')
return
def testHc12Config(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
print('Begin testHc12Config(), ...')
testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print('End testHc12Config(), ...')
return
def testHc12ListConfig(uartPortNumList, writeBytes):
print('Begin testHc12ListConfig(), ...')
testHc12ListLoopBack(uartPortNumList, writeBytes)
print('End testHc12ListConfig(), ...')
return
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Main ***
#testUartListLoopBack([0, 1], bytes('Hello World', 'utf-8'))
#testHc12ListConfig([0, 1], bytes('AT', 'utf-8'))
testUartListLoopBack([0, 1], b'\0x41\0x54\r\n')
# .END
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
''' *** Sample output tlfong01 2021nov05hkt0925 ***
MicroPython v1.16 on 2021-06-18; Raspberry Pi Pico with RP2040
Type "help()" for more information.
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
Remember to short TxD and RxD!!!
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
uartPortNum = 0
writeBytes = b'\x00x41\x00x54\r\n'
readBytes = None
End testUartLoopBack().
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
uartPortNum = 1
writeBytes = b'\x00x41\x00x54\r\n'
readBytes = None
End testUartLoopBack().
End testUartLoopBack().
>>>
'''
# *** End of sample output **
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
Pico HC12 Debugging Notes
I found Pico GP 0, 1, and GP 16, 17 for uart0 always works. However GP14, 15 for uart0 does not work.
I also found nothing works for uart1 (GP 4, 5, or GP 8, 9)
I need to find another Pico to verify my test results.
# hc12_test_v28.py tlfong01 2021nov05hkt1614
#
# Setup notes
# 1. To test UART serialloop back, short TxD pin to RxD pin
# 2. To test HC12 #0, (1) Connect uart0 TxD to HC12 RxD, (2) Connect uart0 RxD to HC12 #0 TxD
# 3. To set TC12 partmeters, connect SET pin to Low,
# 4. To perform normal transmit/receive half duplex communcation, connect SET pin to High
# References
# 1. MicroPython Class UART – duplex serial communication bus
# https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/library/machine.UART.html
# 2. General information about the RP2xxx port
# https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/rp2/general.html
# 3. Understanding and Implementing the HC-12 Wireless Transceiver Module - Mark Hughes, AllAboutCircuits, 2016nov02
# https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/projects/understanding-and-implementing-the-hc-12-wireless-transceiver-module/
# 4. HC-12 vs nRF24L01 modules - Robin66, AllAboutCircuits, 2019may08
# https://forum.allaboutcircuits.com/threads/hc-12-vs-nrf24l01-modules.159540/
# 5. HC-12 433MHz Transceiver 1km serial (Si4438) (Product Sheet, Tutorial) - ¥34
# https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=a1z1r.7974869.0.0.269c3ad4pAu1MO&id=636694630080
# 6. HC Tech (汇承) Official Web Site - HC Tech
# http://www.hc01.com/home
# 7. HC12 Datasheet/User Manual v2.6 - HCTech 2018jul11
# http://www.hc01.com/downloads/HC-12%20english%20datasheets.pdf
# 8. HC-12 433MHz RF Transciver Module (SI4438, 433MHZ, 1KM) - SmartPrototyping, US$12
# https://www.smart-prototyping.com/HC-12-Wireless-Transceiver-Module-SI4438-433MHz-1km - US$12
# 9. Si4438 Transceiver Datasheet - Silicon Labs
# https://www.silabs.com/documents/public/data-sheets/Si4438.pdf
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
from machine import Pin, UART
import utime
# *** UART GP pin assignment and setup/configuration ***
uart0 = UART(0, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(0), rx=Pin(1)) # good
#uart0 = UART(0, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(16), rx=Pin(17)) # good
#uart0 = UART(0, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(12), rx=Pin(13)) # bad
uart1 = UART(1, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(4), rx=Pin(5)) # bad
#uart1 = UART(1, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(8), rx=Pin(9)) # bad
uartPortDict = \
{
'0': uart0,
'1': uart1,
}
# HC12 GP pin assignment and setup/configuration ***
hc12SetPinNum0 = 2
hc12SetPinNum1 = 3
hc12SetPin0 = Pin(hc12SetPinNum0, Pin.OUT)
hc12SetPin1 = Pin(hc12SetPinNum1, Pin.OUT)
def uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
uartPort.write(writeBytes)
return
def uartRead(uartPortNum):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
utime.sleep(0.1)
uartAny = uartPort.any()
print(' uartAny =', uartAny)
readBytes = uartPort.read()
return readBytes
def testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
print('\n Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...')
print(' uartPortNum =', uartPortNum)
uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print(' writeBytes =', writeBytes)
utime.sleep(0.5)
readBytes = uartRead(uartPortNum)
print(' readBytes =', readBytes)
print(' End testUartLoopBack().\n')
return
def testUartListLoopBack(uartPortNumList, writeBytes):
print('\nBegin testUartLoopBack(), ...')
print(' Remember to short TxD and RxD!!!')
for uartPortNum in uartPortNumList:
testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print('End testUartLoopBack().')
return
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Main ***
testUartListLoopBack([0], 'AT') # 'AT' without \r\n works
testUartListLoopBack([0], 'AT\r\n') # 'AT' with \r\n also works
# .END
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
''' *** Sample output tlfong01 2021nov05hkt0925 ***
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
Remember to short TxD and RxD!!!
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
uartPortNum = 0
writeBytes = AT
uartAny = 4
readBytes = b'OK\r\n'
End testUartLoopBack().
End testUartLoopBack().
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
Remember to short TxD and RxD!!!
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
uartPortNum = 0
writeBytes = AT
uartAny = 4
readBytes = b'OK\r\n'
End testUartLoopBack().
End testUartLoopBack().
>>>
'''
# *** End of sample output **
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========/
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
AT+RX Also OK
readBytes = b’OK+B9600\r\nOK+RC001\r\nOK+RP:+20dBm\r\nOK+FU3\r\n’
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
Remember to short TxD and RxD!!!
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
uartPortNum = 0
writeBytes = AT+RX
uartAny = 42
readBytes = b'OK+B9600\r\nOK+RC001\r\nOK+RP:+20dBm\r\nOK+FU3\r\n'
End testUartLoopBack().
End testUartLoopBack().
HC12 uart1 GP4, 5, GP 8,9 not working problem solved!!!
So I setup another Pico at COM7 and tried everything again. This time all is well,
uart1, using GP4,5 or GP8,9 work smoothly.
So I concluded that the first Pico’s GP4,5, GP8,9 are faulty.
# hc12_test_v30.py tlfong01 2021nov06hkt1501
#
# Pico GP Pin Assignment
# GP0 = UART0 TxD - connect to HC12 #0 RxD
# GP1 = UART0 RxD - connect to HC12 #0 TxD
# GP4 = UART0 TxD - connect to HC12 #1 RxD
# GP5 = UART0 RxD - connect to HC12 #1 TxD
# GP8 = UART0 TxD - connect to HC12 #1 RxD
# GP9 = UART0 RxD - connect to HC12 #1 TxD
# GP2 = TC12 #0 set pin - connect to HC12 #0 setPin
# GP3 = TC12 #1 set pin - connect to HC12 #1 setPin
# Setup notes
# 1. To test UART serialloop back, short TxD pin to RxD pin
# 2. To test HC12 #0, (1) Connect uart0 TxD to HC12 RxD, (2) Connect uart0 RxD to HC12 #0 TxD
# 3. To set TC12 partmeters, connect SET pin to Low,
# 4. To perform normal transmit/receive half duplex communcation, connect SET pin to High
# References
# 1. MicroPython Class UART – duplex serial communication bus
# https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/library/machine.UART.html
# 2. General information about the RP2xxx port
# https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/rp2/general.html
# 3. Understanding and Implementing the HC-12 Wireless Transceiver Module - Mark Hughes, AllAboutCircuits, 2016nov02
# https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/projects/understanding-and-implementing-the-hc-12-wireless-transceiver-module/
# 4. HC-12 vs nRF24L01 modules - Robin66, AllAboutCircuits, 2019may08
# https://forum.allaboutcircuits.com/threads/hc-12-vs-nrf24l01-modules.159540/
# 5. HC-12 433MHz Transceiver 1km serial (Si4438) (Product Sheet, Tutorial) - ¥34
# https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=a1z1r.7974869.0.0.269c3ad4pAu1MO&id=636694630080
# 6. HC Tech (汇承) Official Web Site - HC Tech
# http://www.hc01.com/home
# 7. HC12 Datasheet/User Manual v2.6 - HCTech 2018jul11
# http://www.hc01.com/downloads/HC-12%20english%20datasheets.pdf
# 8. HC-12 433MHz RF Transciver Module (SI4438, 433MHZ, 1KM) - SmartPrototyping, US$12
# https://www.smart-prototyping.com/HC-12-Wireless-Transceiver-Module-SI4438-433MHz-1km - US$12
# 9. Si4438 Transceiver Datasheet - Silicon Labs
# https://www.silabs.com/documents/public/data-sheets/Si4438.pdf
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
from machine import Pin, UART
import utime
# *** UART GP pin assignment and setup/configuration ***
uart0 = UART(0, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(0), rx=Pin(1))
#uart1 = UART(1, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(4), rx=Pin(5))
uart1 = UART(1, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(8), rx=Pin(9))
uartPortDict = \
{
'0': uart0,
'1': uart1,
}
# HC12 GP pin assignment and setup/configuration ***
hc12SetPinNum0 = 2
hc12SetPinNum1 = 3
hc12SetPin0 = Pin(hc12SetPinNum0, Pin.OUT)
hc12SetPin1 = Pin(hc12SetPinNum1, Pin.OUT)
def uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
uartPort.write(writeBytes)
return
def uartRead(uartPortNum):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
uartAny = uartPort.any()
print(' uartAny =', uartAny)
readBytes = uartPort.read()
return readBytes
def testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
print('\n Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...')
print(' uartPortNum =', uartPortNum)
uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print(' writeBytes =', writeBytes)
utime.sleep(0.5)
readBytes = uartRead(uartPortNum)
print(' readBytes =', readBytes)
print(' End testUartLoopBack().')
return
def testUartListLoopBack(uartPortNumList, writeBytes):
print(' Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...')
print(' Remember to short TxD and RxD!!!')
for uartPortNum in uartPortNumList:
testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print(' End testUartLoopBack().')
return
def testHc12Config(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
print('Begin testHc12Config(), ...')
testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print('End testHc12Config(), ...')
return
def testHc12ListConfig(uartPortNumList, writeBytes):
print('Begin testHc12ListConfig(), ...')
testHc12ListLoopBack(uartPortNumList, writeBytes)
print('End testHc12ListConfig(), ...')
return
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Main ***
testUartListLoopBack([0, 1], 'AT')
# .END
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
''' *** Sample output tlfong01 2021nov06hkt1501 ***
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
Remember to short TxD and RxD!!!
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
uartPortNum = 0
writeBytes = AT
uartAny = 4
readBytes = b'OK\r\n'
End testUartLoopBack().
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
uartPortNum = 1
writeBytes = AT
uartAny = 4
readBytes = b'OK\r\n'
End testUartLoopBack().
End testUartLoopBack().
>>>
'''
# *** End of sample output **
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
Pico #2 uart0 (GP0, 1) , uart1 (GP 4,5, GP 8,9) HC12 #1, #2 Testing OK notes
Testing OK a new Pico uart0 (GP0,1) uart1 (GP8,9) and 4 HC12’s
Switch mode power supply unit (SMPSU) 12V in 3V3 2A out for the Pico 4WD
Now that testing sending “AT” receives “OK”, means the HC12 transceiver talks with Pico without any problem, next step is to write function to do the following things:
Assign channel number, so that HC12’s can communcate with one another, or broadcast to HC12’s set to the same channle number.
Test if two Pico with its own HC12 (and 4WD) can do serial half duplex communcation with simple test messages such as
“Everybody on this 433MHz Channel #007 go forward”,
“Everybody on this 433MHz Channel #004 stops” etc.
Functions to set HC12 configuration tested OK
Example call:
testHc12ListConfigV02([0], ‘SetChannel#2’)
Full program listing (comments removed) with sample output
# hc12_test_v36.py tlfong01 2021nov08hkt1029
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
from machine import Pin, UART
import utime
# *** UART GP pin assignment and setup/configuration ***
uart0 = UART(0, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(0), rx=Pin(1))
#uart1 = UART(1, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(4), rx=Pin(5)) ### often not working, avoid this for uart1
uart1 = UART(1, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(8), rx=Pin(9))
uartPortDict = \
{
'0': uart0,
'1': uart1,
}
# HC12 GP pin assignment and setup/configuration ***
hc12SetPinNum0 = 2
hc12SetPinNum1 = 3
hc12SetPin0 = Pin(hc12SetPinNum0, Pin.OUT)
hc12SetPin1 = Pin(hc12SetPinNum1, Pin.OUT)
def uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
uartPort.write(writeBytes)
return
def uartRead(uartPortNum):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
uartAny = uartPort.any()
print(' uartAny =', uartAny)
readBytes = uartPort.read()
return readBytes
def testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
print(' Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...')
print(' uartPortNum =', uartPortNum)
uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print(' writeBytes =', writeBytes)
utime.sleep(0.5)
readBytes = uartRead(uartPortNum)
print(' readBytes =', readBytes)
print(' End testUartLoopBack().')
return
def testUartListLoopBack(uartPortNumList, writeBytes):
print(' Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...')
print(' Remember to short TxD and RxD!!!')
for uartPortNum in uartPortNumList:
testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print(' End testUartLoopBack().')
return
def testHc12Config(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
print('Begin testHc12Config(), ...')
testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print('End testHc12Config(), ...')
return
def testHc12ListConfig(uartPortNumList, writeBytes):
print('Begin testHc12ListConfig(), ... hc12_test_v35_2021nov0601.py tlfong01 2021nov07hkt2148')
for uartPortNum in uartPortNumList:
testHc12Config(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print('End testHc12ListConfig().')
return
def testHc12ListConfigV02(uartPortNumList, configParameterName):
print('Begin testHc12ListConfig(), ... hc12_test_v35_2021nov0601.py tlfong01 2021nov07hkt2148')
writeBytes = hc12ConfigParameterDict[configParameterName]
print('configParameterName =', configParameterName)
for uartPortNum in uartPortNumList:
testHc12Config(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print('End testHc12ListConfig().')
return
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
hc12ConfigParameterDict = \
{
'CheckAtReply' : 'AT',
'CheckAllConfigSetting' : 'AT+RX',
'SetChannel#1' : 'AT+C001',
'SetChannel#2' : 'AT+C002',
}
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Main ***
# ***
#testUartListLoopBack([0], 'AT') ### Only test uart0 for HC12 #0
#testUartListLoopBack([0, 1], 'AT') ### Test both uart0 for HC12 #0, and uart1 for HC12 #1
#testHc12Config(0, 'AT')
#testHc12ListConfig([0, 1], 'AT')
#testHc12ListConfig([0, 1], 'AT+RX')
testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'CheckAtReply')
testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'CheckAllConfigSetting')
testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'SetChannel#1')
testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'SetChannel#2')
# .END
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
''' *** Sample output tlfong01 2021nov08hkt1049 ***
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Begin testHc12ListConfig(), ... hc12_test_v35_2021nov0601.py tlfong01 2021nov07hkt2148
configParameterName = CheckAtReply
Begin testHc12Config(), ...
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
uartPortNum = 0
writeBytes = AT
uartAny = 4
readBytes = b'OK\r\n'
End testUartLoopBack().
End testHc12Config(), ...
End testHc12ListConfig().
Begin testHc12ListConfig(), ... hc12_test_v35_2021nov0601.py tlfong01 2021nov07hkt2148
configParameterName = CheckAllConfigSetting
Begin testHc12Config(), ...
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
uartPortNum = 0
writeBytes = AT+RX
uartAny = 42
readBytes = b'OK+B9600\r\nOK+RC002\r\nOK+RP:+20dBm\r\nOK+FU3\r\n'
End testUartLoopBack().
End testHc12Config(), ...
End testHc12ListConfig().
Begin testHc12ListConfig(), ... hc12_test_v35_2021nov0601.py tlfong01 2021nov07hkt2148
configParameterName = SetChannel#1
Begin testHc12Config(), ...
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
uartPortNum = 0
writeBytes = AT+C001
uartAny = 9
readBytes = b'OK+C001\r\n'
End testUartLoopBack().
End testHc12Config(), ...
End testHc12ListConfig().
Begin testHc12ListConfig(), ... hc12_test_v35_2021nov0601.py tlfong01 2021nov07hkt2148
configParameterName = SetChannel#2
Begin testHc12Config(), ...
Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...
uartPortNum = 0
writeBytes = AT+C002
uartAny = 9
readBytes = b'OK+C002\r\n'
End testUartLoopBack().
End testHc12Config(), ...
End testHc12ListConfig().
>>>
'''
# *** End of sample output **
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
Second Pico smart car’s HC12 433MHz transceiver pair also tested OK
Second Pico smart car’s HC12 pair tested OK. The refactored wiring is simple and easy. Next step is to config each HC12 transceiver pair and see if they can talk serial half duplex 9600bd81over 433MHz channel.
(2 x Pico) + (4 x HC12) 433MHz Xmit/Recv Test Plan V0.1
Now I planning to test two Pico 4WDs together communicating to each other using HT12 433MHz transcvivers. Each Pico 4WD with HC12 has been tested OK on parameter setting mode, using microPython. RF 433MHz communication has also been tested, using RealCom. Next is to use Thonny MicroPython to do both parameter setting, and RF communication.
4WD with GPS and LIDAR
I jealously read this morning that some guys are building a food delivery robot are building a robot car with GPS and LIDAR. I am thinking of also adding similar stuff to my not so smart robot, so not to loose too much face.
Local engineer helps develop food delivery robot - Morrowcountysentinel, 2021nov10
Dual Pico, Quad HC12 Communication Testing Notes
Now I have the following setup:
Two Pico’s, one controlled by Windows Thonny MicroPython COM7, the other COM11.
Each Pico controls two HC12’s, one by uart0, the other by uart1.
Now my testing is in two steps:
3.1 Using Pico #2 only, transmit a text message to HC12 #3 (uart0), and see if HC#4 (uart1), over the same 433MHz Channel #1, can receive it.
3.2. Using two Pico’s: Pico #1 sends a text message to HC#1, and see if Pcio #2 HC #3 can receive the message.
Test results for 3.1 is OK. Next test is 3.2.
/ to continue, …
Test 3.1 program listing with sample output
# hc12_test_v46.py tlfong01 2021nov12hkt1740
#
# Pico GP Pin Assignment
# GP0 = UART0 TxD - connect to HC12 #0 RxD
# GP1 = UART0 RxD - connect to HC12 #0 TxD
# GP8 = UART0 TxD - connect to HC12 #1 RxD
# GP9 = UART0 RxD - connect to HC12 #1 TxD
# GP2 = TC12 #0 set pin - connect to HC12 #0 setPin
# GP3 = TC12 #1 set pin - connect to HC12 #1 setPin
# Debugging notes
# GP4, GP5 for uart0 never works
# Setup notes
# 1. To test UART serialloop back, short TxD pin to RxD pin
# 2. To test HC12 #0, (1) Connect uart0 TxD to HC12 RxD, (2) Connect uart0 RxD to HC12 #0 TxD
# 3. To set TC12 partmeters, connect SET pin to Low,
# 4. To perform normal transmit/receive half duplex communcation, connect SET pin to High
# Troubleshooting notes
# 1. Use RealTerm (or miniCom etc) to do offline testing, without Pico
# 2. Remember to short Pico ground with HC12 ground get make a COMMON GROUND
# References
# 1. MicroPython Class UART – duplex serial communication bus
# https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/library/machine.UART.html
# 2. General information about the RP2xxx port
# https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/rp2/general.html
# 3. Understanding and Implementing the HC-12 Wireless Transceiver Module - Mark Hughes, AllAboutCircuits, 2016nov02
# https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/projects/understanding-and-implementing-the-hc-12-wireless-transceiver-module/
# 4. HC-12 vs nRF24L01 modules - Robin66, AllAboutCircuits, 2019may08
# https://forum.allaboutcircuits.com/threads/hc-12-vs-nrf24l01-modules.159540/
# 5. HC-12 433MHz Transceiver 1km serial (Si4438) (Product Sheet, Tutorial) - ¥34
# https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=a1z1r.7974869.0.0.269c3ad4pAu1MO&id=636694630080
# 6. HC Tech (汇承) Official Web Site - HC Tech
# http://www.hc01.com/home
# 7. HC12 Datasheet/User Manual v2.6 - HCTech 2018jul11
# http://www.hc01.com/downloads/HC-12%20english%20datasheets.pdf
# 8. HC-12 433MHz RF Transciver Module (SI4438, 433MHZ, 1KM) - SmartPrototyping, US$12
# https://www.smart-prototyping.com/HC-12-Wireless-Transceiver-Module-SI4438-433MHz-1km - US$12
# 9. Si4438 Transceiver Datasheet - Silicon Labs
# https://www.silabs.com/documents/public/data-sheets/Si4438.pdf
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
from machine import Pin, UART
import utime
# *** UART GP pin assignment and setup/configuration ***
uart0 = UART(0, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(0), rx=Pin(1))
uart1 = UART(1, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(8), rx=Pin(9))
uartPortDict = \
{
'0': uart0,
'1': uart1,
}
# HC12 GP pin assignment and setup/configuration ***
hc12SetupPinNum0 = 2
hc12SetupPinNum1 = 3
hc12SetupPin0 = Pin(hc12SetupPinNum0, Pin.OUT)
hc12SetupPin1 = Pin(hc12SetupPinNum1, Pin.OUT)
hc12SetupPinDict = \
{
'0': hc12SetupPin0,
'1': hc12SetupPin1,
}
hc12ConfigParameterDict = \
{
'CheckAtReply' : 'AT',
'CheckAllConfigSetting' : 'AT+RX',
'SetChannel#1' : 'AT+C001',
'SetChannel#2' : 'AT+C002',
}
hc12TextMsgDict = \
{
'HelloWorld' : 'Hello World',
'HelloPico0' : 'Hello Pico #0',
'HelloPico1' : 'Hello Pico #1',
'MoveForward' : 'Move Forward',
'MoveBackward' : 'Move Backward',
'Stop' : 'Stop'
}
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Uart Functions ***
def uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
uartPort.write(writeBytes)
return
def uartRead(uartPortNum):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
uartAny = uartPort.any()
print(' uartAny =', uartAny)
readBytes = uartPort.read()
return readBytes
# *** test uart loopback functions ***
def testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
print(' Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...')
print(' uartPortNum =', uartPortNum)
uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print(' writeBytes =', writeBytes)
utime.sleep(0.5)
readBytes = uartRead(uartPortNum)
print(' readBytes =', readBytes)
print(' End testUartLoopBack().')
return
def testUartListLoopBack(uartPortNumList, writeBytes):
print(' Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...')
print(' Remember to short TxD and RxD!!!')
for uartPortNum in uartPortNumList:
testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print(' End testUartLoopBack().')
return
# *** Test Functions ***
#testUartListLoopBack([0], 'AT') ### Only test uart0 for HC12 #0
#testUartListLoopBack([0, 1], 'AT') ### Test both uart0 for HC12 #0, and uart1 for HC12 #1
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** HC12 Functions ***
def setHc12ConfigMode(uartPortNum):
hc12SetupPin = hc12SetupPinDict[str(uartPortNum)]
hc12SetupPin.low()
return
def setHc12CommunicationMode(uartPortNum):
hc12SetupPin = hc12SetupPinDict[str(uartPortNum)]
hc12SetupPin.high()
return
# *** HC12 Test Functions ***
def testHc12Config(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
print('Begin testHc12Config(), ...')
testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print('End testHc12Config(), ...')
return
def testHc12ListConfig(uartPortNumList, writeBytes):
print('Begin testHc12ListConfigOperation(), ...')
for uartPortNum in uartPortNumList:
setHc12ConfigMode(uartPortNum)
testHc12Config(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print('End testHc12ListConfigOperation().')
return
def testDualHc12Loopback(xmitUartPortNum, recvUartPortNum, testXmitMsg):
print('Begin testHc12Communication(), ...')
# *** Set both HC12 communication mode, ...')
print(' Begin set both HC12s communication mode, ...')
setHc12CommunicationMode(xmitUartPortNum)
setHc12CommunicationMode(recvUartPortNum)
print(' End set both HC12s communication mode.')
print(' Begin transmit message, ...')
print(' xmitBytes to xmitUartPort =', testXmitMsg)
uartWrite(xmitUartPortNum, testXmitMsg)
print(' End transmit message.')
# *** uart1 recv test message ***
print(' Begin receive message, ...')
utime.sleep(0.1)
recvBytes = uartRead(recvUartPortNum)
print(' recvBytes from receUartPort =', recvBytes)
print(' End receive msaages.')
print('End testHc12Communication(), ...')
return
# *** Sample Tests ***
#testHc12Config(0, 'AT')
#testHc12ListConfig([0, 1], 'AT')
#testHc12ListConfig([0, 1], 'AT+RX')
#testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'CheckAtReply')
#testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'CheckAllConfigSetting')
#testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'SetChannel#1')
#testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'SetChannel#2')
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Main ***
#testHc12ListConfig([0, 1], 'AT')
testDualHc12Loopback(xmitUartPortNum = 0, recvUartPortNum = 1, testXmitMsg = 'Hello Pico #2')
# .END
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
''' *** Sample output tlfong01 2021nov12hkt1739 ***
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Begin testHc12Communication(), ...
Begin set both HC12s communication mode, ...
End set both HC12s communication mode.
Begin transmit message, ...
xmitBytes to xmitUartPort = Hello Pico #2
End transmit message.
Begin receive message, ...
uartAny = 13
recvBytes from receUartPort = b'Hello Pico #2'
End receive msaages.
End testHc12Communication(), ...
>>>
'''
# *** End of sample output **
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
Pico #1 sends message to Pico #2 through same 433MHz Channel
Now I am going to test Pico #1 sending a text message to Pico #2 on the same 433MHz channel. I need to change the Thonny > Tools > Option >
> Disable > Allow only single Thonny instance
Testing Pico #1 and Pico #2 at the same time, both doing uart0 sending, uart1 receiving. Results = OK.
Testing Pico #1 transmitting text message to Pico #2 OK
Transmit program
# hc12_v50.py tlfong01 2021nov13hkt1752
#
# Pico GP Pin Assignment
# GP0 = UART0 TxD - connect to HC12 #0 RxD
# GP1 = UART0 RxD - connect to HC12 #0 TxD
# GP8 = UART0 TxD - connect to HC12 #1 RxD
# GP9 = UART0 RxD - connect to HC12 #1 TxD
# GP2 = TC12 #0 set pin - connect to HC12 #0 setPin
# GP3 = TC12 #1 set pin - connect to HC12 #1 setPin
# Debugging notes
# GP4, GP5 for uart0 never works
# Setup notes
# 1. To test UART serialloop back, short TxD pin to RxD pin
# 2. To test HC12 #0, (1) Connect uart0 TxD to HC12 RxD, (2) Connect uart0 RxD to HC12 #0 TxD
# 3. To set TC12 partmeters, connect SET pin to Low,
# 4. To perform normal transmit/receive half duplex communcation, connect SET pin to High
# Troubleshooting notes
# 1. Use RealTerm (or miniCom etc) to do offline testing, without Pico
# 2. Remember to short Pico ground with HC12 ground get make a COMMON GROUND
# References
# 1. MicroPython Class UART – duplex serial communication bus
# https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/library/machine.UART.html
# 2. General information about the RP2xxx port
# https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/rp2/general.html
# 3. Understanding and Implementing the HC-12 Wireless Transceiver Module - Mark Hughes, AllAboutCircuits, 2016nov02
# https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/projects/understanding-and-implementing-the-hc-12-wireless-transceiver-module/
# 4. HC-12 vs nRF24L01 modules - Robin66, AllAboutCircuits, 2019may08
# https://forum.allaboutcircuits.com/threads/hc-12-vs-nrf24l01-modules.159540/
# 5. HC-12 433MHz Transceiver 1km serial (Si4438) (Product Sheet, Tutorial) - ¥34
# https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=a1z1r.7974869.0.0.269c3ad4pAu1MO&id=636694630080
# 6. HC Tech (汇承) Official Web Site - HC Tech
# http://www.hc01.com/home
# 7. HC12 Datasheet/User Manual v2.6 - HCTech 2018jul11
# http://www.hc01.com/downloads/HC-12%20english%20datasheets.pdf
# 8. HC-12 433MHz RF Transciver Module (SI4438, 433MHZ, 1KM) - SmartPrototyping, US$12
# https://www.smart-prototyping.com/HC-12-Wireless-Transceiver-Module-SI4438-433MHz-1km - US$12
# 9. Si4438 Transceiver Datasheet - Silicon Labs
# https://www.silabs.com/documents/public/data-sheets/Si4438.pdf
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
from machine import Pin, UART
import utime
# *** UART GP pin assignment and setup/configuration ***
uart0 = UART(0, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(0), rx=Pin(1))
uart1 = UART(1, baudrate = 9600, tx=Pin(8), rx=Pin(9))
uartPortDict = \
{
'0': uart0,
'1': uart1,
}
# HC12 GP pin assignment and setup/configuration ***
hc12SetupPinNum0 = 2
hc12SetupPinNum1 = 3
hc12SetupPin0 = Pin(hc12SetupPinNum0, Pin.OUT)
hc12SetupPin1 = Pin(hc12SetupPinNum1, Pin.OUT)
hc12SetupPinDict = \
{
'0': hc12SetupPin0,
'1': hc12SetupPin1,
}
hc12ConfigParameterDict = \
{
'CheckAtReply' : 'AT',
'CheckAllConfigSetting' : 'AT+RX',
'SetChannel#1' : 'AT+C001',
'SetChannel#2' : 'AT+C002',
}
hc12TextMsgDict = \
{
'HelloWorld' : 'Hello World',
'HelloPico0' : 'Hello Pico #0',
'HelloPico1' : 'Hello Pico #1',
'MoveForward' : 'Move Forward',
'MoveBackward' : 'Move Backward',
'Stop' : 'Stop'
}
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Uart Functions ***
def uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
uartPort.write(writeBytes)
return
def uartRead(uartPortNum):
uartPort = uartPortDict[str(uartPortNum)]
uartAny = uartPort.any()
print(' uartAny =', uartAny)
readBytes = uartPort.read()
return readBytes
# *** test uart loopback functions ***
def testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
print(' Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...')
print(' uartPortNum =', uartPortNum)
uartWrite(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print(' writeBytes =', writeBytes)
utime.sleep(0.5)
readBytes = uartRead(uartPortNum)
print(' readBytes =', readBytes)
print(' End testUartLoopBack().')
return
def testUartListLoopBack(uartPortNumList, writeBytes):
print(' Begin testUartLoopBack(), ...')
print(' Remember to short TxD and RxD!!!')
for uartPortNum in uartPortNumList:
testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print(' End testUartLoopBack().')
return
# *** Test Functions ***
#testUartListLoopBack([0], 'AT') ### Only test uart0 for HC12 #0
#testUartListLoopBack([0, 1], 'AT') ### Test both uart0 for HC12 #0, and uart1 for HC12 #1
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** HC12 Functions ***
def setHc12ConfigMode(uartPortNum):
hc12SetupPin = hc12SetupPinDict[str(uartPortNum)]
hc12SetupPin.low()
return
def setHc12CommMode(uartPortNum):
hc12SetupPin = hc12SetupPinDict[str(uartPortNum)]
hc12SetupPin.high()
return
# *** HC12 Test Functions ***
def testHc12Config(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
print('Begin testHc12Config(), ...')
testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print('End testHc12Config(), ...')
return
def testHc12ListConfig(uartPortNumList, writeBytes):
print('Begin testHc12ListConfigOperation(), ...')
for uartPortNum in uartPortNumList:
setHc12ConfigMode(uartPortNum)
testHc12Config(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print('End testHc12ListConfigOperation().')
return
def testDualHc12Loopback(xmitUartPortNum, recvUartPortNum, testXmitMsg):
print('Begin testHc12Communication(), ...')
# *** Set both HC12 communication mode, ...')
print(' Begin set both HC12s communication mode, ...')
setHc12CommMode(xmitUartPortNum)
setHc12CommMode(recvUartPortNum)
print(' End set both HC12s communication mode.')
print(' Begin transmit message, ...')
print(' xmitBytes =', testXmitMsg)
uartWrite(xmitUartPortNum, testXmitMsg)
print(' End transmit message.')
# *** uart1 recv test message ***
print(' Begin receive message, ...')
utime.sleep(0.1)
recvBytes = uartRead(recvUartPortNum)
print(' recvBytes =', recvBytes)
print(' End receive msaages.')
print('End testHc12Communication(), ...')
return
def testPico1TransmitTextMsgEverySecond():
print('Begin testPico1TransmitTextMsgEverySecond(), ...')
# *** Set both HC12 communication mode, ...')
print(' Begin set HC12 #1 communication mode, ...')
uartPortNum = 0
setHc12CommMode(uartPortNum = 0)
print(' End set HC12 #1 communication mode.')
print(' Begin transmit message, ...')
for count in range(100000):
testXmitMsg = str(count) + ' Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg'
print(' xmitBytes =', testXmitMsg)
uartWrite(uartPortNum, testXmitMsg)
utime.sleep(1)
print(' End transmit message.')
print('End testPico1TransmitTextMsgEverySecond(), ...')
return
# *** Sample Tests ***
#testHc12Config(0, 'AT')
#testHc12ListConfig([0, 1], 'AT')
#testHc12ListConfig([0, 1], 'AT+RX')
#testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'CheckAtReply')
#testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'CheckAllConfigSetting')
#testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'SetChannel#1')
#testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'SetChannel#2')
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Main ***
#testHc12ListConfig([0, 1], 'AT')
#testDualHc12Loopback(xmitUartPortNum = 0, recvUartPortNum = 1, \
# testXmitMsg = 'Pico #1 at COM 11, uart0 transmitting, ...')
testPico1TransmitTextMsgEverySecond()
# .END
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
''' Sample output tlfong 1021nov13hkt1930
xmitBytes = 990 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg
xmitBytes = 991 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg
xmitBytes = 992 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg
xmitBytes = 993 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg
xmitBytes = 994 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg
xmitBytes = 995 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg
xmitBytes = 996 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg
xmitBytes = 997 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg
xmitBytes = 998 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg
xmitBytes = 999 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg
xmitBytes = 1000 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg
# *** End of sample output **
'''
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ==
Receive Program
# *** HC12 Functions ***
def setHc12ConfigMode(uartPortNum):
hc12SetupPin = hc12SetupPinDict[str(uartPortNum)]
hc12SetupPin.low()
return
def setHc12CommMode(uartPortNum):
hc12SetupPin = hc12SetupPinDict[str(uartPortNum)]
hc12SetupPin.high()
return
# *** HC12 Test Functions ***
def testHc12Config(uartPortNum, writeBytes):
print('Begin testHc12Config(), ...')
testUartLoopBack(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print('End testHc12Config(), ...')
return
def testHc12ListConfig(uartPortNumList, writeBytes):
print('Begin testHc12ListConfigOperation(), ...')
for uartPortNum in uartPortNumList:
setHc12ConfigMode(uartPortNum)
testHc12Config(uartPortNum, writeBytes)
print('End testHc12ListConfigOperation().')
return
def testDualHc12Loopback(xmitUartPortNum, recvUartPortNum, testXmitMsg):
print('Begin testHc12Communication(), ...')
# *** Set both HC12 communication mode, ...')
print(' Begin set both HC12s communication mode, ...')
setHc12CommMode(xmitUartPortNum)
setHc12CommMode(recvUartPortNum)
print(' End set both HC12s communication mode.')
print(' Begin transmit message, ...')
print(' xmitBytes =', testXmitMsg)
uartWrite(xmitUartPortNum, testXmitMsg)
print(' End transmit message.')
# *** uart1 recv test message ***
print(' Begin receive message, ...')
utime.sleep(0.1)
recvBytes = uartRead(recvUartPortNum)
print(' recvBytes =', recvBytes)
print(' End receive msaages.')
print('End testHc12Communication(), ...')
return
def testPico2ReceiveTextMsgEverySecond():
print('Begin testPico2ReceiveTextMsgEverySecond(), ...')
# *** Set both HC12 communication mode, ...')
print(' Begin set HC12 #1 communication mode, ...')
uartPortNum = 0
setHc12CommMode(uartPortNum = 0)
print(' End set HC12 #1 communication mode.')
print(' Begin receive message, ...')
for count in range(100000):
recvMsg = uartRead(uartPortNum)
print(' recvBytes =', recvMsg)
utime.sleep(1)
print(' End transmit message.')
print('End testPico2ReceiveTextMsgEverySecond(), ...')
return
# *** Sample Tests ***
#testHc12Config(0, 'AT')
#testHc12ListConfig([0, 1], 'AT')
#testHc12ListConfig([0, 1], 'AT+RX')
#testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'CheckAtReply')
#testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'CheckAllConfigSetting')
#testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'SetChannel#1')
#testHc12ListConfigV02([0], 'SetChannel#2')
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Main ***
#testHc12ListConfig([0, 1], 'AT')
#testDualHc12Loopback(xmitUartPortNum = 0, recvUartPortNum = 1, \
# testXmitMsg = 'Pico #2 at COM 7, uart0 transmitting, ...')
testPico2ReceiveTextMsgEverySecond()
# .END
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
''' Sample output tlfong01 2021nov13hkt1932
recvBytes = b'1075 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg'
uartAny = 46
recvBytes = b'1076 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg'
uartAny = 46
recvBytes = b'1077 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg'
uartAny = 46
recvBytes = b'1078 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg'
uartAny = 43
recvBytes = b'0 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg'
uartAny = 43
recvBytes = b'1 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg'
uartAny = 43
recvBytes = b'2 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg'
uartAny = 43
recvBytes = b'3 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg'
uartAny = 43
recvBytes = b'4 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg'
uartAny = 43
recvBytes = b'5 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg'
uartAny = 43
recvBytes = b'6 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg'
uartAny = 43
recvBytes = b'7 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg'
uartAny = 43
recvBytes = b'8 Pico #1 HC12 #1 (uart0) transmit this msg'
uartAny = 43
'''
# *** End of sample output **
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
BlueTooth Android Phone Accelerometer 4WD
So I more or less completed the task of using HC12 433MHz transceiver to let my three Pico 4WD to talk to each other. But then this morning I read MagPi that a guy using an Android phone with built in accelerometer to control a 4WD with BlueTooth module. I am getting jealous again. So I will also do that - using BleuTooth! 
[BlueTooth] Raspberry Pi Pico robot - 12th Nov 2021 Ashley Whittaker
[Youtube] Raspberry Pi Pico robot - 12th Nov 2021 Ashley Whittaker
Now I am reading the TB6612FNG’s cheat sheet, before wiring it up to Pico #1 with HC12 433MHz transceiver.
Intergration of Pico MCU, HC12 RF Transceiver, TB6612FNG DC Motor Driver
TB6612FNG DC Motor Driver Test
Pico # 1 + HC12 x 2 + TB6612FNG x 2 Pin Assignment
Pico has barely enough GP pins for 4WD. For 6WD, I need to use GPIO expanders, such as MCP23017
The jealous guy, ie, me read the following PC Mag article this morning.
Refactoring old Pico 4WD TB6612FNG program to merge HC12 functions
Note - hitting 32k words limit, need new reply
/ to continue, …
BlueTooth UART Modules for Pico Smart 4WD
Now I am adding two BlueTooth UART slave modules to the smart 4WD, so I can use an Android smart phone with built in accelerometer and magnetometer to play with the 2WD through 2.4GHz BlueTooth.
# *** pico_4wd_v85.py - tlfong01, 2021nov17hkt1937 ***
# Brief Description
# 1. Smart 4WD based on Rpi Pico, TB6612FNG, DC/BLDC motors, 433MHz HC12, 2.6GHz BLE HC02, Androd smart phone with
# acceleromter and magnetometer
# Contents
# 1. Pico 4WD with TB6612 DC Motor Drivers and gear encoder motors N20, tt130, and TM310
# 1.1 Interrupt functions
# 1.2 DC motor function
# 2. Pico 4Wd with BLDC motors with built motor drivers (ie, TB6612FNG is not required
# 3. HC12 433MHz RF transceivers
# 3.1 uart loop back functions
# 3.2 HC12 transmit/receive echo functions
# 4. HC02 2.6GHz BLE slave modules
# 5. Integrating Parts 1, 2 with Parts 3, 4
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
from machine import Pin, PWM
import utime
# *** Pico GP pin assignments ***
uart0TxDNum = 0 # HC12 #1 TxD
uart0RdDNum = 1 # HC12 #2 RxD
hc12Setup1 = 2 # Reserved for SPI0 Sck
hc12Setup2 = 3 # Reserved for SPI0 Tx
i2c0Sda = 4 # Reserved for SPI0 Rx
i2c0Scl = 5 # Reserved for SPI0 Csn
# *** PWM Pins ***
aPwmPinNum0 = 6 #0
bPwmPinNum0 = 7 #1
uart1TxdNum = 8 # HC12 #2 TxD
uart1RxdNum = 9 # HC12 #2 RxD
aPwmPinNum1 = 10 #2
bPwmPinNum1 = 11 #3
# *** Inrerrupt Pins ***
intPinNum0 = 12 #4
intPinNum1 = 13 #5
intPinNum2 = 14 #6
intPinNum3 = 15 #7
# *** Motor Driver Control Pins (TB6612FNG) ***
stdByPinNum0 = 16 #8
stdByPinNum1 = 17 #9
aIn1PinNum0 = 18 #10
aIn2PinNum0 = 19 #11
bIn1PinNum0 = 20 #12
bIn2PinNum0 = 21 #13
aIn1PinNum1 = 22 #14
aIn2PinNum1 = 23 #15
bIn1PinNum1 = 27 #16
bIn2PinNum1 = 28 #17
# *** Interrupt Pin Dicts ***
intGpPinNumDict = {'0': intPinNum0,
'1': intPinNum1,
'2': intPinNum2,
'3': intPinNum3,
}
intPinNumList = [intPinNum0, intPinNum1, intPinNum2, intPinNum3]
# Comments
# 1. There are 4 GP pins to read interrupts: intPinNum0, inPinNum1, intPinNum2, intPinNum3.
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Sleep time dicts ***
secondsDict = {'OneSecond' : 1,
'TwoSeconds' : 2,
'FourSeconds' : 4,
'TenSeconds' : 10,
'SixtySeconds' : 60,
'ThreeMinutes' : 180,
}
def hold(secondsName):
utime.sleep(secondsDict[secondsName])
return
# Comments
# 1. Hold function is friendly version of utime.sleep.
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Interrupt global variables and dicts ***
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
intCountDict = {
'0': intCount0,
'1': intCount1,
'2': intCount2,
'3': intCount3,
}
# Comments
# 1. There are four global variable to hold interrupt event counts.
# 2. For this 4WD, the four interrupt signals are the four motor's rotary encoder output signals.
# *** Interrupt Callback Functions ***
def intCallBack0(pin):
global intCount0
intCount0 = intCount0 + 1
return
def intCallBack1(pin):
global intCount1
intCount1 = intCount1 + 1
return
def intCallBack2(pin):
global intCount2
intCount2 = intCount2 + 1
return
def intCallBack3(pin):
global intCount3
intCount3 = intCount3 + 1
return
intCallBackDict = {
'0': intCallBack0,
'1': intCallBack1,
'2': intCallBack2,
'3': intCallBack3,
}
def countIntPinIntPeriod(intPinNum, countPeriod):
global intCount0
global intCount1
global intCount2
global intCount3
intCount0 = 0
intCount1 = 0
intCount2 = 0
intCount3 = 0
utime.sleep(countPeriod)
if intPinNum == 0:
intCount = intCount0
elif intPinNum == 1:
intCount = intCount1
elif intPinNum == 2:
intCount = intCount2
else:
intCount = intCount3
return intCount
def countIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod):
intCountList = [0] * len(intPinNumList)
for index in range(len(intPinNumList)):
intCountList[index] = countIntPinIntPeriod(intPinNumList[index], countPeriod)
return intCountList
# Comments
# 1. countIntPinIntPeriod(intPinNum, countPeriod) is to count the number of interrupts at the interrupt pin denoted by the
# interrupt pin number.
# *** Test functions ***
def repeatCountIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod, pauseTime, repeatTimes):
print('\n countIntPinNumListIntPeriod()')
intGpPinNumList = [0] * len(intPinNumList)
for index in range(len(intGpPinNumList)):
intGpPinNumList[index] = intGpPinNumDict[str(index)]
print(' intPinNumList =', intPinNumList)
print(' intGpPinNumList =', intGpPinNumList)
print(' countPeriod (seconds) =', countPeriod)
print(' pauseTime (seconds) =', pauseTime)
print(' repeat count times =', repeatTimes)
print('')
for count in range(repeatTimes):
ppsList = countIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod)
print(' countList =', ppsList, end = '')
print(' , min ', min(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , max ', max(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , dif ', max(ppsList) - min(ppsList), end = '')
print(' , avg ', int(sum(ppsList) / len(ppsList)))
utime.sleep(pauseTime)
return
# Comments
# 1. repeatCountIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList, countPeriod, pauseTime, repeatTimes)
# repeatedly counts and prints tinterrupt events in countPeriod and p
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Part 3 - TB6612FNG Motor Driver Functions ***
# Comments
# 1. This 4WD uses two TB6612FNG DC motor drivers, each with two driver channels, with a total of 4 channels for four motors.
# 2. BLDC motor have built in motor drivers, therefor is not handled by TB6612 motor driver.
defaultPwmFreq = 1000
defaultDutyCycle = 90
dutyCycleDict = {
'VeryVerySlow' : 95,
'VeryFast' : 90,
'Fast' : 80,
'Normal' : 50,
'Slow' : 40,
'VerySlow' : 30,
'VeryVerySlow' : 25,
}
'''
motorConfigDict00 = {'MotorDriverNum': 0, 'ChannelNum': 0}
motorConfigDict01 = {'MotorDriverNum': 0, 'ChannelNum': 1}
motorConfigDict10 = {'MotorDriverNum': 1, 'ChannelNum': 0}
motorConfigDict11 = {'MotorDriverNum': 1, 'ChannelNum': 1}
motorConfigDictList_00_01_10_11 = [motorConfigDict00, motorConfigDict01, motorConfigDict10, motorConfigDict11]
motorConfigDictList01 = motorConfigDictList_00_01_10_11
motorConfigDictListDict = {'FourMotorsList' : motorConfigDictList01,
}
'''
motorConfigDictDict = \
{
'0': {'MotorDriverNum': 0, 'ChannelNum': 0},
'1': {'MotorDriverNum': 0, 'ChannelNum': 1},
'2': {'MotorDriverNum': 1, 'ChannelNum': 0},
'3': {'MotorDriverNum': 1, 'ChannelNum': 1},
}
# Comment
# 1. There are four DC motors, each denoted/represented by a Motor Config Dictionary.
# 2. A motor config dict has two elementa:
# (a) MotorDriverNum which the the number of one of the two TB6612FNG motor drivers.
# (b) Channel Number, denoting each of the two channel of the motor driver.
# 3. motorConfigDictList01 = motorConfigDictList_00_01_10_11 = the list of all four motor confict dictionaries.
# 4. motorConfigDictListDict is the Dict of motorConfigDictLists (only one such dict list for now)
motorDriverGpPinNumDict = { \
'0': {'StdByPinNum' : stdByPinNum0,
'0' : {'In1PinNum' : aIn1PinNum0,
'In2PinNum' : aIn2PinNum0,
'PwmPinNum' : aPwmPinNum0,
'PwmFreq' : defaultPwmFreq,
'DutyCycle' : defaultDutyCycle,
'IntPinNum' : intPinNum0,
'IntPinCallBack' : intCallBack0,
},
'1' : {'In1PinNum' : bIn1PinNum0,
'In2PinNum' : bIn2PinNum0,
'PwmPinNum' : bPwmPinNum0,
'PwmFreq' : defaultPwmFreq,
'DutyCycle' : defaultDutyCycle,
'IntPinNum' : intPinNum1,
'IntPinCallBack' : intCallBack1,
},
},
'1': {'StdByPinNum' : stdByPinNum1,
'0' : {'In1PinNum' : aIn1PinNum1,
'In2PinNum' : aIn2PinNum1,
'PwmPinNum' : aPwmPinNum1,
'PwmFreq' : defaultPwmFreq,
'DutyCycle' : defaultDutyCycle,
'IntPinNum' : intPinNum2,
'IntPinCallBack' : intCallBack2,
},
'1' : {'In1PinNum' : bIn1PinNum1,
'In2PinNum' : bIn2PinNum1,
'PwmPinNum' : bPwmPinNum1,
'PwmFreq' : defaultPwmFreq,
'DutyCycle' : defaultDutyCycle,
'IntPinNum' : intPinNum3,
'IntPinCallBack' : intCallBack3
},
},
}
# Comment
# 1. motorDriverGpPinNumDict specifies
# (a) the GP pin numbers for the two TB6612FNG motor drivers ecah with two channels.
# (b) the default values such as PWM frequency, duty cycles
def setupMotorOld(motorConfigDict):
motorDriverNum = motorConfigDict['MotorDriverNum']
channelNum = motorConfigDict['ChannelNum']
stdByPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['StdByPinNum']
in1PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In1PinNum']
in2PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In2PinNum']
pwmPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['PwmPinNum']
pwmFreq = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['PwmFreq']
dutyCycle = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['DutyCycle']
intPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['IntPinNum']
intPinCallBack = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['IntPinCallBack']
# *** Motor Driver Control Pin Setup ***
stdByPin = Pin(stdByPinNum, Pin.OUT)
in1Pin = Pin(in1PinNum, Pin.OUT)
in2Pin = Pin(in2PinNum, Pin.OUT)
intPin = Pin(intPinNum, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
stdByPin.high()
in1Pin.low()
in2Pin.high()
# *** PWM Pin Setup ***
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(pwmFreq)
u16DutyCycle = int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536)
pwmPin.duty_u16(u16DutyCycle)
# *** Interrupt Pin Setup ***
intPin.irq(intPinCallBack, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
# *** Motor Control Dict ***
motorControlDict = {'StdByPin': stdByPin,
'In1Pin' : in1Pin,
'In2Pin' : in2Pin,
'PwmPin' : pwmPin,
'IntPin' : intPin,
}
return motorControlDict
def setupMotor(motorNum):
motorConfigDict = motorConfigDictDict[str(motorNum)]
motorDriverNum = motorConfigDict['MotorDriverNum']
channelNum = motorConfigDict['ChannelNum']
stdByPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['StdByPinNum']
in1PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In1PinNum']
in2PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In2PinNum']
pwmPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['PwmPinNum']
pwmFreq = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['PwmFreq']
dutyCycle = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['DutyCycle']
intPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['IntPinNum']
intPinCallBack = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['IntPinCallBack']
# *** Motor Driver Control Pin Setup ***
stdByPin = Pin(stdByPinNum, Pin.OUT)
in1Pin = Pin(in1PinNum, Pin.OUT)
in2Pin = Pin(in2PinNum, Pin.OUT)
intPin = Pin(intPinNum, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
stdByPin.high()
in1Pin.low()
in2Pin.high()
# *** PWM Pin Setup ***
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(pwmFreq)
u16DutyCycle = int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536)
pwmPin.duty_u16(u16DutyCycle)
# *** Interrupt Pin Setup ***
intPin.irq(intPinCallBack, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
# *** Motor Control Dict ***
motorControlDict = {'StdByPin': stdByPin,
'In1Pin' : in1Pin,
'In2Pin' : in2Pin,
'PwmPin' : pwmPin,
'IntPin' : intPin,
}
return motorControlDict
# Comments
# 1. setupMotor(motorNum) perfroms the following things:
# 1.1 setup and intiralize control/pwm/interrupt pin objects from controlPinNum controlPin objects
# 1.2 setup interrupt call back functions
# 1.3 returns motorControlDict which is a dictionary of the motor's pin objects (stdBy, Input, Pwm, Interrupt)
def setupMotorList(motorNumList):
motorControlDictList = [0] * len(motorNumList)
for motorNum in motorNumList:
motorControlDict = setupMotor(motorNum)
motorControlDictList[motorNum] = motorControlDict
return motorControlDictList
def moveMotorDirection(motorControlDict, directionName):
if directionName =='Forward':
motorControlDict['In1Pin'].low()
motorControlDict['In2Pin'].high()
elif directionName == 'Backward':
motorControlDict['In1Pin'].high()
motorControlDict['In2Pin'].low()
return
def moveMotorSpeed(motorControlDict, speedName):
pwmPin = motorControlDict['PwmPin']
dutyCycle = dutyCycleDict[speedName]
pwmPin.duty_u16(int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536) )
return
def moveMotorDirectionSpeed(motorControlDict, directionName, speedName):
moveMotorDirection(motorControlDict, directionName)
moveMotorSpeed(motorControlDict, speedName)
return
def moveMotorDirectionSpeedList(motorControlDictList, directionName, speedName):
for motorControlDict in motorControlDictList:
moveMotorDirectionSpeed(motorControlDict, directionName, speedName)
return
def stopMotor(motorControlDict):
motorControlDict['In1Pin'].low()
motorControlDict['In2Pin'].low()
return
def stopMotorList(motorControlDictList):
for motorControlDict in motorControlDictList:
stopMotor(motorControlDict)
return
# *** Test functions ***
def testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList(motorNumList, directionName, speedName, secondsName):
print('Begin testSetupMoveMotorList(), ...')
motorControlDictList = setupMotorList(motorNumList)
moveMotorDirectionSpeedList(motorControlDictList, directionName, speedName) # move motor list driection and speed
utime.sleep(2)
print('After 2 seconds, ...')
repeatCountIntPinNumListIntPeriod(intPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3], countPeriod = 0.1, pauseTime = 0.1, repeatTimes = 10)
utime.sleep(1)
stopMotorList(motorControlDictList)
print('End testSetupMoveMotorList(), ...')
return
# *** Sample test functions calls ***
#testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList([0, 1, 2, 3], 'Forward', 'VerySlow', 'FourSeconds')
#testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList([0, 1, 2, 3], 'Backward', 'VeryFast', 'FourSeconds')
#testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList([0, 1, 2, 3], 'Forward', 'Normal', 'TwoSeconds')
#testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList([0, 1, 2, 3], 'Forward', 'Normal', 'SixtySeconds')
#testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList([0, 1, 2, 3], 'Forward', 'Normal', 'ThreeMinutes')
#testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList([0, 1, 2, 3], 'Forward', 'VerySlow', 'TenSeconds')
#testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList([0, 1, 2, 3], 'Forward', 'Normal', 'FourSeconds')
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
'''
# *** BLDC Config/Fuctnions ***
dutyCycleDictBldc = {
'VeryVerySlow' : 95,
'VeryFast' : 90,
'Fast' : 80,
'Normal' : 50,
'Slow' : 40,
'VerySlow' : 30,
'VeryVerySlow' : 25,
}
def changeBldcMotorSpeed(motorControlDict, speedName):
pwmPin = motorControlDict['PwmPin']
dutyCycle = dutyCycleDict[speedName]
pwmPin.duty_u16(int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536) )
return
def setupBldcMotor(motorConfigDict):
motorDriverNum = motorConfigDict['MotorDriverNum']
channelNum = motorConfigDict['ChannelNum']
stdByPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)]['StdByPinNum']
in1PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In1PinNum']
in2PinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['In2PinNum']
pwmPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['PwmPinNum']
pwmFreq = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['PwmFreq']
dutyCycle = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['DutyCycle']
intPinNum = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['IntPinNum']
intPinCallBack = motorDriverGpPinNumDict[str(motorDriverNum)][str(channelNum)]['IntPinCallBack']
# *** Motor Driver Control Pin Setup ***
stdByPin = Pin(stdByPinNum, Pin.OUT)
in1Pin = Pin(in1PinNum, Pin.OUT)
in2Pin = Pin(in2PinNum, Pin.OUT)
intPin = Pin(intPinNum, Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_DOWN)
stdByPin.high()
in1Pin.low()
in2Pin.high()
# *** PWM Pin Setup ***
pwmPin = PWM(Pin(pwmPinNum))
pwmPin.freq(pwmFreq)
u16DutyCycle = int((dutyCycle / 100) * 65536)
pwmPin.duty_u16(u16DutyCycle)
# *** Interrupt Pin Setup ***
intPin.irq(intPinCallBack, Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
# *** Motor Control Dict ***
motorControlDictBldc = {'StdByPin': stdByPin,
'In1Pin' : in1Pin,
'In2Pin' : in2Pin,
'PwmPin' : pwmPin,
'IntPin' : intPin,
}
# Test functions
def testBldcMotor00():
print(' Begin testBldcMotor00(), ...')
motorConfigDict = {'MotorDriverNum': 0, 'ChannelNum': 0}
setupBldcMotor(motorConfigDict)
hold('TwoSeconds')
changeBldcMotorSpeed(motorConfigDict, 'VeryFast')
hold('TwoSeconds')
utime.sleep(2)
changeBldcMotorDirection(motorConfigDict, 'CCW')
utime.sleep(2)
changeBldcMotorDirection(motorConfigDict, 'CW')
changeBldcMotorSpeed(motorConfigDict, 'VerySlow')
utime.sleep(2)
print(' End testSetupMotor00(), ...')
return
# *** Sample test function call
#testBldcMotor00()
'''
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
''' Old main test sample outputs
*** Sample Output tlfong01 2021oct11hkt1955 ***
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Begin testSetupMoveMotorList(), ...
After 2 seconds, ...
countIntPinNumListIntPeriod()
intPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3]
intGpPinNumList = [4, 5, 6, 7]
countPeriod (seconds) = 0.1
pauseTime (seconds) = 0.1
repeat count times = 10
countList = [296, 219, 291, 205] , min 205 , max 296 , dif 91 , avg 252
countList = [286, 215, 295, 208] , min 208 , max 295 , dif 87 , avg 251
countList = [288, 217, 300, 213] , min 213 , max 300 , dif 87 , avg 254
countList = [301, 223, 298, 207] , min 207 , max 301 , dif 94 , avg 257
countList = [271, 223, 308, 207] , min 207 , max 308 , dif 101 , avg 252
countList = [287, 223, 305, 203] , min 203 , max 305 , dif 102 , avg 254
countList = [277, 233, 306, 226] , min 226 , max 306 , dif 80 , avg 260
countList = [282, 240, 299, 222] , min 222 , max 299 , dif 77 , avg 260
countList = [294, 225, 307, 209] , min 209 , max 307 , dif 98 , avg 258
countList = [299, 223, 303, 229] , min 223 , max 303 , dif 80 , avg 263
End testSetupMoveMotorList(), ...
>>>
'''
# *** Main Test ***
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= ========= =========
# *** Main ***
print('Begin setupMotor(), ... tlfong01 2021nov1701')
testSetupMoveMotorDirectionSpeedList([0, 1, 2, 3], 'Forward', 'Normal', 'TwoSeconds')
print('End setupMotor(), ...')
# *** End ***
''' Sample output tlfong01 2021nov17hkt2033
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
Begin setupMotor(), ... tlfong01 2021nov1701
Begin testSetupMoveMotorList(), ...
After 2 seconds, ...
countIntPinNumListIntPeriod()
intPinNumList = [0, 1, 2, 3]
intGpPinNumList = [12, 13, 14, 15]
countPeriod (seconds) = 0.1
pauseTime (seconds) = 0.1
repeat count times = 10
countList = [0, 0, 0, 0] , min 0 , max 0 , dif 0 , avg 0
countList = [0, 0, 0, 0] , min 0 , max 0 , dif 0 , avg 0
countList = [0, 0, 0, 0] , min 0 , max 0 , dif 0 , avg 0
countList = [0, 0, 0, 0] , min 0 , max 0 , dif 0 , avg 0
countList = [0, 0, 0, 0] , min 0 , max 0 , dif 0 , avg 0
countList = [0, 0, 0, 0] , min 0 , max 0 , dif 0 , avg 0
countList = [0, 0, 0, 0] , min 0 , max 0 , dif 0 , avg 0
countList = [0, 0, 0, 0] , min 0 , max 0 , dif 0 , avg 0
countList = [0, 0, 0, 0] , min 0 , max 0 , dif 0 , avg 0
countList = [0, 0, 0, 0] , min 0 , max 0 , dif 0 , avg 0
End testSetupMoveMotorList(), ...
End setupMotor(), ...
>>>
'''
HC12 References
HC-02 bluetooth serial port uart 3.3v TTL Datasheet
http://www.hc01.com/downloads/HC-02%20english%20datasheet.pdf
Edge Impulse and TinyML References
Build TinyML Models Using Your Mobile Phone TINYML - Jan Jongboom 2020apr11
Machine Learning Using Your Mobile Phone with Edge Impulse - 2020apr03
What Is Edge Impulse and tinyML? - 2020nov20
Top 5 Projects on Raspberry Pi Pico - Abhishek Jadhav 2021nov16
Pico Motor Driver
Kitronix Zoom Tech Talks - Motor Driver/Robotics Board For Raspberry Pi Pico - 2021may14
Now I am looking into TinyML. I have almost made up my mind to try it on my Pico 4WD.
Why TinyML Is Such A Big Deal - Bryon Moyer 2021sep02
About tinyML
tinyML Vision Challenge – Winners October 08, 2021
The Ultimate pi-top Holiday Gift Guide
Pico Smart 4WD Part 2
My part 1 project blog is getting too long for the forum’s editor to handle, so the response time is now unbearingly long. So I need to end this TLDR part 1 and start Part 2.
Update 2021nov23hkt1219 - I opened the project’s Part 2 as a new topic but found the forum’s editor is also very long. So I am using offline Penzu editing to save time and space.
/ to continue in Part 2, …
The tcbscabs is notable for having a large selection of books and novels spanning a wide range of genres. Literature enthusiasts looking for a digital haven for exploration often turn to the platform because of its dedication to providing high-quality scans and a vast selection of literary content.